Freescale and then NXP have been talking about i.MX8 processors for several years, and this spring unveiled i.MX 8 Multisensory Enablement Kit without giving much details about the processor except it would include both Cortex A72 & A53 cores. But NXP put out a press release yesterday about “Multisensory Automotive eCockpit Platform to Advance Multimedia Experiences in Future Cars” which appears to be the same news but with different words, except the content of the PR has more interesting bits such as: The new family, which is based on up to six 64-bit ARMv8-A technology processor cores and includes a HiFi 4 DSP, LPDDR4 and DDR4 memory support as well as dual Gigabit Ethernet with audio video bridging (AVB) capability, is designed to advance automotive dashboard graphics such as instrument clusters, infotainment visuals, heads-up displays, rear-seat screens and more. Capable of driving four HD screens with independent content or a […]
NXP i.MX 6ULL Cortex A7 Processor is the Latest Member of i.MX6 32-bit ARM Processor Family
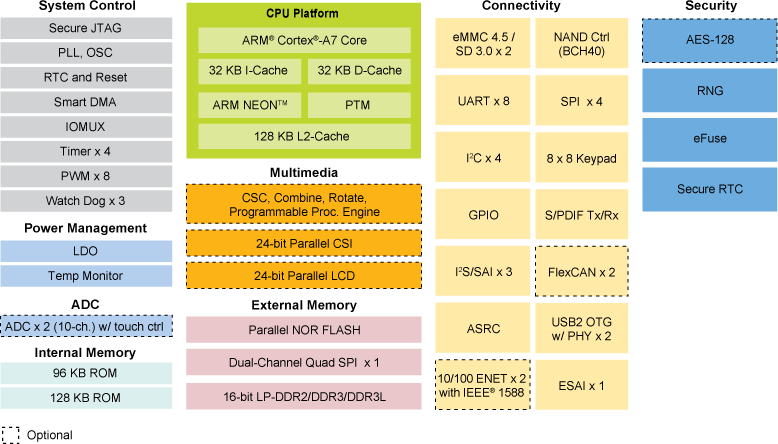
Freescale first unveiled i.MX6 processor family at CES 2011. Since then NXP has acquired Freescale, and kept working on the processors and even recently unveiled NXP i.MX 6ULL Cortex A7 processor promising 30 percent more power efficiency than its nearest competitors, and designed for “cost-effective solutions for the growing IoT consumer and industrial, mass markets”. NXP i.MX 6ULL key features and specifications: CPU – ARM Cortex A7 core @ up to 528 MHz with 128KB L2 cache Memory I/F – 16-bit DDR3/DDR3L, LPDDR2 memory support Storage I/F – 8/16-bit parallel NOR flash / PSRAM, dual-channel Quad-SPI NOR flash, 8-bit raw NAND flash with 40-bit ECC, 2x MMC 4.5/SD 3.0/SDIO Port Display & Camera I/F Parallel LCD Display up to WXGA (1366×768) Electrophoretic display controller support direct-driver for E-Ink EPD panel, with up to 2048×1536 resolution at 106 Hz 8/10/16/24-bit Parallel Camera Sensor Interface Peripherals 2x USB 2.0 OTG, HS/FS, Device […]
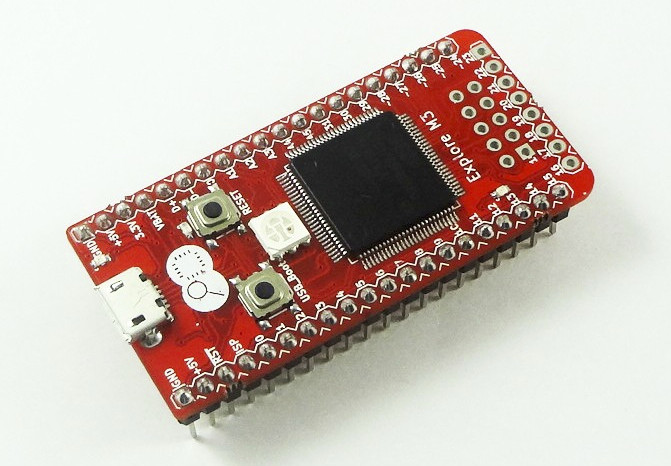
Explore M3 Board based on NXP LPC1768 Cortex M3 MCU Comes with Lots of Tutorials (Crowdfunding)
Explore M3 is an ARM Cortex M3 development board powered by a micro USB port, with plenty of I/Os, Arduino compatible, and the developers have also written many tutorials to help people getting started as fast and easily as possible. A starter kit with cables and sensors is also available with the board. Specifications: MCU – NXP LPC1768 ARM Cortex M3 @ up to 100MHz with 512KB flash, 64KB RAM, USB – 1x micro USB 2.0 OTG port for programming and power Expansion Headers – 2x 20-pin male headers + 8-pin unpopulated header with 38x GPIOs, 4x UARTs, 2x CAN, 2x SPI, 2x I2C, 6x PWM, 5x ADC, 1x DAC, 2x interrupt pins, I2S audio, and power signal Debugging – JTAG/SWD Debug connector Misc – USB boot and reset buttons Dimensions – 55mm x 25mm The hardware is somewhat similar to mbed LPC1768 board but with a few more I/Os. […]
