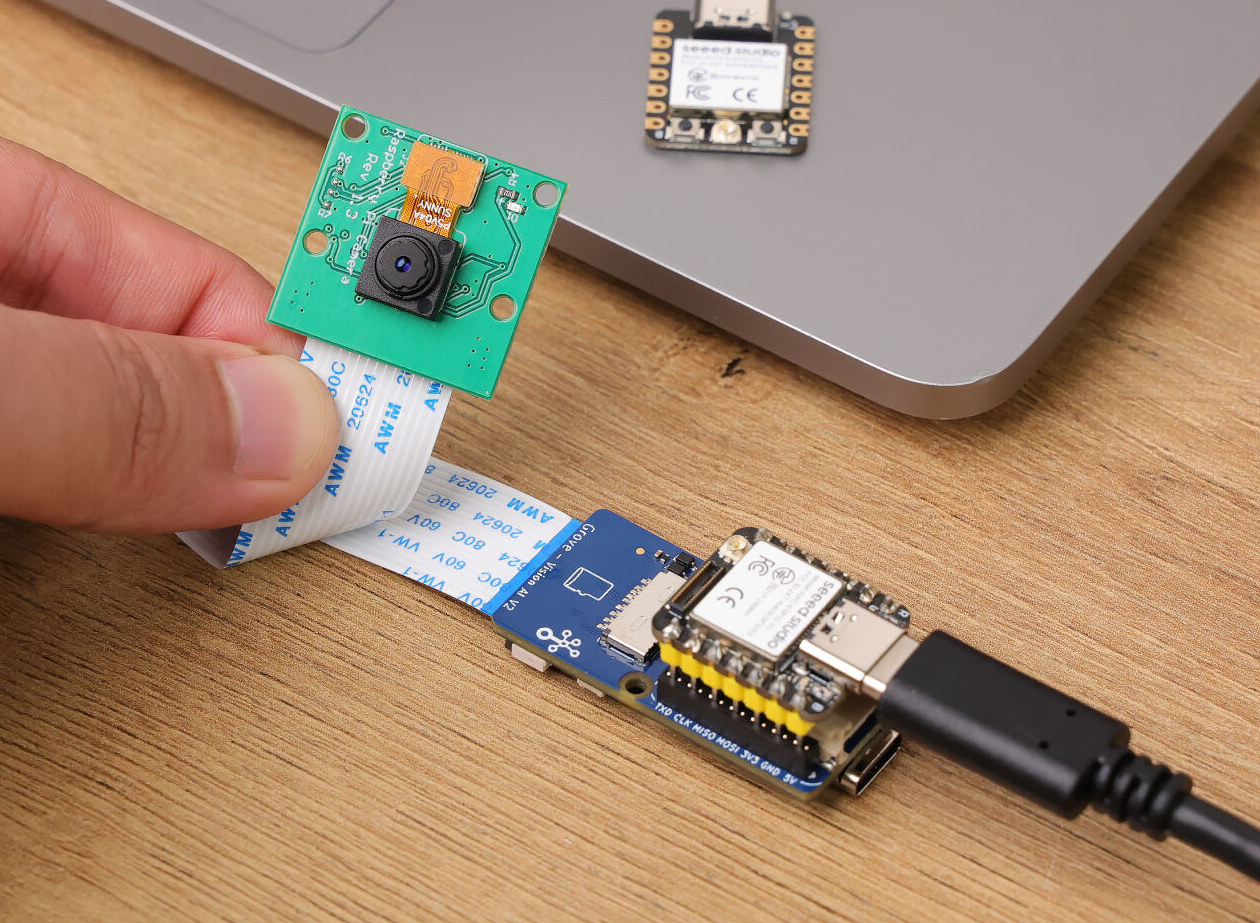
Seeed Studio’s Grove Vision AI V2 module is based on the HiMax WiseEye2 HX6538 dual-core Cortex-M55 AI microcontroller with an Arm Ethos-U55 microNPU and features a MIPI CSI connector for an OV5647 camera. It is designed for AI computer vision applications using TensorFlow and PyTorch frameworks and connects to hosts such as Raspberry Pi SBCs, ESP32 IoT boards, Arduino, and other maker boards over I2C. We tested the previous generation Grove Vision AI module based on the 400 MHz HX6537-A DSP-based AI accelerator using the SenseCAP K1100 sensor prototype kit with LoRaWAN connectivity, and managed to have the kit perform face detection and send the data over LoRaWAN. The Grove Vision AI V2 builds on that but with a modern Arm MCU core and more powerful AI accelerator that can run models such as Mobilenet V1/V2, Efficientnet-lite, and Yolo v5 & v8 using the SenseCraft low-code/no-code platform. Grove Vision AI […]
Infineon launches PSoC Edge Cortex-M55/M33 microcontrollers for enhanced AI and ML applications
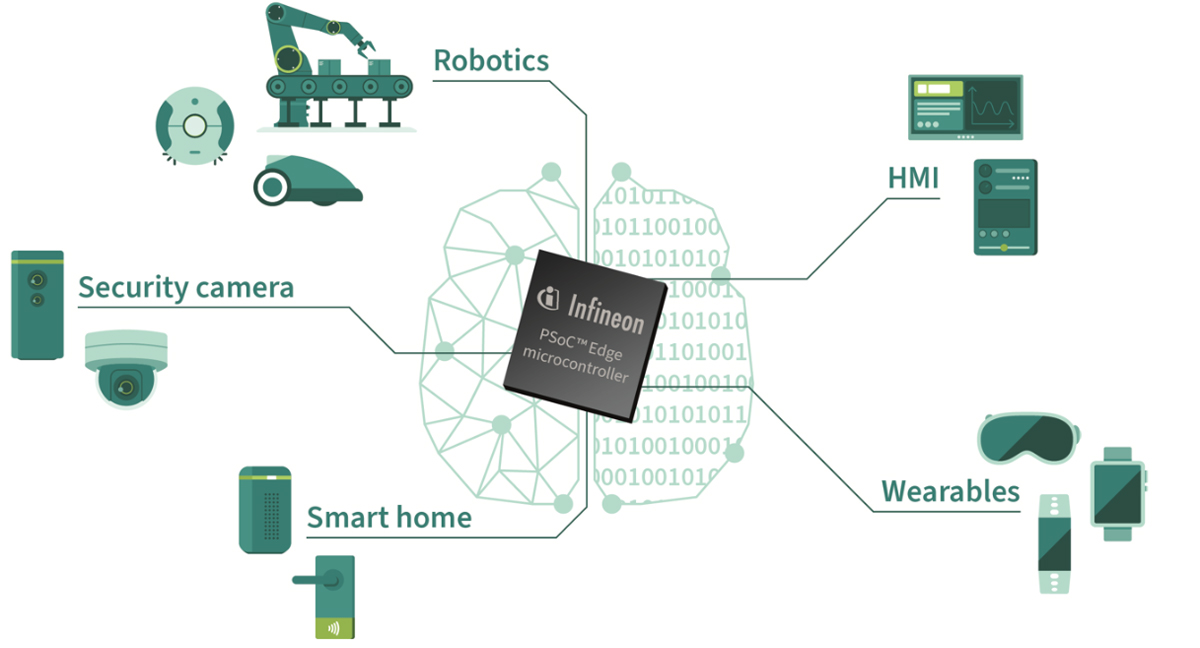
