Ambiq Micro is a US company founded in 2010 that focuses on “extremely low power” semiconductors leveraging their patented Subthreshold Power Optimized Technology (SPOT) platform. Earlier this year, they announced their first low power Cortex-M4F MCU Apollo family with claims of 5 to 10 times lower power consumption compared to other micro-controllers with the same performance. According to an EETimes article, they’ve at least partially backed their claims with a live demonstration at ARM TechCon 2015. Before checking out the test results, let’s have a look at the main features of Apollo MCU family: 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F processor @ up to 24 MHz, with FPU, and wake-up interrupt controller with 12 interrupts Up to 512KB flash, 64-KB low-leakage RAM “Rich set of timing peripherals” Peripherals I2C/SPI master; I2C/SPI; UART; 10-bit, 13-channel, 1MS/s ADC Temperature sensor with ±2°C accuracy Voltage Range – 1.8 to 3.8V Power Consumption: active mode: 30µA/MHz (executing […]
Run x86 Linux and Windows applications in Raspberry Pi and other ARM Linux Devices with Exagear
A few weeks ago, I finally decided to buy a Raspberry Pi 2 board as it could always be useful for some testing, at least for comparison purposes. I ended up buying it from Ebay for $40, as it’s $3 to $5 more expensive locally. Nevertheless, I was not sure what I’ll use it first for, but after seeing a tweet for Exagear Desktop software that allows ARM boards to run x86 Linux or Windows applications, the latter through wine. The program is available for Raspberry Pi, Raspberry Pi 2, and ARMv7 devices for $19.95 to $29.95. I asked for a version for testing purposes, and I was given a Google Drive link to download Exagear for Raspberry Pi 2, as well as a 3-month trial key. Installation is very easy. I started by downloading and installing Raspbian Jessie the usual way on a 32GB micro SD card. It went […]
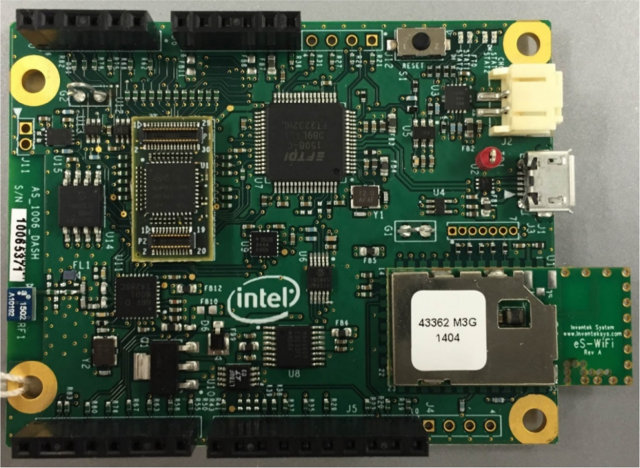
Intel Quark D1000 Customer Reference Board and Intel System Studio for Microcontrollers
Intel unveiled Intel Quark D1000, D2000 and SE micro-controllers last week, with Intel Quark D1000 available now for $2.5 to $4 depending in quantities, and to my knowledge the first Intel MCU that can be considered ultra low power. I could not see a development board at the time, but Intel does have an Intel Quark D1000 Customer Reference Board with a familiar Arduino form factor. Intel Quark D1000 board specifications: MCU – Intel Quark D1000 32-bit CISC micro-controller @ 32 MHz Storage – 4MB SPI flash (Microchip ) Connectivity – Bluetooth LE radio, Wi-Fi (Inventek Systems Serial to Wifi module) Sensor – 3-axis accelerometer Expansion – Arduino compatible headers with GPIOs, I2C, SPI, UART, analog inputs, and 5V, 3.3V and GND. Debugging – mini USB port for programming and debugging; JTAG pins Power – 5V via mini USB port, or LiPo / Li-ion battery Dimensions – N/A Information about […]
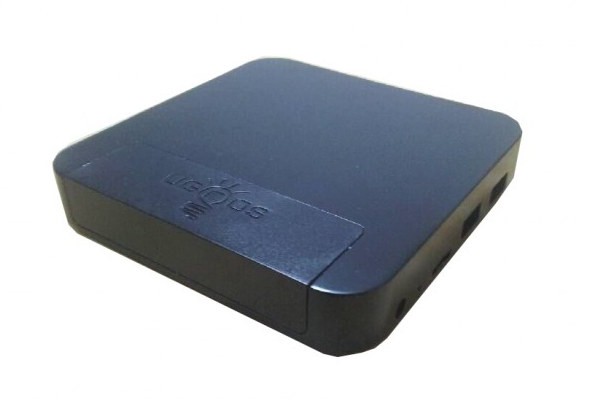
Ugoos AM1 TV Box and Some Amlogic S905 Benchmarks
A few TV boxes based on Amlogic S905 processor are currently up for pre-order such as MXQ Pro and Beelink MINI MX mini PCs with 1GB RAM, 8GB storage, and which are due to ship later this month. Ugoos is also working on their own AM1 TV box and AM2 TV stick based on Amlogic S905 processor, with some better specs, and today released a few more details about Ugoos AM1. Ugoos AM1 specifications: SoC – Amlogic S905 quad core ARM Cortex-A53 @ up to 2.0GHz with penta-core Mali-450MP GPU @ 750 MHz System Memory – 2GB DDR3 (Samsung); 4GB version likely later on Storage – 16GB eMMC flash + SD card slot Video Output – HDMI 2.0 Audio – HDMI, optical S/PDIF Connectivity – 10/100/1000M Ethernet (Realtek RTL8211F), 802.11 b/g/n/ac Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 4.0 (AP6335 module) USB – 3x USB 2.0 host ports Misc – IR receiver Power Supply – […]