Teensy 3.5 & 3.6 Boards Feature NXP Kinetis K64 & K66 MCUs (Crowdfunding)
Paul Stoffregen has been making Teensy USB MCU development boards since 2008, and has just launched the latest Teensy 3.5 & 3.6 boards powered by NXP (previously Freescale) Kinetis K64 & K66 ARM Cortex-M4 MCUs with a micro USB port for power and programming, a micro SD slot, and several I/Os. Boards specifications: MCU Teensy 3.5 (T3.5) – NXP Kinetis K64 ARM Cortex M4 MCU @ 120 MHz with FPU, 512KB flash, 192 KB RAM, 4K EEPROM Teensy 3.6 (T3.6) – NXP Kinetis K66 ARM Cortex M4 MCU @ 180 MHz with FPU, 1MB flash, 256KB RAM, 4K EEPROM Storage – micro SD card port USB – 1x USB Full Speed (12 Mbit/sec) Port; T3.6 only: 480 Mbit/sec host port Connectivity – 10/100M Ethernet mac 62x I/O Pins (42 breadboard friendly) 25x Analog Inputs to 2 ADCs with 13 bits resolution 2x Analog Outputs (DACs) with 12 bit resolution 20x […]
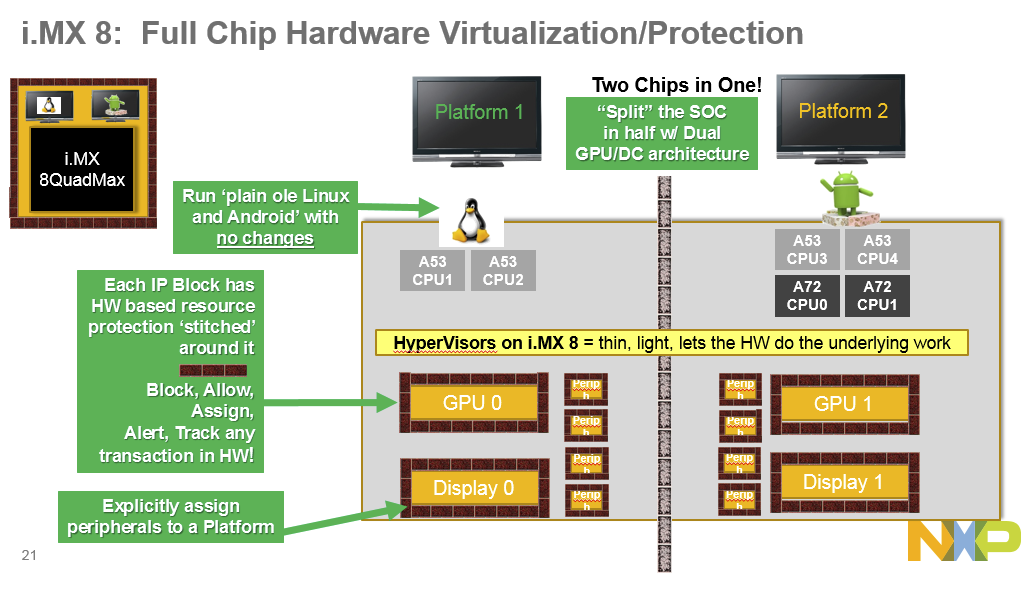
NXP Unveils i.MX 8 Multisensory Enablement Kit with Hexa Core ARMv8 Processor
Freescale, now NXP, i.MX 8 processors have been a long time coming, but finally the company has now unveiled a Multisensory Enablement Kit based on i.MX 8 hexa core ARMv8 processor combined with a Vulkan-ready & OpenCL capable GPU. Key features of the development kit: Multisensory Processor Board Multisensory Expansion Board Isolation and separation of secure, safe and open domains Rich compute (6x ARMv8 64-bit main CPUs, OpenCL GPU) Vulkan-ready GPU with HW tessellation and geometry shading Efficient, multi-screen (4x) support via HW virtualization Failover-ready display path Up to 8x camera input for 360 degree vision Integrated vision processing HDR enhanced video Multi-sensor fusion and expansion Multi-core audio and speech processing NXP radio solution integration However, at the time of writing, there’s very little information about i.MX8 processors themselves, but I’m confident much more info should soon surface as NXP FTF 2016 is taking place now until May 19, 2016. […]
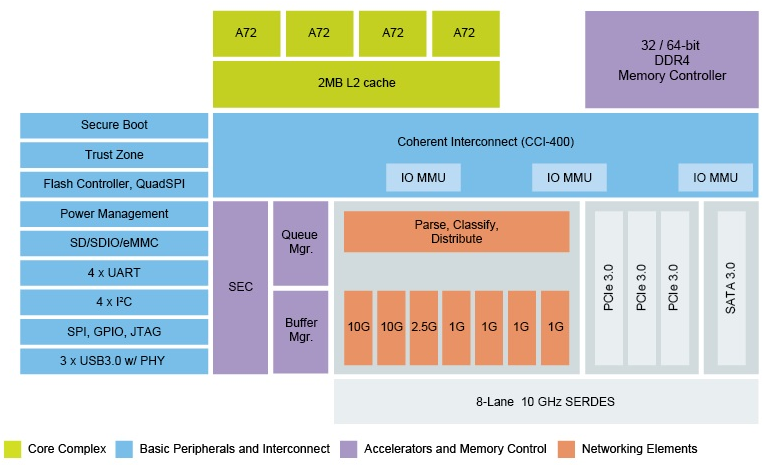
NXP Introduces QorIQ LS1046A Quad Cortex A72 Communication Processor with 10 GbE, SATA 3.0, PCIe 3.0, etc…
NXP has unveiled a new QorIQ communication processor with LS1046A based on quad ARM Cortex-A72 cores, and including 10GbE, PCIe Gen.3, SATA 3.0, and USB 3.0 interfaces. The processors targets CPE and vCPE (virtual Customer Premise Equipment), routers, NAS, and service provider gateways for the home and small office, as well as single board computers. QorIQ LS1046A key specifications: CPU – Four ARM Cortex -A72 cores with 