Infineon’s new PSoC Edge series of microcontrollers integrates the Arm Cortex-M55 core with Helium DSP and the Ethos U55 NPU unit for advanced AI tasks. It also includes a power-efficient Arm Cortex-M33 core paired with an NNLite(DSP/NPU) for simpler AI tasks. This setup allows the device to be more efficient in varying load conditions. Infineon’s PSoC lineup is a configurable microcontroller powered by Arm Cortex-M4, Cortex-M3, or Cortex-M0+ cores. The main USP (Unique Selling Point) of this lineup is its configurable digital and analog components. This feature makes them somewhat similar to an FPGA, but an FPGA is far more difficult to program than these microcontrollers and they are also very power-hungry. The device is equipped with advanced HMI and “Always-on” capability. “Always-on” is a feature of this device to constantly monitors and responds to signals automatically, making it suitable for smart homes, security, wearables, robotics, and many more. Key […]
Renesas RA8D1 Arm Cortex-M85 SoC features LCD display interfaces, 2D graphics accelerator
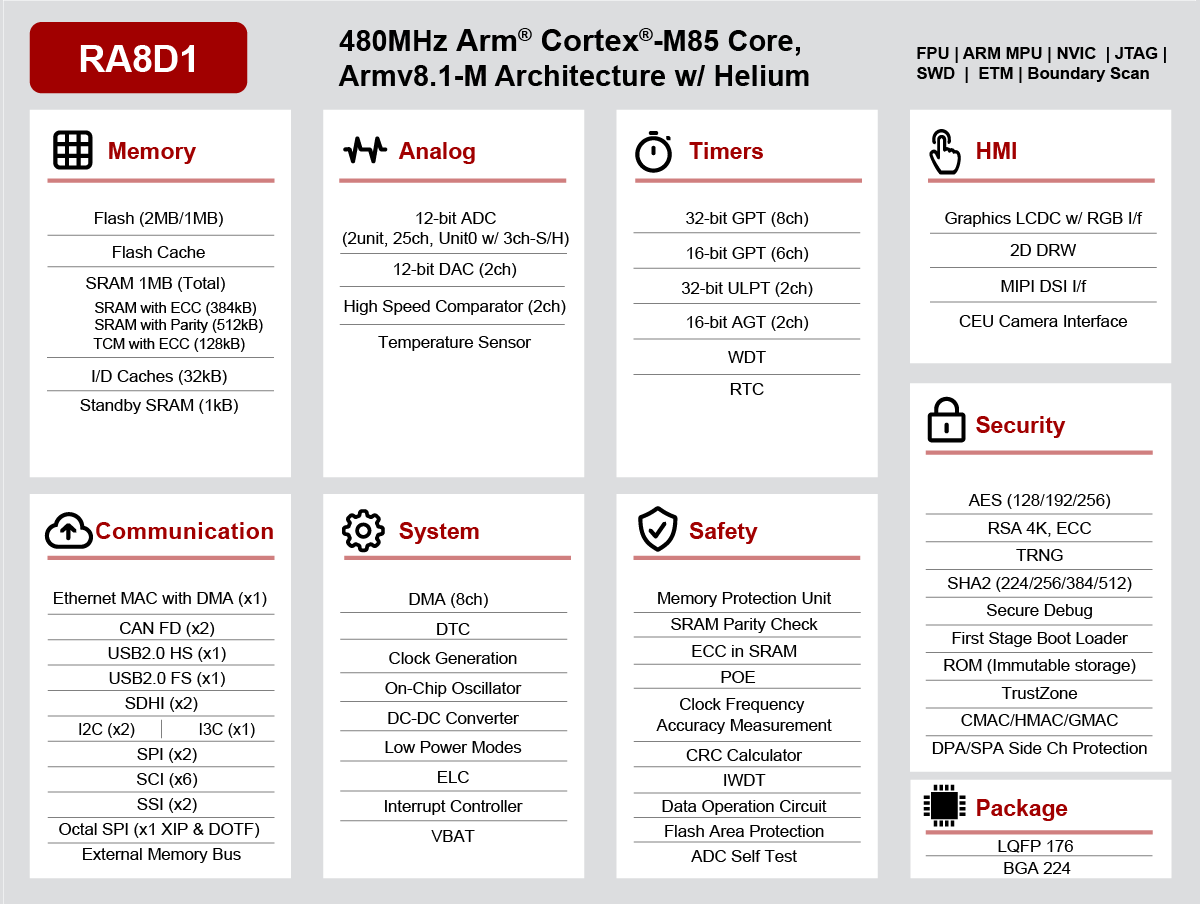
Renesas RA8D1 is a new Arm Cortex-M85 microcontroller with graphics capabilities such as a 2D graphics accelerator and MIPI DSI and parallel RGB interfaces to connect an LCD that will make the chip suitable for HMI