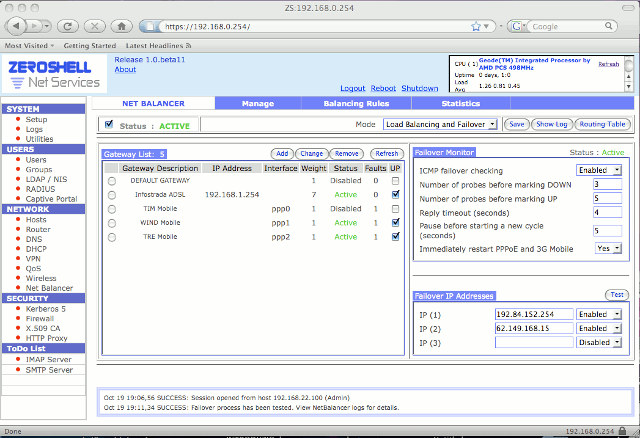
We’ve just seen pfSense is now available for Arm via firewall appliances such as Netgate SG-3100, but AFAIK there’s no pfSense community Arm firmware images yet. Several Arm SoCs & boards are now supported by FreeBSD, so in theory pfSense could be ported to those, but the page on FreeBSD does not seem to have been updated for a while. If you want a firewall distributions with an easy-to-user web interface like pfSense, but that also works on cheaper Arm hardware, Linux based ZeroShell distribution could be worth a try, as beside working on Intel & AMD x86 platforms, the developers also provides images for Raspberry Pi 2 & 3 boards, and several Orange Pi boards, namely Orange Pi R1, Orange Pi Zero, Orange Pi PC, and Orange Pi Plus/Plus2. The latter is the only supported Arm board with Gigabit Ethernet. Some of ZeroShell features include: Load Balancing and Failover of […]
Netgate SG-3100 is an ARM based pfSense Firewall Appliance
pfSense software is a popular open source firewall distribution based on FreeBSD operating system that is entirely managed via a web interface. Up until recently, FreeBSD (see comments section) pfSense would only support x86-64 (Intel or AMD hardware). But progress has been made with pfSense (and FreeBSD) for ARM, and Netgate, the company behind pfSense, is now selling two ARM based firewall appliances with SG-1000 microFirewall powered by Texas Instruments AM3352 Cortex A8 SoC, and sine a little over of month, SG-3100 firewall appliance based on a more suitable Marvell dual core Cortex A9 processor. Netgate SG-3100 hardware specifications: Processor – Marvell ARMADA 38x 88F6820 dual core ARM Cortex-A9 @ 1.6 GHz with NEON SIMD and FPU System Memory – 2GB DDR4L Non ECC Storage – 8GB eMMC Flash Network Interfaces 2x Gigabit Ethernet configured as dual WAN or one WAN one LAN 4x ports Gigabit Marvell 88E6141 switch, uplinked […]
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4 Now Fully Supports Arm servers
When hardware vendors announced Arm based servers they also claim support for operating systems such as Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, so I assumed software support was more or less where it needed to be with regards to Arm server. But apparently, it may not have been so, as Red Hat only announced full support for Arm servers in Red Hat Enterprise Linux for ARM a few days ago. It also started with SBSA (Server Base System Architecture) specifications in 2014, that aimed to provide a single operating platform that works across all 64-bit ARMv8 server SoCs that complies with the said specification. Red Hat then released a developer preview of the OS for silicon and OEM vendors in 2015, and earlier this week, the company released Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4 for Arm, the first commercial release for this architecture. RHEL 7.4 for Arm come with […]
