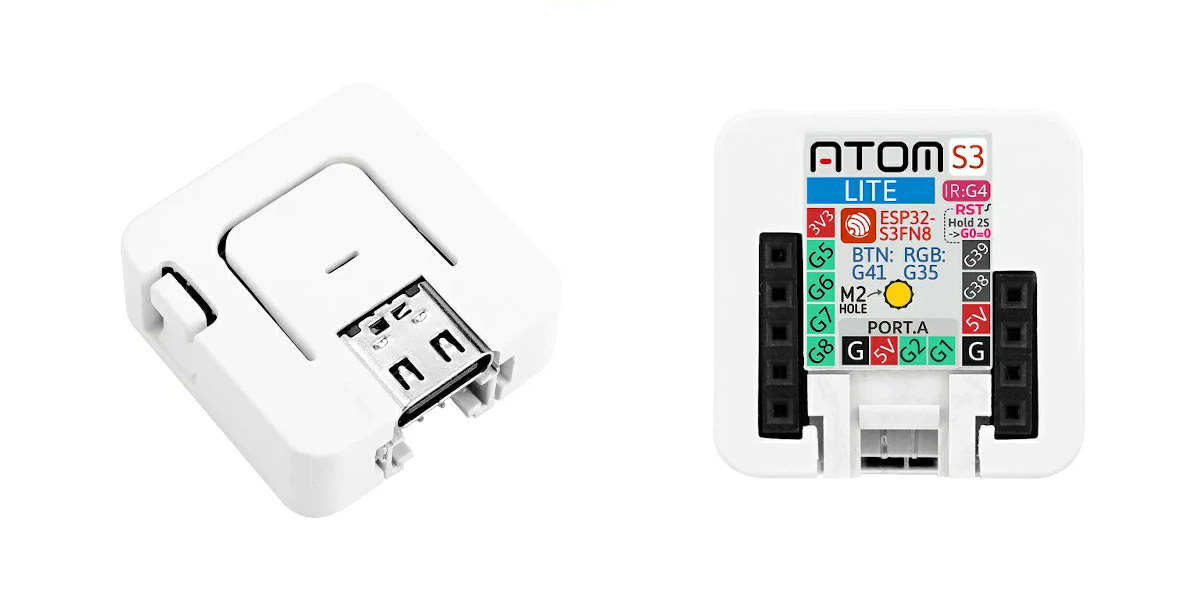
ATOMS3 Lite is the latest ESP32-S3 IoT platform from the M5Stack Atom series wireless programmable controllers, doing without the 0.85-inch display and IMU sensor found in the ATOM S3 development kit simply using an RGB LED instead. M5Stack ATOM S3 Lite features the ESP32-S3FN8 WiFi and Bluetooth SoC with 8MB SPI flash, an infrared transmitter, a USB-C port for power and programming, a few I/O pins, user and reset buttons all in just a 24x24x9.5mm housing. ATOMS3 Lite specifications: Wireless MCU – Espressif Systems ESP32-S3FN8 dual-core 32-bit Xtensa LX7 microcontroller with AI vector instructions up to 240MHz, RISC-V ULP co-processor, 512KB SRAM, 2.4GHz WiFi 4 (802.11b/g/n), Bluetooth 5.0 BLE + Mesh, 8MB flash Antenna – Internal “3D” antenna Expansion 9x pins with G5, G6, G7, G8, G38, and G39 GPIOs, 5V, 3.3V, and GND 4-pin Grove connector Misc IR LED (infrared transmitter/blaster) WS2812B-2020 RGB LED Reset and user buttons M.2 […]
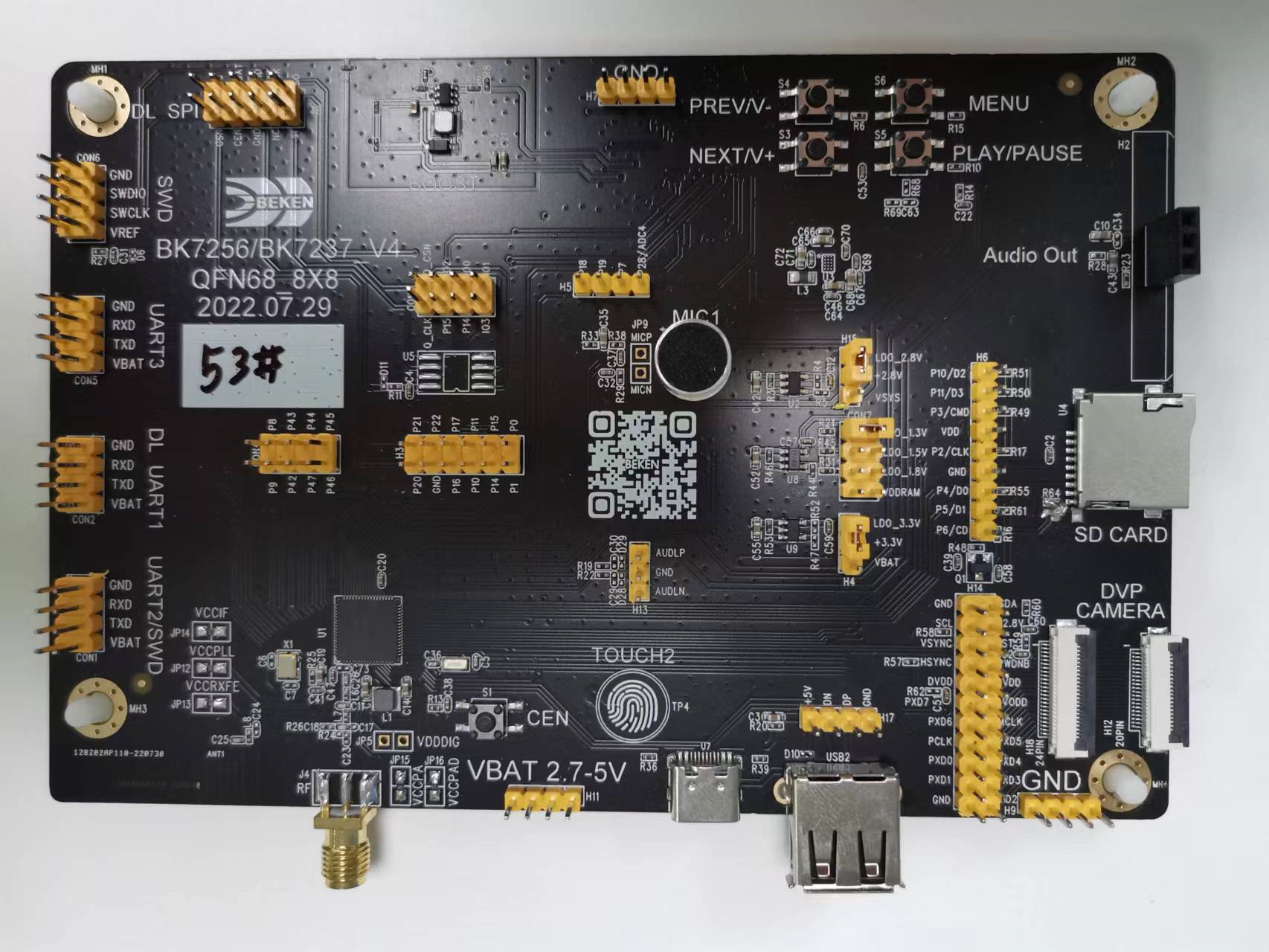
Beken BK7256 320 MHz dual-core RISC-V IoT MCU offers WiFi 6, Bluetooth 5.2, JPEG video encoder/decoder
Until now, I had only heard about Beken Bluetooth audio chips, but I’ve just been informed the company is also making WiFi chips such as the BK7256 that are notably found in some Tuya Smart Home modules. Beken offers both RISC-V