applications. Renesas introduced the world’s first Arm Cortex-M85 microcontroller with the RA8M1 just a few weeks ago, but the MCU has limited multimedia capabilities with just a 16-bit Capture Engine Unit (CEU) interface to connect a camera. The second member of the Renesas RA8 family fills this void with the RA8D1 microcontroller adding an LCD controller and a 2D graphics drawing engine on top of the CEU camera interface. Renesas RA8D1 specifications: MCU core – Arm Cortex-M85 clocked at 480 MHz with Helium MVE (M-Profile Vector Extension) with 32KB I/D caches, 12KB data flash Memory & Storage 1MB SRAM with TCM (128KB) 1MB to 2MB Flash memory 32-bit external SDRAM interface Display interfaces and […]
Tokay Lite – A battery-powered no-code AI camera based on ESP32-S3 WiSoC (Crowdfunding)
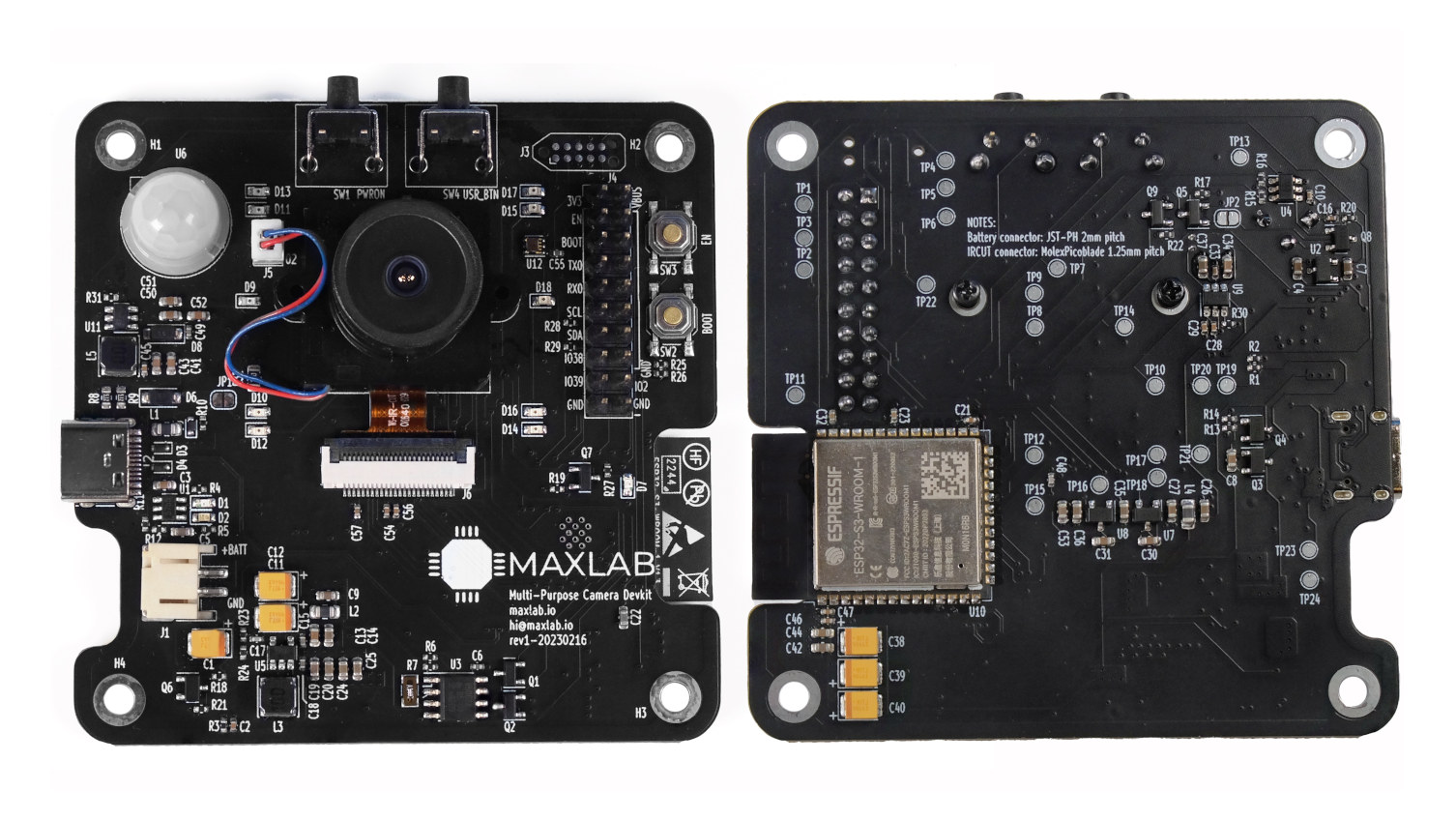
Maxlab’s Tokay Lite is an OHSWA-certified AI camera based on ESP32-S3 WiFI and Bluetooth SoC that can be used for computer vision (e.g. facial recognition & detection) and robotics applications without the need to know programming languages since a web interface is used for configuration. The WiFi and Bluetooth AI camera also features night vision with four IR LEDs, an IR cut