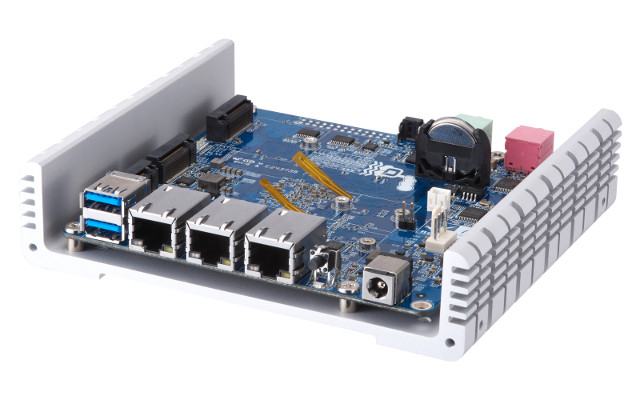
QNAP QBoat Sunny IoT Mini Server Board Officially Announced with Annapurna Labs AL-314 ARM Processor
We first had a glance at QNAP QBoat Sunny at CES 2017. At the time, QNAP IoT development board was powered by an Intel AnyWAN GRX750 dual core Atom based processor with 2GB RAM, 4GB flash, three Gigabit Ethernet ports, some mSATA slot and so on. The company has now officially announced the board, but with a twist, as the Intel processor has been replaced by Annapurna Labs (now part of Amazon) AL-314 quad core ARM Cortex-15 processor instead, and left most of the other features pretty much unchanged. QBoard Sunny board specifications: Processor – Annapurna Labs AL-314 quad core ARM Cortex-15 processor up to 1.7 GHz System Memory – 2GB DDR3L Storage – 512MB NAND flash, 2x M.2 2260/2280 SATA slots for SSDs (Key M) Network connectivity – 3x Gigabit Ethernet USB – 2x USB 3.1 Gen1 ports Audio – 3.5mm audio out jack, 3.5mm audio in jack Expansion […]
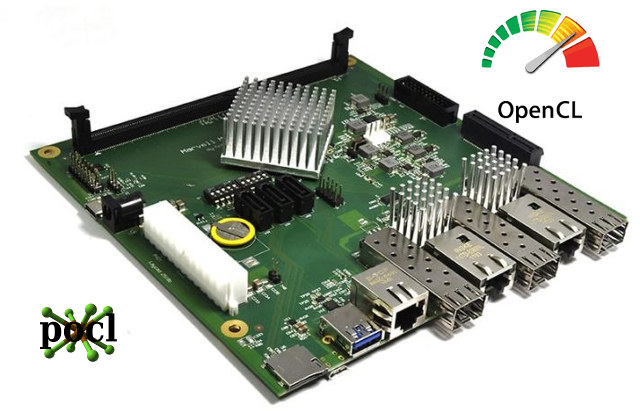
First OpenCL Encounters on Cortex-A72: Some Benchmarking
This is a guest post by blu about his experience with OpenCL on MacchiatoBin board with a quad core Cortex A72 processor and an Intel based MacBook. He previously contributed several technical articles such as How ARM Nerfed NEON Permute Instructions in ARMv8 or OpenGL ES development on Ubuntu Touch. Qualcomm launched their long-awaited server ARM chip the other day, and we started getting the first benchmarks. Incidentally, I too managed to get some OpenCL ray-tracing code running on an ARM Cortex-A72 machine that same day (thanks to pocl – an LLVM-based open-source OCL multi-platform implementation), so my benchmarking curiosity got me. The code in question is an OCL (half-finished) port of a graphics demo from 2014. Some remarks of what it does: For each frame: a single thread builds a sparse voxel octree from a dynamic voxel scene; the octree, along with current camera settings are passed to an […]
Linux 4.14 Release – Main Changes, ARM & MIPS Architecture