and Arm WiFi and Bluetooth chips with features summarized as follows: BK7235 single-core RISC-V MCU up to 320 MHz with 2.4 GHz WiFi 6 802.11ax and Bluetooth 5.2 LE, 4MB flash, 512KB SRAM, optional 4MB PSRAM BK7236 dual-core Arm MCU up to 120 to 240 MHh with 2.4 GHz WiFi 6 802.11ax and Bluetooth 5.3 dual mode, 4MB flash, 512KB SRAM, optional 4MB PSRAM BK7237 dual-core RISC-V MCU up to 320 MHz with 2.4 GHz WiFi 6 802.11ax and Bluetooth 5.2 dual mode, 4 or 8MB flash, 512KB SRAM, optional 4MB PSRAM BK7256 dual-core RISC-V MCU up to 320 MHz with 2.4 GHz WiFi 6 802.11ax and Bluetooth 5.2 […]
FOSDEM 2023 schedule – Open-source Embedded, Mobile, IoT, Arm, RISC-V, etc… projects
After two years of taking place exclusively online, FOSDEM 2023 is back in Brussels, Belgium with thousands expected to attend the 2023 version of the “Free and Open Source Developers’ European Meeting” both onsite and online. FOSDEM 2023 will take place on February 4-5 with 776 speakers, 762 events, and 63 tracks. As usual, I’ve made my own little virtual schedule below mostly with sessions from the Embedded, Mobile and Automotive devroom, but also other devrooms including “Open Media”, “FOSS Educational Programming Languages devroom”, “RISC-V”, and others. FOSDEM Day 1 – Saturday February 4, 2023 10:30 – 10:55 – GStreamer State of the Union 2023 by Olivier Crête GStreamer