filter, light and PIR motion sensors, a 20-pin expansion connector with SPI and UART, support for an external RTC, and can take power from USB-C or a LiPo battery. Tokay Lite specifications: Wireless module ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 MCU – ESP32-S3 dual-core LX7 microprocessor @ up to 240 MHz with Vector extension for machine learning, 512 KB SRAM Memory – 8MB PSRAM Storage – 8MB SPI flash Connectivity – WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5 with LE/Mesh PCB antenna Certifications – FCC/CE certification Camera OV2640 camera sensor (replaceable) via DVP interface Image Capabilities: […]
Arm Cortex-M52 aims to bring AI to small, low-cost IoT devices
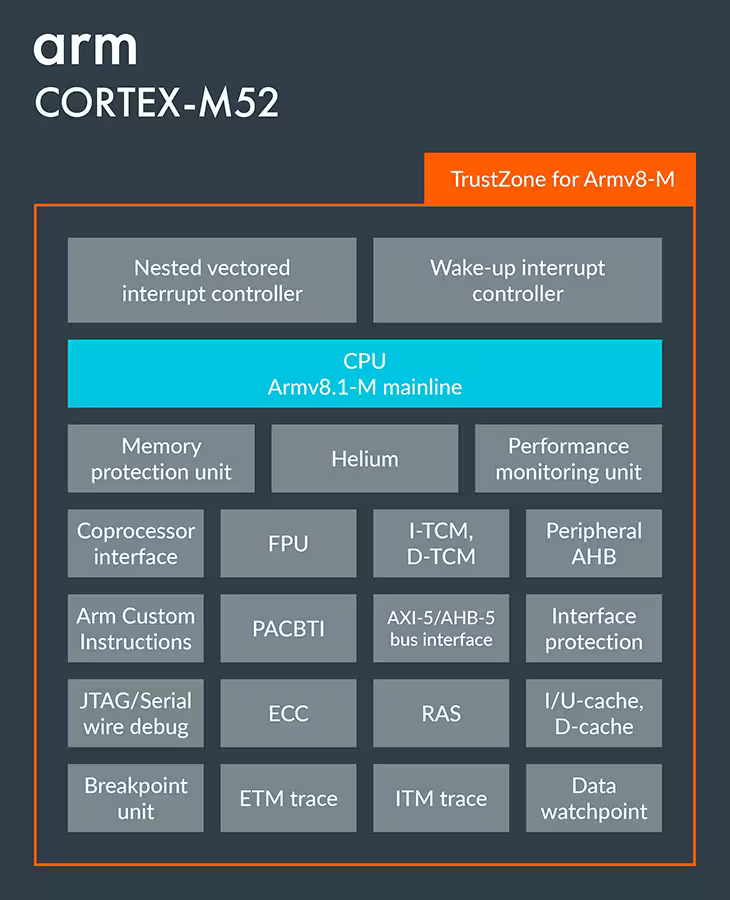
Arm Cortex-M52 is a new microcontroller core featuring Arm Helium technology and designed to bring AI capabilities to smaller and lower-cost IoT devices than what is already possible with SoCs based on the Arm Cortex-M55 core. Arm Cortex-M52 key features and specifications: Architecture – Armv8.1-M Bus interfaces AMBA 5 AXI 32-bit or AMBA 5 AHB 32-bit Main system bus AMBA 5 AHB 32-bit Peripheral bus AMBA 5 AHB 32-bit TCM Access bus (subordinate port) Pipeline – 4-stage pipeline