Linus Torvalds has announced the release of Linux 4.14: No surprises this week, although it is probably worth pointing out how the 0day robot has been getting even better (it was very useful before, but Fengguang has been working on making it even better, and reporting the problems it has found). Sure, some of the new reports turned out to be just 0day doing things that just don’t work (ie KASAN with old gcc versions, but also doing things like loading old ISA drivers in situations that just don’t make sense – remember when you couldn’t even ask if the hardware existed or not, and just had to know), but even then it’s been all good. The appended shortlog is obviously only for the (small) haul since rc8, and it really is tiny. Not very many commits, and they are small. The biggest thing that stands out in the diffstat […]
Qualcomm Centriq 2400 ARM SoC Launched for Datacenters, Benchmarked against Intel Xeon SoCs
Qualcomm Centriq 2400 ARM Server-on-Chip has been four years in the making. The company announced sampling in Q4 2016 using 10nm FinFET process technology with the SoC featuring up to 48 Qualcomm Falkor ARMv8 CPU cores optimized for datacenter workloads. More recently, Qualcomm provided a few more details about the Falkor core, fully customized with a 64-bit only micro-architecture based on ARMv8 / Aarch64. Finally, here it is as the SoC formally launched with the company announcing commercial shipments of Centriq 2400 SoCs. Qualcom Centriq 2400 key features and specifications: CPU – Up to 48 physical ARMv8 compliant 64-bit only Falkor cores @ 2.2 GHz (base frequency) / 2.6 GHz (peak frequency) Cache – 64 KB L1 instructions cache with 24 KB single-cycle L0 cache, 512 KB L2 cache per duplex; 60 MB unified L3 cache; Cache QoS Memory – 6 channels of DDR4 2667 MT/s for up to 768 […]
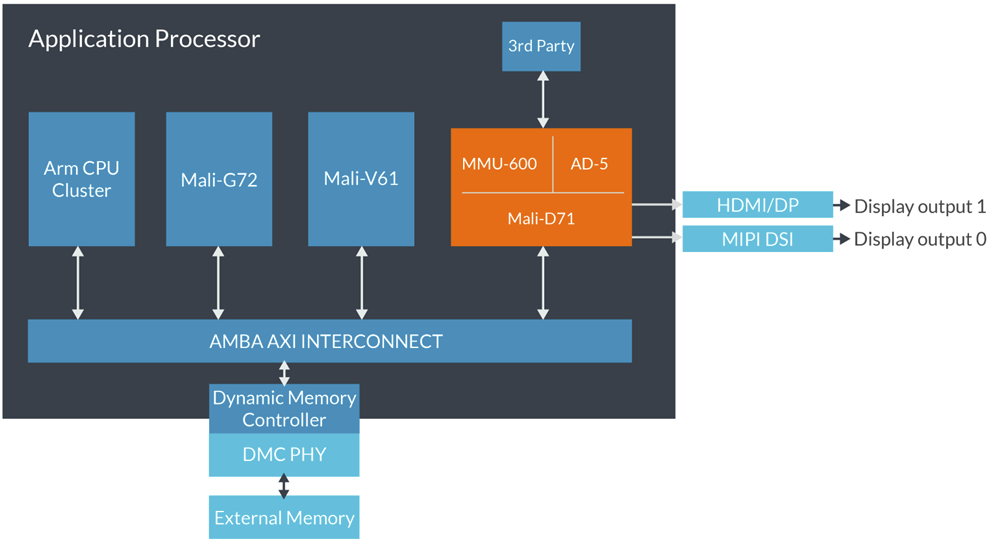
Arm Announces Mali-D71 for 4K/120 Hz Displays, Assertive Display 5 with HDR
Arm has just announced Mali-D71 display processor optimized for 4K120 displays used for virtual reality, Assertive Display 5 display management core which adds support for high dynamic range (HDR10 / HLG), as well as CoreLink MMU-600 system memory management unit to handle data feed to Mali-D71, with the integration leading to a 55% area saving for the combined solution and a 50% latency improvement. Mali-D71 Display Processor The main advantages of D71 display processor include: 30% system power savings by fully offloading GPU workloads before output such as composition, rotation, high-quality scaling, and other imaging processing in fixed function hardware. 2x area efficiency compared to Mali-DP650. When driving a single display, it can re-use the resources of a secondary display, doubling the performance. 4x latency tolerance – Mali-D71 can sustain up to 4x the delay on the system bus for the same throughput, helping maintaining high refresh rates up to […]