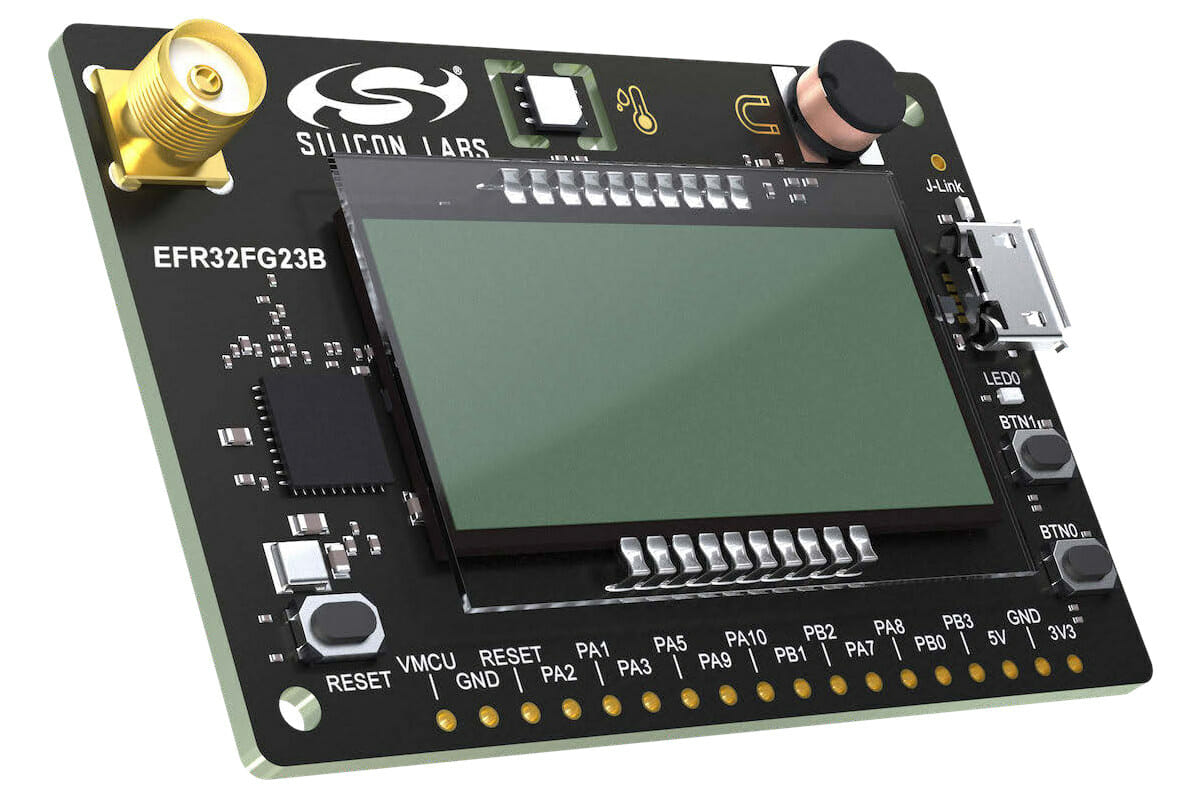
Silicon Labs has announced two new sub-GHz wireless SoCs with EFR32FG23 (FG23) and EFR32ZG23 (ZG23) devices adding to the company’s Gecko Series 2 Cortex-M33 platform. Both FG23 and ZG23 support up to one mile (~1.6 km) wireless range, 10+ year battery life on a coin-cell battery, are certified with Arm PSA Level 3 security, and support “advanced wireless technologies” such as Amazon Sidewalk, mioty, Wireless M-Bus (WM-Bus), Z-Wave, and proprietary IoT networks. Silicon Labs explains the chips’ ultra-low transmit and receive radio power (13.2 mA TX at 10 dBm, 4.2 mA RX at 920 MHz) and RF implementation (+20 dBm output power and -125.3 dBm RX at 868 MHz, 2.4 kbps GFSK), makes the long-range and long battery life possible. The ZG23 is designed for Z-Wave applications with Long Range and Mesh connectivity and can be integrated into either end devices or gateways. The company is also working on ZG23-based […]
cuplTag battery-powered NFC tag logs temperature and humidity (Crowdfunding)
Temperature and humidity sensors would normally connect to a gateway sending data to the cloud, the coin-cell battery-powered cuplTag NFC tag instead sends data to your smartphone after a tap. CulpTag is controlled by an MSP430 16-bit microcontroller from Texas Instruments which reads and stores sensor data regularly into an EEPROM, and the data can then be read over NFC with the tag returning an URL with the data from the sensor and battery, then display everything on the phone’s web browser (no app needed). cuplTag specifications: MCU – Texas Instruments MSP430FR2155 16-bit microcontroller @ 24 MHz Storage – 2K bytes EEPROM part of