Security Arm TrustZone technology (optional), with optional Security Attribution Unit (SAU) of up to 8 regions. Stack limit checking. Optional support for PACBTI extension (Pointer Authentication, Branch Target Identification) Memory Protection – Optional Memory Protection Units (MPU) for process isolation with up to 16 MPU regions and a background region – if TrustZone is implemented, there can be a Secure and a Non-secure MPUs. DSP extension – 32-bit DSP/SIMD extension Optional single-beat […]
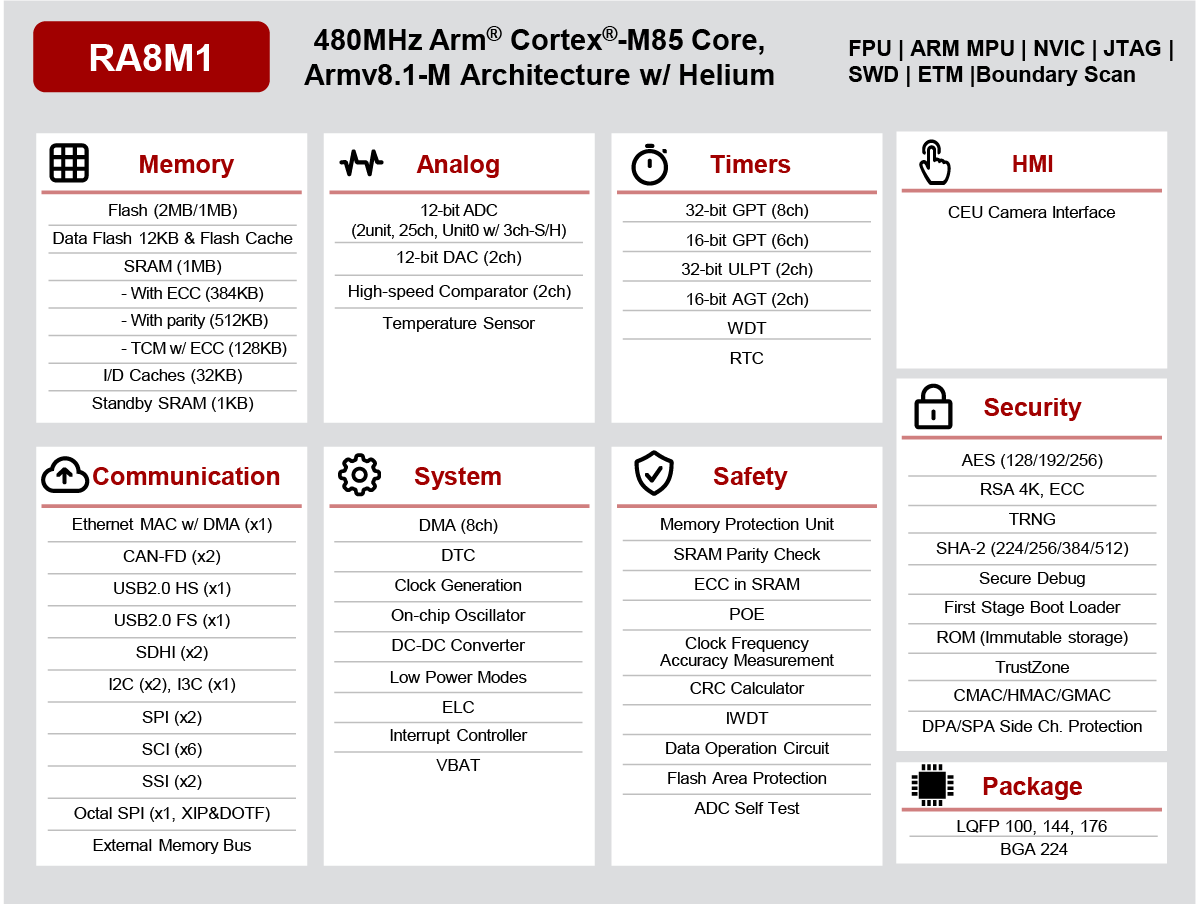
Renesas RA8M1 is the world’s first Arm Cortex-M85 microcontroller
Renesas RA8M1 is an up to 480 MHz Arm Cortex-M85 microcontroller with Arm Helium technology to improve DSP and machine learning performance on Cortex-M microcontrollers, and delivering up to 6.39 CoreMark/MHz performance using EEMBC’s CoreMark, or over 3,000 CoreMark at 480 MHz. The Arm Cortex-M85 core was first unveiled in April 2022 as a faster Cortex-M7 alternative and new Arm Helium technology that delivers machine learning performance similar to Cortex-M55 application processor. We had some teases about the upcoming Renesas Cortex-M85 in the last year, but the world’s first Cortex-M85 microcontroller