is a popular multimedia framework making it possible to create a large variety of applications dealing with audio and video. Since the last FOSDEM, it has received a lot of new features: its RTP & WebRTC stack has greatly improved, Rust […]
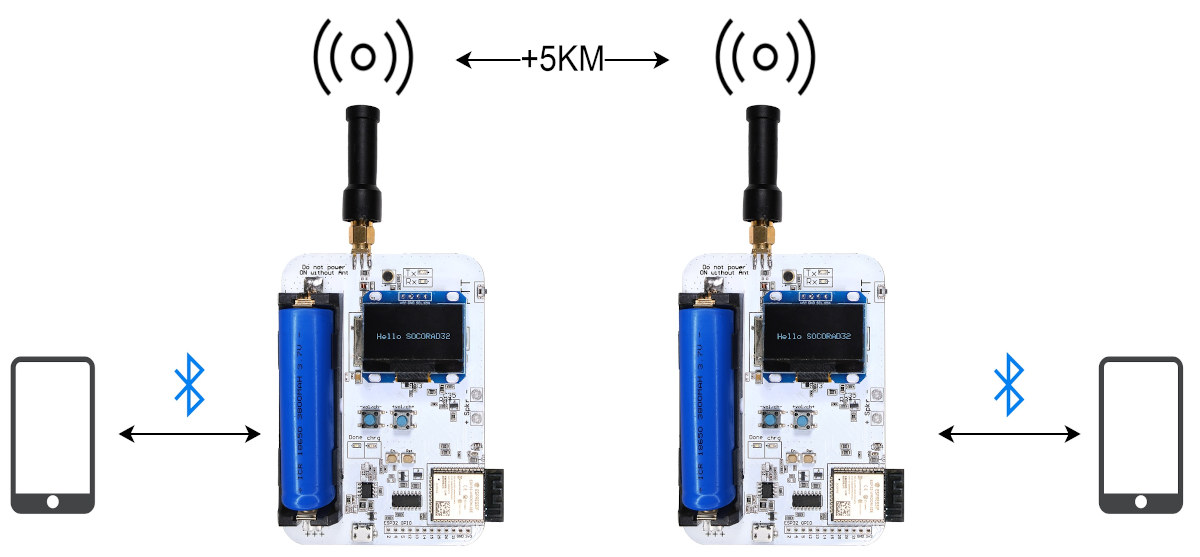
SOCORAD32 ESP32 walkie-talkie board also supports data communication (Crowdfunding)
SOCORAD32, aka ESP32 Software Controlled Radio, is a hackable, open-source hardware ESP32-based amateur radio board for walkie-talkie and data communication applications. The board comes with an ESP32 module with WiFi 4 and Bluetooth connectivity, an RDA Microelectronics RDA1846 RF IC used in many commercial walkie-talkies and offering a range up of to 5 km, a small display, a speaker, and a 18650 battery holder. SOCORAD32 specifications: Microcontroller module – ESP32-WROOVER-32E with ESP32 dual-core microcontroller, 4MB flash, 2.4 GHz WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity, built-in PCB antenna Walkie-talkie chip – RDA1846 single-chip transceiver for Walkie-Talkie applications (See datasheet and programming guide for details) Frequency Range: ISM 400 – 470 MHz Frequency Step: 5 K / 6.25 K / 12.5 K / 25 K RF Output Power: 2 W / 0.5 W (+5 KM @ 2 W) set to what the local law permits RF Input Sensitivity: -122 dBm Voice Scrambling: 8 type […]