NT3H2111 for up to 188 temperature & humidity data points or 376 temperature-only data points Connectivity – Passive NFC, tap-to-read via NXP NT3H2111 NFC tag Sensors – HDC2021 temperature and humidity sensors Measurement interval – 3 minutes to 65535 minutes (Default: 10 minutes) Battery – CR1220 battery […]
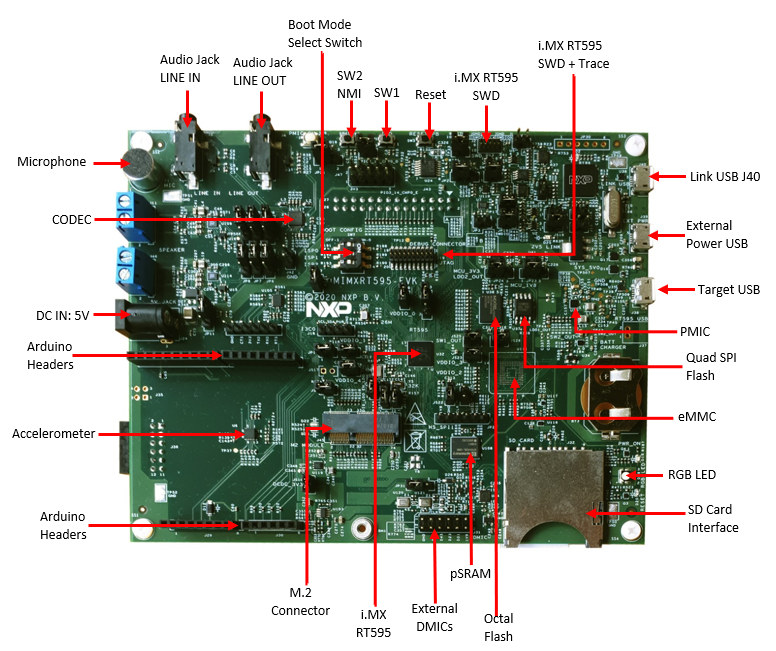
NXP i.MX RT500 Cortex-M33 Crossover MCU integrates DSP, 2D GPU for wearables and IoT devices
NXP i.MX RT500 is the second Cortex-M33 Crossover MCU following the NXP i.MX RT600 Series announced in 2018, and optimized for low-power HMI applications such as wearables and Smart Home & IoT devices. NXP Crossover MCUs are typically clocked at 600 MHz or more, but NXP i.MX RT500 Cortex-M33 is limited to 200 MHz, and combined with 200 MHz Tensilica Fusion F1 DSP as well as a 2D GPU, and power optimizations that enable long battery life of up to 40 days on a charge for wearables like smartwatches. NXP i.MX RT500 key features and specifications: MCU Core – Cortex-M33 @ up to 200 MHz with Arm TrustZone, M33 built-in Memory Protection Unit (MPU), PowerQuad hardware accelerator for DSP functions, CASPER crypto coprocessor for asymmetric cryptographic algorithms DSP Core – Cadence Tensilica Fusion F1 DSP @ up to 200 MHz On-Chip Memory Up to 5 MB of system SRAM accessible […]
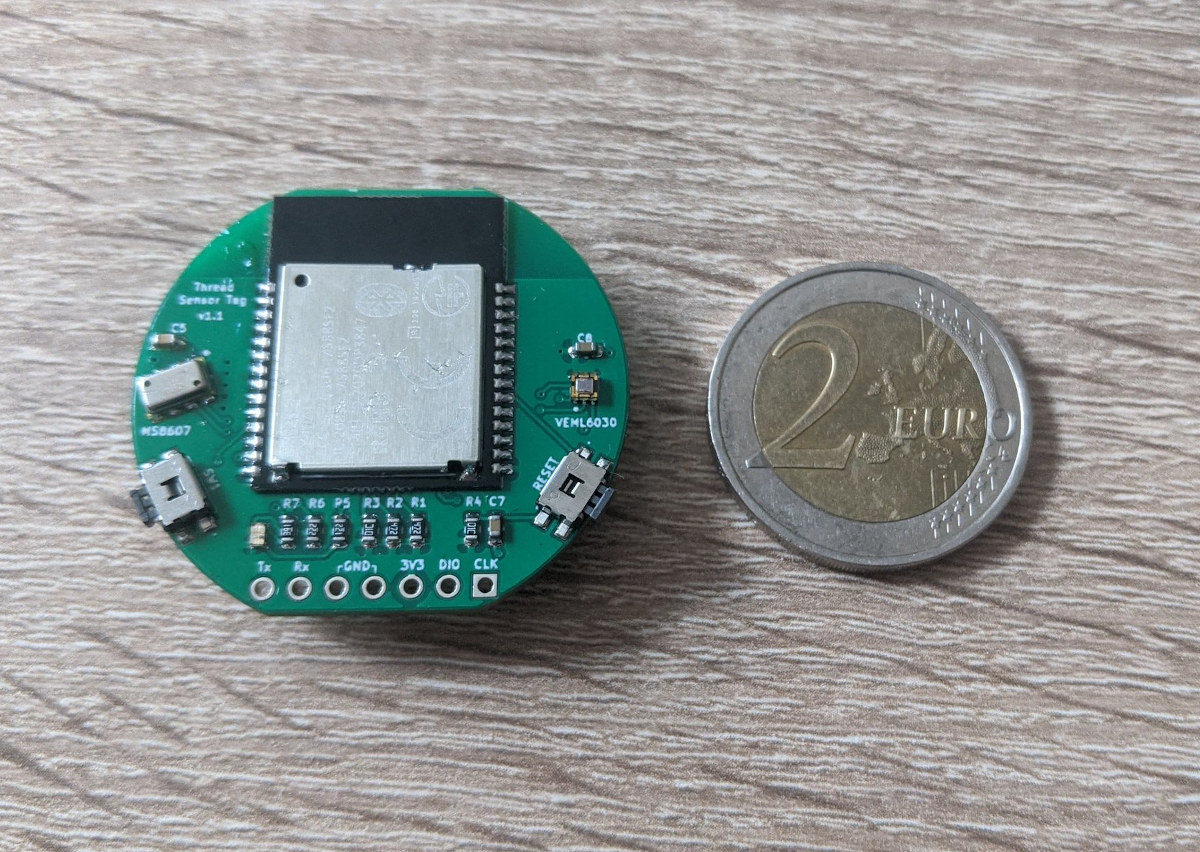
Coin cell-powered OpenThread sensor board can send data every 20 seconds for three years