is finally here. Renesas RA8M1 key features and specifications: MCU core – Arm Cortex-M85 clocked at 240 to 480 MHz with Helium MVE (M-Profile Vector Extension) with 32KB I/D Caches and 12KB Data Flash Memory & Storage 1MB SRAM with TCM 1MB to 2MB Flash memory External memory interfaces (CS/SDRAM) Camera – 16-bit Capture Engine Unit (CEU) interface Communication […]
ESP32-S3-BOX-3 devkit comes with 2.4-inch display, dual microphone, PCIe expansion connector
Espressif Systems has launched an update to their ESP32-S3-Box development kit for online and offline voice assistants with the ESP32-S3-BOX-3 devkit that still features a 2.4-inch capacitive touchscreen display with 320×240 resolution, two microphones, a built-in speaker, and a USB-C port, but replaces the PMOD connector by a PCIe connector for various expansion modules. The open-source ESP32-S3 development kit is powered by the ESP32-S3 SoC with AI extensions and can be used to implement all sorts of solutions using the company’s ESP-SR, ESP RainMaker, and Matter solutions such as an offline voice assistant, a chatbot powered by ChatGPT, a handheld gaming console, a tiny robot, a Matter-compatible Smart Home hub, and more. ESP32-S3-BOX-3 specifications: WiSoC – ESP32-S3 dual-core Tensilica LX7 up to 240 MHz with Wi-Fi 4 & Bluetooth 5, AI instructions, 512KB SRAM Memory and Storage – 16MB octal PSRAM and 16MB QSPI flash Display – 2.4-inch capacitive touchscreen […]
TRACEPaw sensorized paw helps legged robots “feel the floor” with Arduino Nicla Vision
Our four-legged friends don’t walk on tarmac the same way as they do on ice or sand as they can see and feel the floor with their eyes and nerve endings and adapt accordingly. The TRACEPaw open-source project, which stands for “Terrain Recognition And Contact force Estimation through Sensorized Legged Robot Paw“, aims to bring the same capabilities to legged robots. Autonomous Robots Lab achieves this through the Arduino Nicla Vision board leveraging its camera and microphone to run machine learning models on the STM32H7 Cortex-M7 microcontroller in order to determine the type of terrain and estimate the force exercized on the leg. But the camera is apparently not used to look at the terrain, but instead, at the deformation of the silicone hemisphere – made of “Dragon Skin” – at the end of the leg to estimate 3D force vectors, while the microphone is used to recognize terrain types […]