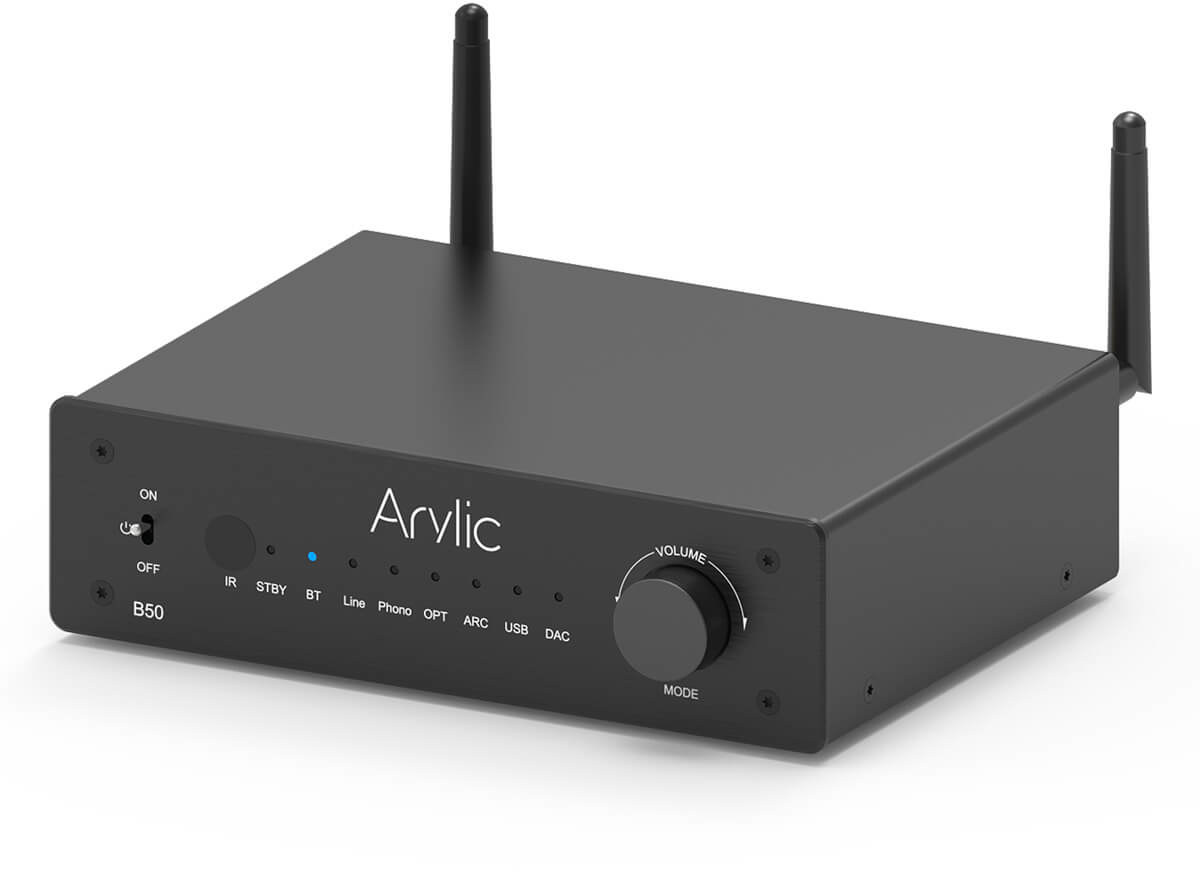
Arylic B50 – A Qualcomm QCC3040 based Bluetooth stereo amplifier with audio transmitter (Sponsored)
Arylic B50 is a Bluetooth 5.2 stereo amplifier with an audio transmitter based on Qualcomm QCC3040 low-power Bluetooth Audio SoC that’s typically used in wireless earbuds. The all-in-one Bluetooth amplifier supports aptX HD audio transmission and reception, can handle two Bluetooth sources or two Bluetooth speakers or earbuds, and offers a wide range of interfaces including HDMI ARC, Phono in, RCA in, optical S/PDIF in, subwoofer out, and more. The system can also be connected to two wired speakers up to 50W @ 4 Ohms. Arylic B50 specifications: SoC – Qualcomm QCC3040 with 32-bit application processor @ 32 MHz, 32-bit system processor @ 32 MHz, Kalimba DSP @ 120 MHz, Bluetooth 5.2 and aptX HD support. Bluetooth Version 5.2 with up to 15m range Transmit – 2x Bluetooth Tx for up to 2 Bluetooth speakers or earbuds Receiver – 2x Bluetooth Rx for up to 2 Bluetooth transmitter devices Supported […]
Bouffalo Lab BL616/BL618 RISC-V MCU supports WiFi 6, Bluetooth 5.2, and Zigbee
Bouffalo Lab BL616/BL618 is a 32-bit RISC-V wireless microcontroller with support for 2.4 GHz WiFi 6, Bluetooth 5.2 dual-mode, and an 802.15.4 radio for Zigbee, Thread, and Matter designed for IoT applications. We first spotted the BL616 RISC-V IoT MCU