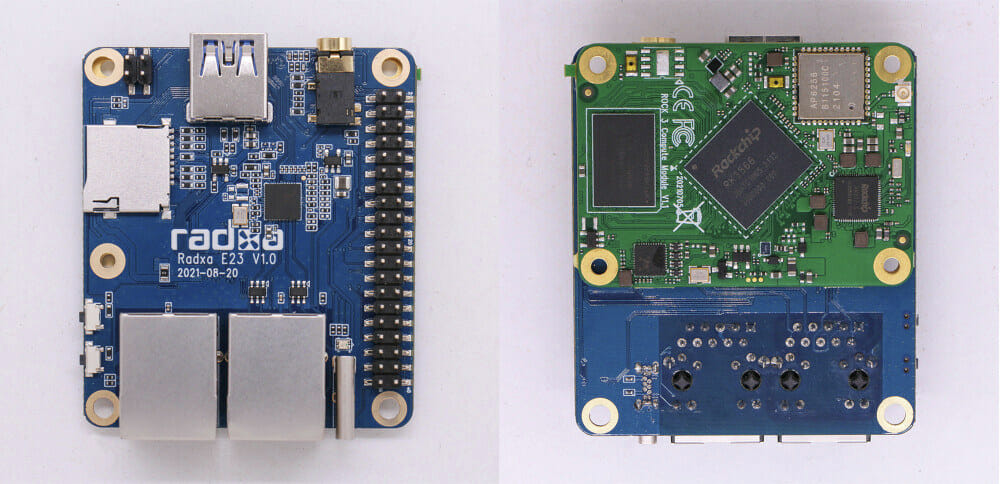
Radxa CM3 is a system-on-module that offers an alternative to the Raspberry Pi CM4, with the same form factor allowing it to become a drop-in replacement, but switching from a Broadcom BCM2711 processor to a Rockchip RK3566 quad-core Cortex-A55 SoC. Radxa CM3 will work with existing carrier boards for the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4, albeit some features such as dual HDMI are not available, instead, providing a single HDMI, but the module also offers extra features through an additional 100-pin board-to-board with interfaces such as SATA III and USB 3.0. Let’s compare Radxa CM3 specifications to the ones of Raspberry Pi CM4. Comparing Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core processor and Rockchip RK3566, as the Cortex-A72 may still be faster on some workloads despite the lower frequency, and some other workloads may be dramatically faster on RK3566, for example for those using Armv8 Crypto extensions missing on all Raspberry Pi, which we […]
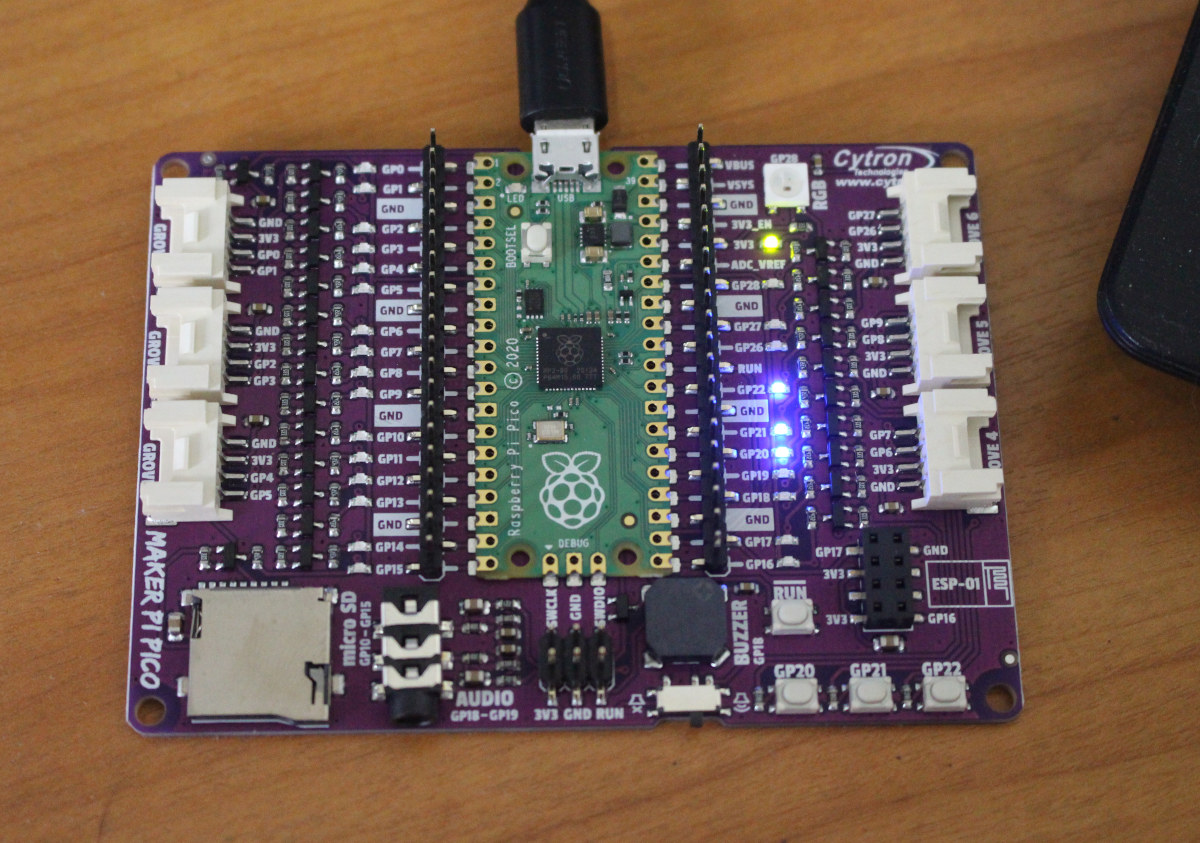
Giveaway Week – Maker Pi Pico board
If you have not played with Raspberry Pi Pico board, here’s an opportunity, as the third prize of our giveaway week is the Maker Pi Pico board fitted with the Raspberry Pi RP2040 MCU board, and providing easy access to I/Os with headers and Grove connector, plus a buzzer, an audio jack, and