2MB L2 cache; 32,000 CoreMarks. Memory – 32-/64-bit DDR4 memory controller Storage – SATA 3.0 controller, quad SPI Connectivity 2x 10 Gigabit Ethernet controllers 1x 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet controller 4x Gigabit Ethernet controllers Other peripherals 3x PCIe 3.0 Controllers, x4, x2, x 1 3x USB 3.0 with integrated PHY 4x UART, 4x I2C, SPI, GPIO JTAG Support for hardware-based virtualization via ARM SMMU Packet processing acceleration – Packet classification and distribution; hardware work scheduling, shaping, and buffer management. Integrated security engine – High-speed […]
Hexiwear is an Open Source Wearable Development Kit Expandable with Add-on Boards (Crowdfunding)
MikroElektronika has designed Hexiwear, a wearable development kit that you can wear and hack as a smartwatch thanks to an (optionally) included wristband, or use a an IoT development kit thanks to its docking station taking up to three “Click” boards among a choice of over 180 modules. . Hexiwear hardware specifications: MCU – NXP Kinetis K64x ARM Cortex-M4 MCU @ 120 MHz with 1MB Flash and 256KB SRAM Storage – 8 MB Flash memory Display – 1.1” full color OLED display with capacitive touch Connectivity – Bluetooth 4.0 LE and 802.15.4 via NXP Kinetis KW4x Cortex-M0+ wireless MCU Sensors -3D accelerometer and magnetometer (NXP FXOS8700CQ), 3-Axis gyroscope (NXP FXAS21002), pressure sensor (NXP MPL3115A2R1), light-to-digital converter, humidity and temperature sensor, heart-rate sensor (HRM) USB – micro USB cable for power and charging Misc – RGB LED, haptic feedback engine, docking connector Battery – 190 mAh 2C Li-Po battery; 600 mA […]
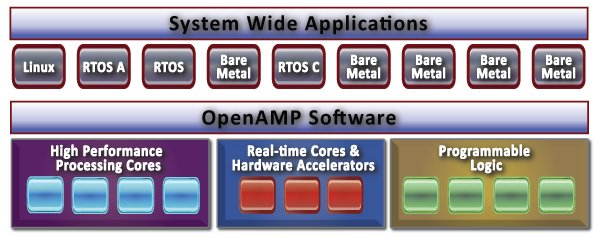
OpenAMP Open Source Framework Provides the Glue between Linux, RTOS, and Bare Metal Apps in Heterogeneous SoCs
SoCs becoming more complex, and go beyond homogeneous multicore systems by mixing different type of cores such as high performance cores, low power real-time cores, or even FPGA fabric. Examples include NXP i.MX6 SoloX with an ARM Cortex A9 core for Linux apps, and an ARM Cortex M4 core for real-time tasks, or Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC with Cortex A53 core for higher level apps, Cortex R5 cores for real-time processing, and Ultrascale FPGA logic. All these different cores are running their own Linux based OS, real-time operating system or bare metal application, and all this makes software development an even greater difficult tasks. In order to reduce the complexity, and address some of the issues, the Multicore Association has launched a new working group targeting the management, expansion, and standardization of OpenAMP (Open Asymmetric Multi Processing), an open source framework that allows operating systems to interact within a broad […]