during the BL602/BL606 announcement in November 2020, but we had virtually no additional information about it so far. It appears both BL616 and BL618 will be launched next month with the main difference between the two being that BL616 has 19 GPIOs and BL618 comes with 35 GPIOs. Bouffalo Lab BL616 and BL618 specifications: MCU core – 32-bit RISC-V CPU (RV32IMAFCP) @ up to 320 MHz with FPU and DSP, 32KB instruction cache & 16KB data cache VPU – MJPEG video encoder Memory – 480KB SRAM, 4KB HBN RAM, embedded 4 or 8MB pSRAM (optional) Storage – 128KB ROM, 4Kb eFuse, embedded 2, 4, or 8MB flash (optional), XIP QSPI […]
Merlot is an open-source hardware tricolor wireless E-paper display
paperd.ink Merlot is a tricolor E-paper display with an open-source hardware control board based on ESP32 wireless SoC that is programmable with Arduino, MicroPython, or the ESP-IDF framework. We first wrote about the paperd.ink 4.2-inch ESP32-based monochrome e-Paper display last year, but the company has now refined its design with the “paperd.ink Classic” replacing the 3D printed enclosure with a vacuum cast enclosure and adding a 1,900 mAh battery. They also launched a new model, the Merlot, based on the same design but with a display supporting three colors: black, white, and red. Merlot specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-WROOM-32 module