a MicroSD card socket for people needing storage. I reviewed the Maker Pi Pico board with CircuitPython, and it was more convenient than the bare Raspberry Pi Pico thanks to the reset button and an LED is assigned for each I/O. You could also add an ESP-01 module for WiFi connectivity since there’s an 8-pin header for that purpose. The CNXSoft signature on the back of the board clearly brings infinite value to the board. It’s just like an NFT, except it’s real ;). If you don’t think so, you could always use some alcohol to wipe […]
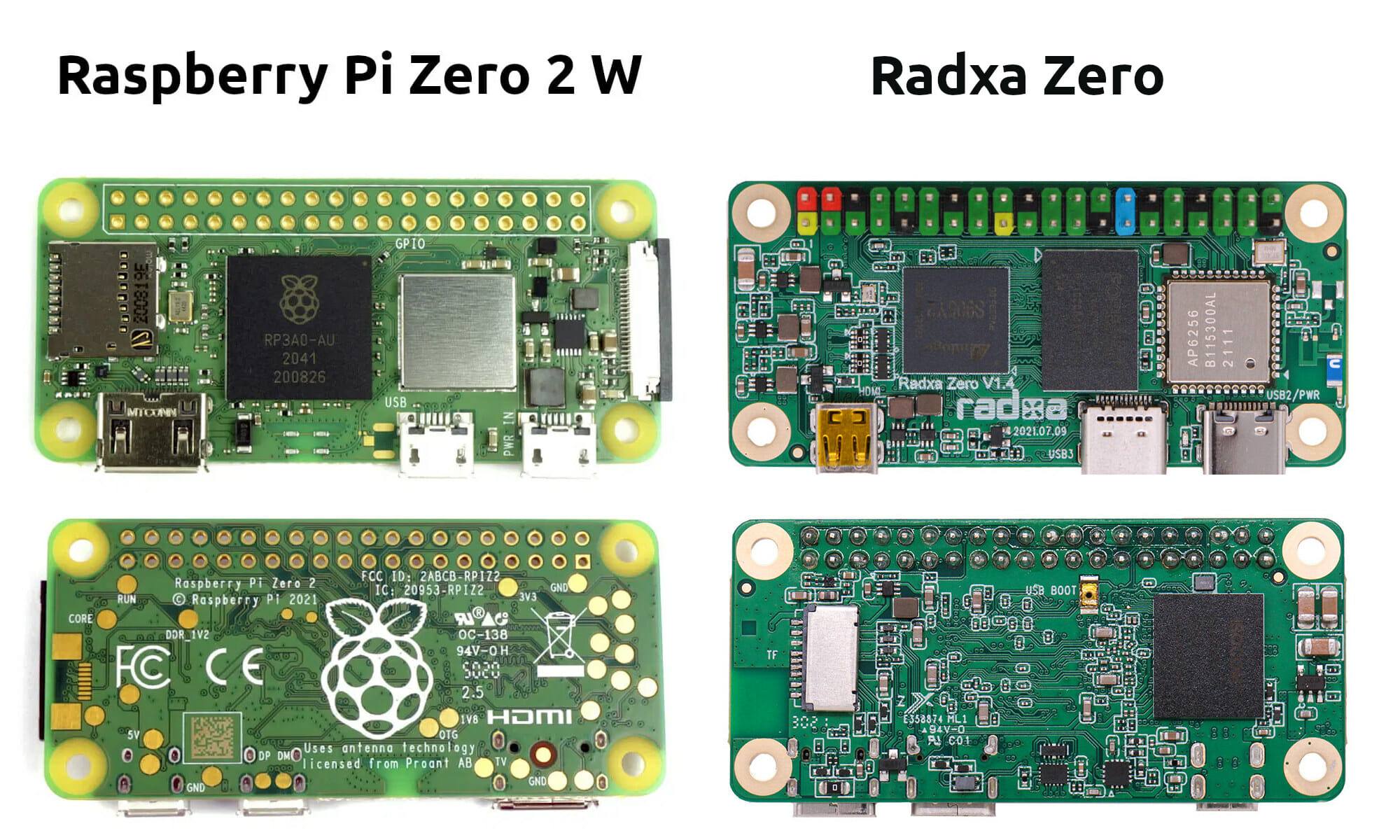
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W vs Radxa Zero – Features and benchmarks comparison
The just-announced Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W is not the first quad-core Arm SBC following Raspberry Pi Zero form factor, and back in 2017, the Banana Pi BPI-M2 Zero was introduced for $15, and the Radxa Zero was unveiled last June with an Amlogic S905Y2 SoC with price starting at $15 as well. With its Allwinner H2+ quad-core Cortex-A7 processor clocked at 1 GHz and a price bumped up to $23, the Banana Pi M2 Zero has mostly become irrelevant, but the Radxa Zero may still be considered by some people with a 1.8 GHz processor, and options for up to 4GB RAM, so let’s see how features compare against Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W, followed by some benchmark numbers. Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W vs Raxda Zero – Features If we just look at the comparison table, the Radxa Zero is equivalent or superior in almost every way, except […]