Monkey Store’s Thread Sensor Tag is a pressure, humidity, temperature, and light sensor that connects to the OpenThread network, and is capable of transmitting MQTT/UDP data every 20 seconds over a period of around three years from a single coin cell battery. As a reminder, OpenThread is an implementation of the Thread IoT network protocol that was unveiled in 2016 by Nest Labs (now Google/Alphabet). This has not been widely used so far, but we did write about MKR SharkyPro development board with OpenThread support via STMicro STM32WB5MMG wireless module earlier this year, and Monkey Store is telling us both Google and Apple are working on devices with support for the IoT protocol. Thread Sensor Tag specifications: Wireless module – Minew MS88SF2 based on Nordic Semi nRF52840 multi-protocol 2.4GHz wireless Cortex-M4 microcontroller Sensor VEMLS6030 I2C light sensor MS8607 pressure, humidity, and temperature sensor I/Os – 7x through holes with Tx/Rx, […]
Ultra-Low-Power RISC-V System-on-Chip features Adaptive Body Biasing Technology
CSEM and USJC together have developed an ultra-low-power RISC-V chip for electronic gadgets such as wearables. The semiconductor companies, from Switzerland and Japan respectively, have been in the market for a while, developing technologies for low-power chips. Their latest collaboration uses Adaptive Body Biasing (ABB) and Deeply Depleted Channel (DDC) to build an ultra-low-power RISC-V chip with all the required and necessary components. Originating from the labs of CSEM, the Adaptive Body Biasing dwells into the operating efficiency of all the modes of ON, Standby, and OFF. There has been the problem of power leakage in Standby and OFF operating modes, but the Adaptive Body Biasing technology helps design to minimize power leakage when the processor is not operating while keeping the best performance in ON mode. For most of the designs, the processor is in Standby mode waiting for the incoming data or the next event to be offered. […]