with ESP32 dual-core processor, 4 MB SPI flash, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 & Bluetooth LE connectivity Storage – MicroSD card slot for storing images, files, etc Display – 4.2″ tricolor e-Paper display with 400 x 300 resolution; full refresh: ~ 17 seconds; partial update: also 17 seconds… USB – 1x […]
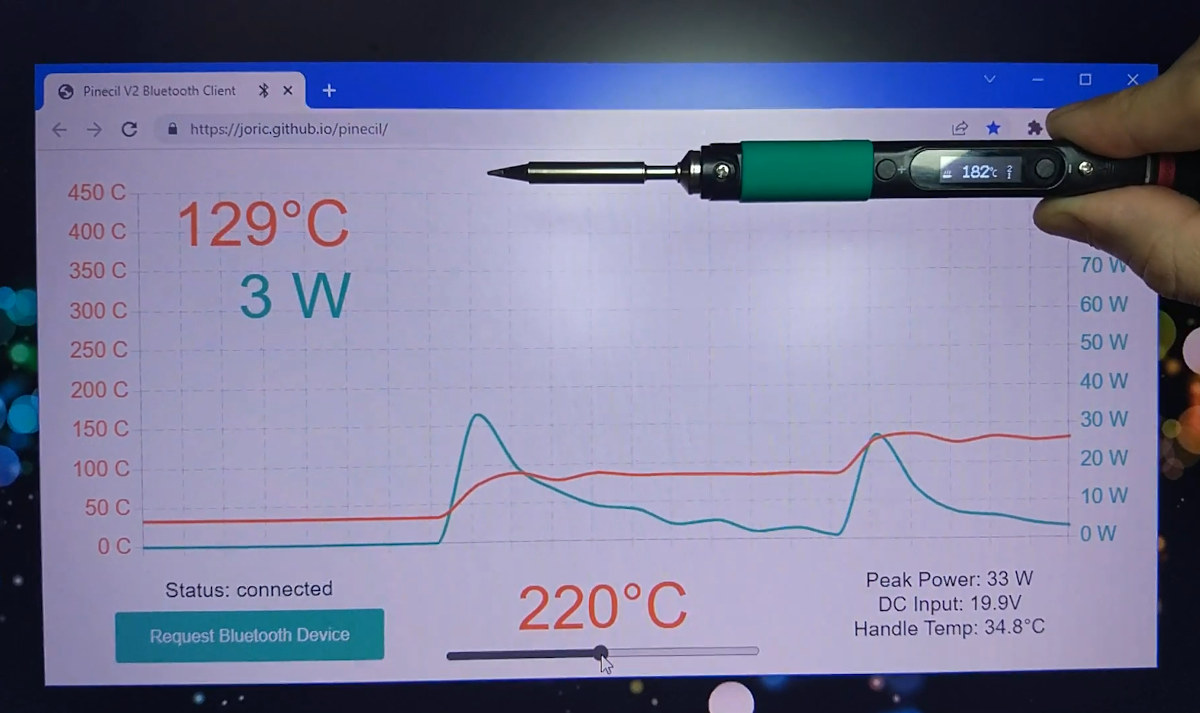
Pinecil V2 Bluetooth LE soldering iron gets a web interface
It’s now possible to make use of the Pinecil V2 soldering iron‘s Bluetooth LE connectivity through a web-based interface used to monitor and/or set the temperature and power of the RISC-V soldering iron. When the Pinecil V2 soldering iron was launched with a Bouffalo Lab BL706 RISC-V Bluetooth microcontroller last summer, we were told there were main potential cases to make use of the Bluetooth LE features: OTA firmware upgrade and remote telemetry and control. The latter is now being taken care of by Joric who has written a web application to visualize telemetry data and even control the temperature of the soldering iron. To be able to use the Bluetooth features, you’ll first need to install the latest Pinecil V2 firmware with blisp flashing utility before going to https://joric.github.io/pinecil to pair your soldering iron as explained in the wiki. Note the implementation relies on the Web Bluetooth API which […]