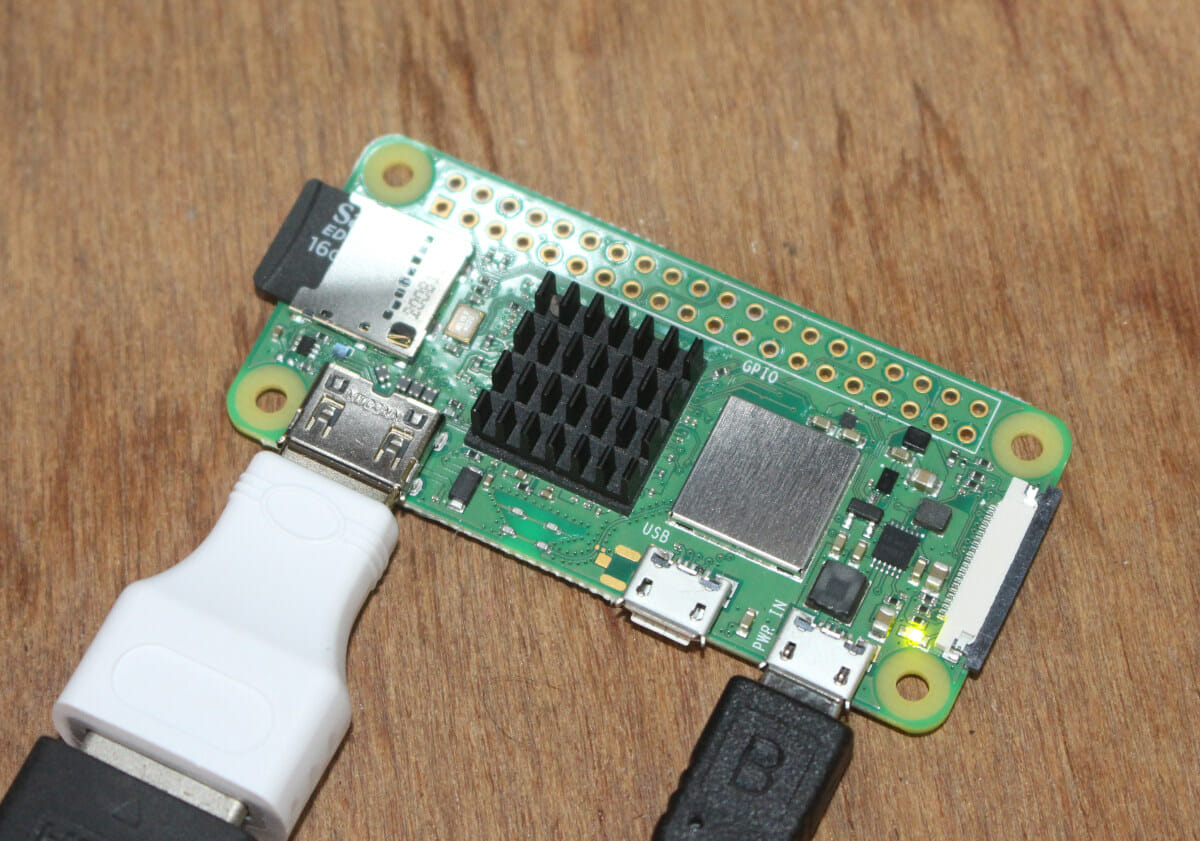
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W mini review – Benchmarks and thermal performance
The Raspberry Pi Foundation launched the Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W board yesterday with the main difference against Raspberry Pi Zero W board being the much faster Raspberry Pi RP3A0 SiP with a Broadcom quad-core Cortex-A53 processor clocked at 1.0 GHz and overclockable to 1.2 GHz. I received my sample shortly after publishing the announcement, and I had time to test it. Since the main difference is the processor, I’ll focus this review on benchmarks and whether additional cooling is required for the board. Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W kit unboxing If you purchase the board for $15, that’s all you’ll get, but Raspberry Pi Trading sent me a kit with Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W SBC, a USB OTG adapter, a mini HDMI to HDMI adapter, the CSI camera cable, and four rubber pad for the enclosure that comes with three covers: full, hole for 40-pin GPIO header, or […]
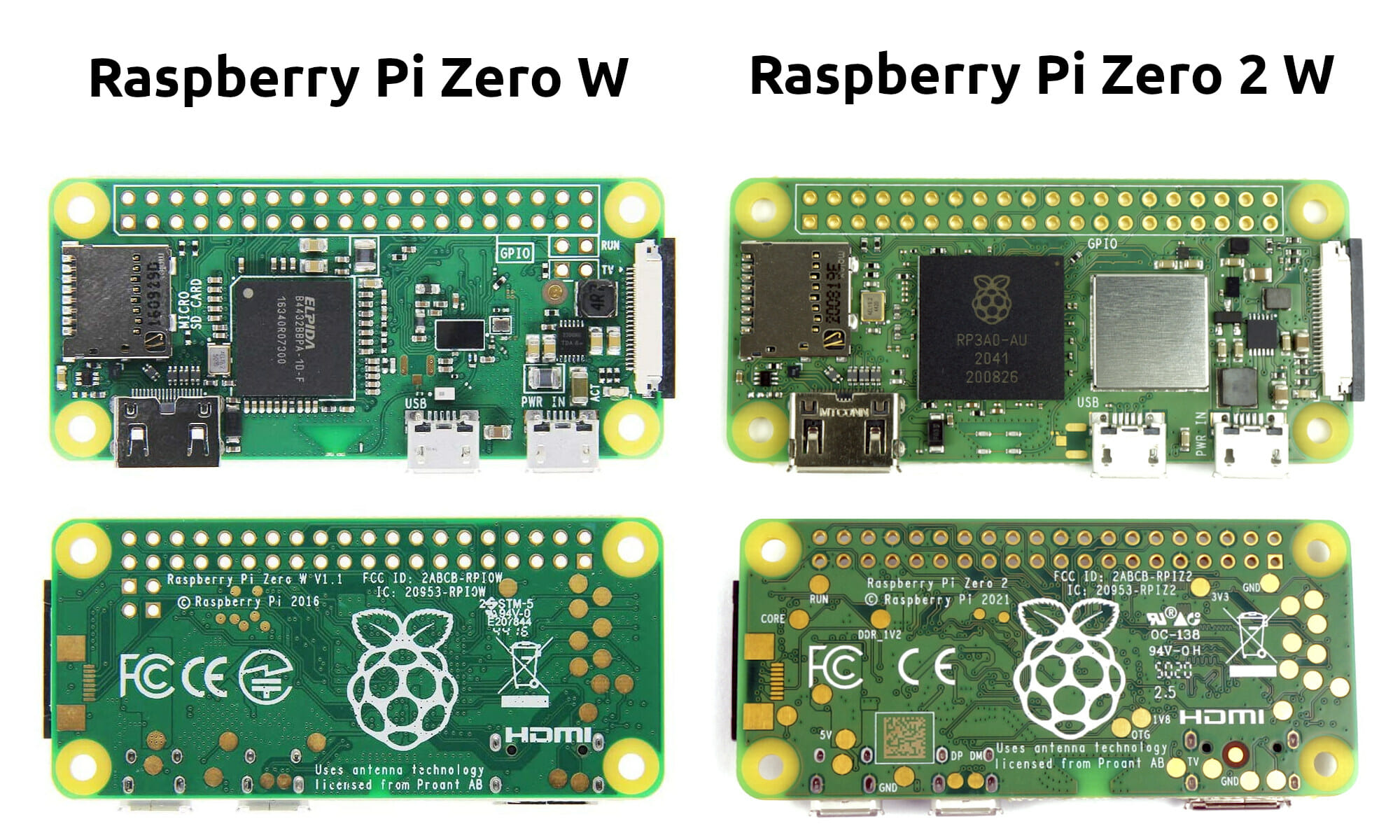
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W and Zero W features comparison