Bluetooth 5.3 new features lower latency, interference, improve battery life, security
Bluetooth 5.3 Core Specification was adopted on July 13, 2021, without fanfare, and the only related announcement that I could find is CEVA RivieraWaves Bluetooth IP getting support for Bluetooth 5.3. Bluetooth 5.3 brings four new features or enhancements and removes one extension from the core specification: Periodic Advertising Enhancement – The AdvDataInfo (ADI) field of the common extended advertising payload format may now be included in AUX_SYNC_IND protocol data units (PDUs) which are broadcast when a device is performing periodic advertising. The Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) controllers may now use the information in the ADI field to recognize packets that contain retransmitted copies of identical or semantically equivalent data, and discard those packets in order to prevent unnecessary processing on the nodes, and make sure the overall throughput is not affected due to retransmitted packets. Encryption Key Size Control Enhancement – In Bluetooth BR/EDR, encryption key sizes are negotiated […]
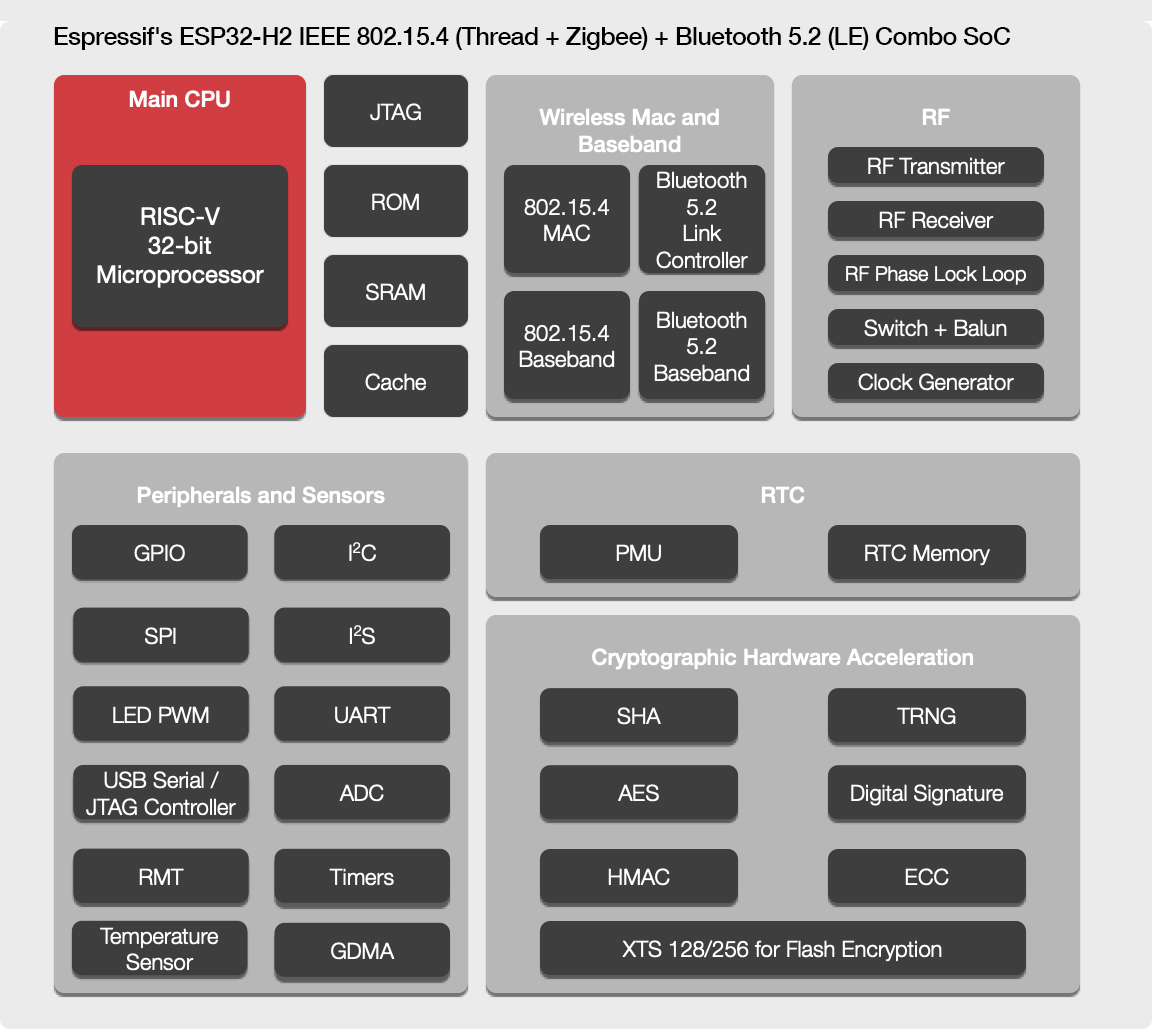
ESP32-H2 RISC-V WiSoC announced with Zigbee 3, Thread, and Bluetooth LE 5.2
Just a few days ago, we noted ESP32-H2 802.15.4 & BLE RISC-V SoC had shown up in the source code, and tried to derive specs and a block diagram from the info seeing it was similar to ESP32-C3, but swapping the WiFi radio for an 802.15.4 radio. We don’t need to guess anymore, as Espressif Systems has just announced ESP32-H2 RISC-V