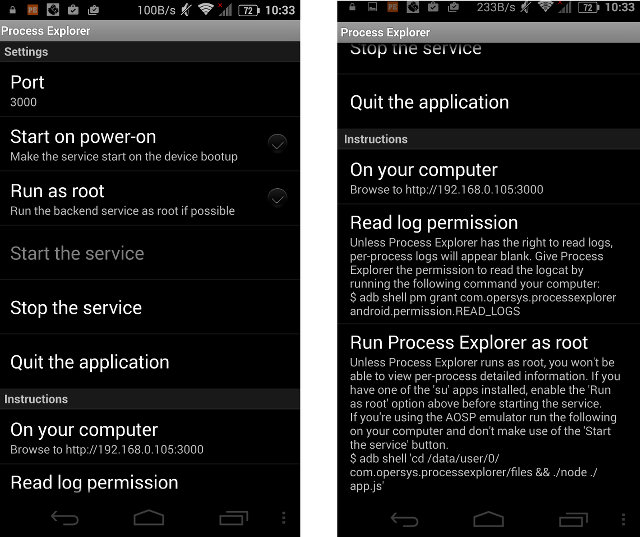
Operys Process Explorer App Shows Android Processes in Your Computer’s Web Browser
Opersys is an Android and Embedded Linux company providing both development and training services, and they regularly attend conferences and release their training materials. The company has also developed a few Android apps to export the file system, the process list and info, and interaction between apps and Android system services exposed via Binder to your computer’s web browser. I found the most interesting app to be Process Explorer, so I gave it a try on Iocean M6752 smartphone. The application requires very little permissions to install, and it’s very simple to use. Simply tap on Start the service, and the app will provide the URL to browse the processes on your computer, in my case http://192.168.0.105:3000. The output is pretty useful, as you get much more information than you could get on your smartphone or tablet screen with CPU and memory usage, running time, logcat, etc… If you click […]
How to Use Nextion Serial Touchscreen Displays – Part 1: Standalone Mode
Itead Studio launched an Indiegogo campaign earlier this year for their Nextion TFT displays that can be connected to external board such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi via the serial interface, or even a standard computer provided you have a USB to TTL debug board. The campaign was successful with over 1,700 backers, and the company recently sent me two samples for review: a 2.4″ display and a 5″ display. In this post, I’ll look at the boards, and make a small standalone demo with Nextion Editor in Windows. Nextion NX3224T024 2.4″ Display The first item is a 2.4″ TFT display called NX3224T024_011N (non-touch) or NX3224T024_011R (Resistive touch) with 65536 color, 320×240 pixel resolution, LED backlight and up to 200nit brightness. It ships with a cable for the serial connection (5V, Tx, Rx, and GND). The back of the display features the serial connector, a micro SD used to load the […]
Getting Started with NodeMCU Board Powered by ESP8266 WiSoC
Since ESP8266 is now so popular, I’ve recently bought a NodeMCU board to try it. I selected this board because the latest version of the board is breadboard-friendly, integrates a USB to serial chip, and it can be powered by a simple USB to micro USB cable. I also noticed a ESP8266 tutorial with NodeMCU firmware by SwitchDoc Labs the other day (using ESP-12 and Adafruit Huzzah), which I applied to my NodeMCU board, but since I encountered a few issues, I decided to report my findings, and write my own little getting started guide to switch on/off LED and GPIOs using a web interface. NodeMCU v0.9 and NodeMCU v1.0 If you are going to purchase a NodeMCU board it’s important to know there are two official versions: NodeMCU v0.9 with ESP-12 module NodeMCU v1.0 with ESP-12E module The main complain about NodeMCU v0.9 is that while it fits on […]
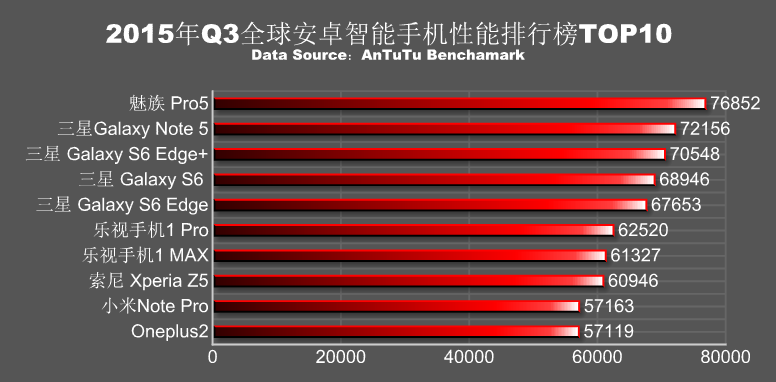
Top 10 Antutu Scores of 2015 for Smartphones So Far
I’m mainly focusing on Android mini PCs, and not so much on mobile devices. But this year, silicon vendors launched 64-bit ARM processor for TV boxes based on the low power Cortex A53 cores, lowering costs instead of improving performance of their 32-bit ARM processors, as media player don’t usually need very fast processor simply because video decoding is normally handled by the video engine. Two exceptions being Amazon Fire TV 2015 which gets over 51,000 points mostly thanks to MediaTek MT8173‘s two Cortex A72 cores, and Nvidia Shield Android TV box getting over 68,000 points, but sadly these two devices are not (easily) available worldwide yet. But on the mobile space, the race to faster and faster performance is still on, and according to a recent post on Antutu website (in Chinese), the fastest smartphones now reach over 75,000 points in the popular benchmark. I had to look up the […]