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W quad-core board has just launched, and in this post, we’ll look at how the new board compares to the original Raspberry Pi Zero W SBC. From the photos above they are nearly identical, but looking at the detailed specifications, we’ll find some interesting differences. So the main reasons to get a Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W over a Raspberry Pi Zero W is the extra performance enabled by the quad-core Cortex-A53 processor and possibly better wireless performance. The downsides are at the new board costs $5 more, and power consumption might be higher, but this would have to be tested under various scenarios. Another reason you may end up getting the Zero 2 W board that is not shown in the specifications is the recent shortage of chips, so the new board may be more likely to be in stock at your local distributor. […]
$15 Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W launched with quad-core CPU, 512MB RAM
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W is the first quad-core SBC from the Raspberry Pi Foundation with the Raspberry Pi Zero form factor. Based on the RP3A0 system-in-package (SiP) comprised of a Broadcom BCM2710A1 quad-core Cortex-A53 processor and 512MB LPDDR2, the new Pi Zero W 2 board offers the exact same interfaces as its predecessor. This includes a MicroSD card socket, a mini HDMI port, two micro USB ports, a MIPI CSI-2 camera connector, as well as an unpopulated 40-pin GPIO header. The wireless module appears to have changed but still offers WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 4.x BLE, and it’s using the same VideoCore IV GPU to handle 3D graphics and video encoding and decoding up to 1080p30. Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W specifications: SiP – Raspberry Pi RP3A0 system-in-package with: SoC – Broadcom BCM2710A1 quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 @ 1GHz (overclockable to 1.2 GHz) with VideoCore IV CPU supporting OpenGL ES […]
Picovoice Cobra Voice Activity Detection Engine shown to outperform Google WebRTC VAD
Picovoice Cobra Voice Activity Detection (VAD) engine has just been publicly released with support for Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone, NVIDIA Jetson Nano, Linux 64-bit, macOS 64-bit, Windows 64-bit, Android, iOS, and web browsers that support WebAssembly. Support for other Cortex-M and Cortex-A based SoCs can also be made available but only to enterprise customers. Picovoice already offered custom wake word detection with an easy and quick web-based training and offline voice recognition for Raspberry Pi, and even later ported their voice engine to Arduino. Cobra VAD is a new release, and, like other VADs, aims to detect the presence of a human