WiSoC with support for Zigbee 3.x, Thread 1.x through the 802.15.4 radio, as well as Bluetooth LE 5.2. So overall it’s very close to what we discussed from the information in the source code with ESP32-H2 highlights including: CPU – 32-bit RISC-V core (at up to 96 MHz) RAM – 256 KB SRAM Storage – External flash support Wireless connectivity IEEE 802.15.4 radio with Zigbee 3.x and Thread 1.x support, Matter protocol Bluetooth 5.2 (LE) radio designed in-house, with support for direct connection, Bluetooth Mesh, Bluetooth LE Audio Future […]
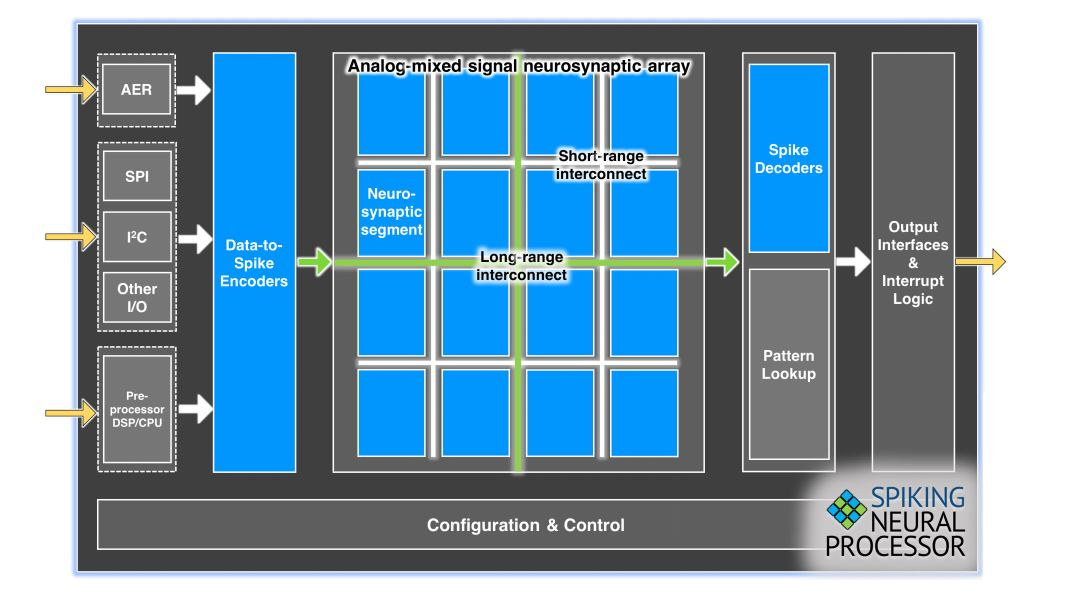
Innatera neuromorphic AI accelerator for spiking neural networks (SNN) enables sub-mW AI inference
Most AI accelerators currently rely on CNN (convolutional neural network) to perform AI inference in a much faster and efficient way than on CPU cores, or even GPUs. But there’s another type of neural network, namely spiking neural networks (SNN) that uses the timing of spikes in an electrical signal to perform pattern recognition tasks in a way similar to neurons in the brain. The claims in terms of efficiency are quite unbelievable, with up to 10,000 times more performance per watts than in microprocessor and digital accelerometer, 500 times lower energy, and 100 times shorter latency. Several companies are working on neuromorphic AI accelerators for spiking neural networks, with notably Prophesee focusing on image processing, and Innatera that is working on an ultra-low-power AI accelerator handling audio, health, and radar for sound and speech recognition, vital signs monitoring, elderly person fall sensors, etc… Innatera recently provided additional information about […]