voice within an audio stream. Picovoice Cobra can be found on Github, but note this is not an open-source solution, and instead, libpv_cobra.so dynamic library is provided for various targets, together with header files and demos in C, Python, Rust, and WebAssembly, as well as demo apps for iOS […]
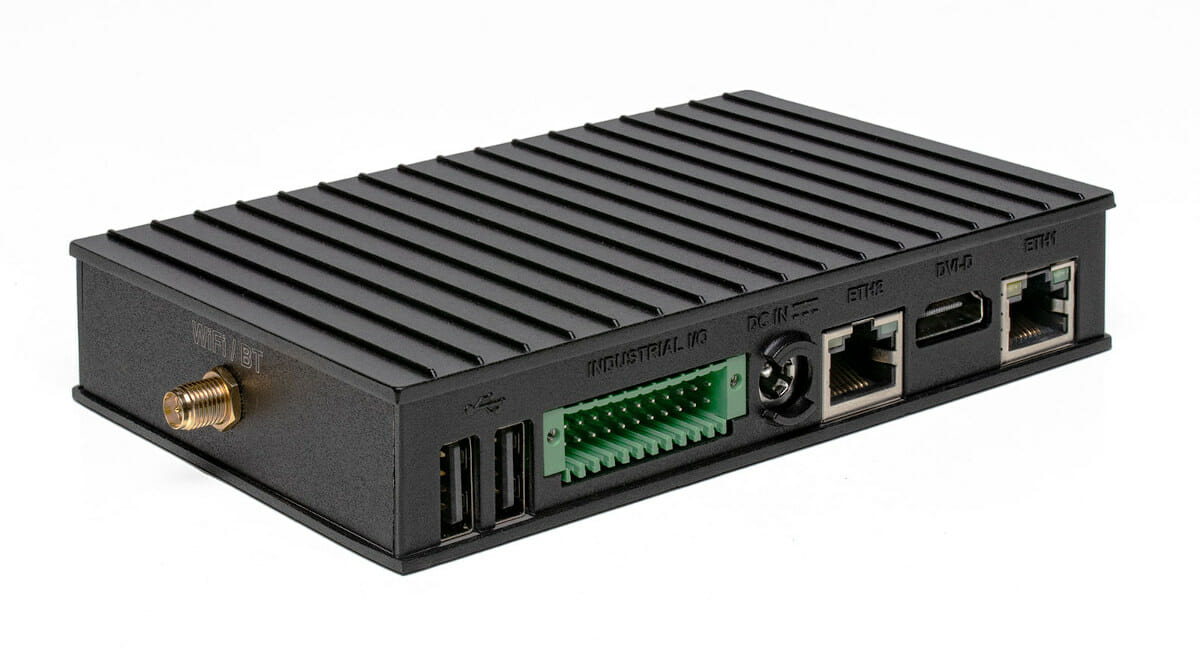
CompuLab IOT-GATE-RPI4 gateway targets industrial control and monitoring
Compulab IOT-GATE-RPI4 is another industrial gateway based on the Raspberry Pi CM4 module that offers a different feature set and form factor compared to solutions like TECHBASE iModGATE-AI gateway or QWave Systems CatsPi Industrial carrier board. Designed with industrial control and monitoring in mind, the IOT-GATE-RPI4 gateway offers multiple RS485, RS232 and CAN FD ports, Ethernet, 4G LTE/4G, WiFi 802.11ac, and Bluetooth 5.0 connectivity, as well as a wide -40°C to 80°C operating temperature range, plus a wide input voltage from 8V to 36V as well as PoE support. Compulab IOT-GATE-RPI4 specifications: SoM – Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 (CM4) with SoC – Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 @ 1.5GHz plus VideoCore IV GPU with H.265 (4Kp60 decode), H.264 (1080p60 decode, 1080p30 encode) System Memory – 1GB to 8GB LPDDR4 Storage – 16GB to 128GB eMMC flash soldered on-board Secondary Storage – 64GB – 256GB NVMe flash via optional module […]