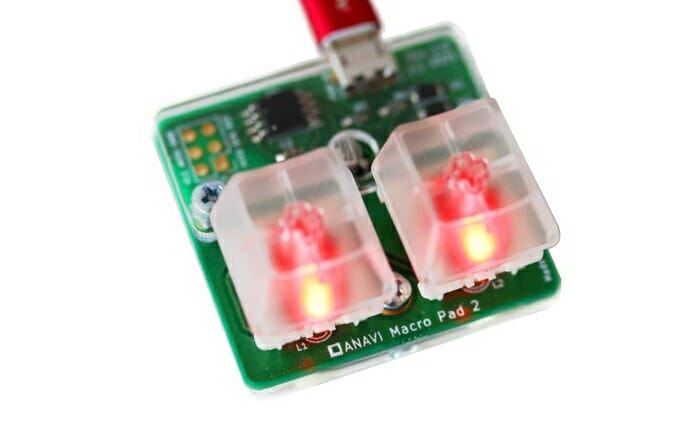
System76 Launch high-end customizable keyboard for PC’s that we covered earlier this week, and ANAVI Macro Pad 2 2-key mechanical USB keypad should not have anything in common, but they do to some extent. Both happen to feature backlit mechanical keys, are open-source hardware, and run the same Quantum Mechanical Keyboard Firmware (QKM) open-source firmware. ANAVI Macro Pad 2 specifications: MCU – Microchip ATtiny85 8-bit AVR microcontroller with 8 KB ISP Flash memory, 512 bytes EEPROM, 512 bytes SRAM Keys – Two Gateron Red mechanical switches with 3 mm LED backlighting and translucent keycaps Host connection – MicroUSB port Dimensions – 40×38 mm OSHWA certification – BG000077. ANAVI Technology says the key is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and GNU/Linux support, but as a USB keypad, it should probably just work with any host device supporting the USB HID class. ANAVI Macro Pad 2 is a smaller version of the earlier […]
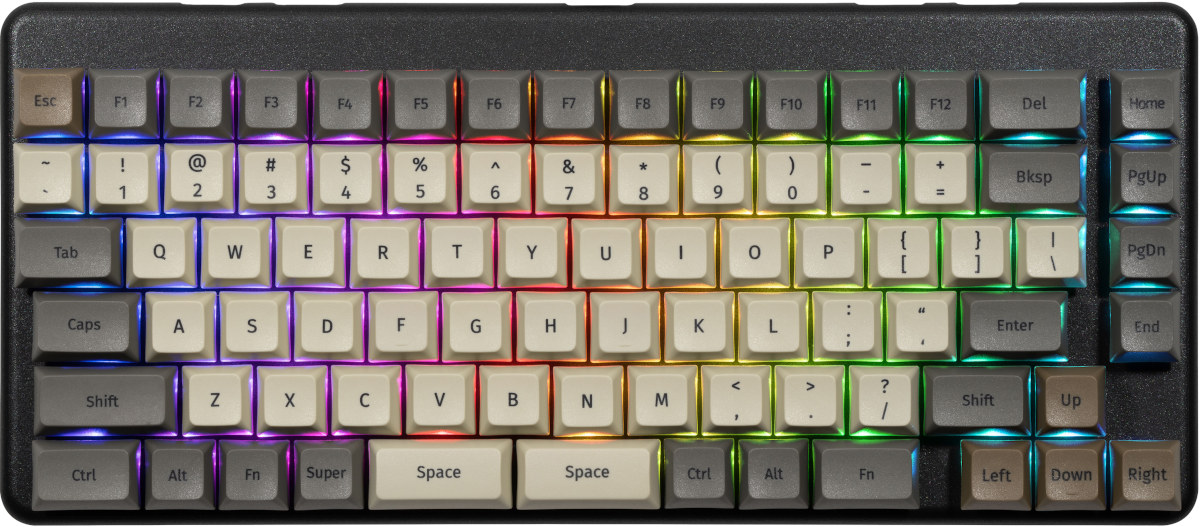
System76 Launch is an open-source hardware, configurable keyboard
System76, the company better known for its Linux laptops, has launched an open-source hardware, configurable keyboard. Meet System76 Launch. The keyboard firmware, schematics, and mechanical files are all open-source. Launch ships with an ANSI US QWERTY layout but can be customized through a configuration program for Windows, Linux, and macOS, and a key puller is included to easily replace/change keycaps as needed. System76 Launch keyboard specifications: Open-source custom PCB Individually addressable RGB LED backlighting N-Key Rollover to detect all keystrokes no matter how many keys are pressed simultaneously Sockets and Switches Kailh MX Hotswap Sockets Kailh Box Jade or Kailh Box Royal Switches Key Caps – PBT plastic, dye sublimated legend, XDA profile Layout – ANSI US QWERTY Integrated USB hub with 2x USB 3.2 Gen 2 Type C (Up to 10 Gbps), 2x USB 3.2 Gen 2 Type A (Up to 10 Gbps) Open-source milled chassis design with detachable […]
Why you should request open-source software for your IoT devices
I usually think of open-source hardware and/or software are enabling skilled people to more easily fix bugs, improve on the design, get feedback from the community, etc… But in a world where IoT devices become more prevalent, there’s another reason why you should request open-source software: Long term support. What made me think about are two things. The first one if that I own WeLoop Hey 3S smartwatch, which I love and wear since March 2018. That’s quite a feat since most cheap devices I own often only last a few months or a year or so. I’m also used to the watch face and Weloop app interface. So what’s the problem exactly? WeLoop company closed on December 31, 2019, and while the app worked fine for about a year after that, recently I have been unable to login to the app to access my data and/or update settings for […]
HybridOS is an open-source operating system designed for smart IoT devices and cloud computing environment
As I wrote about the “Summer 2021 of Open Source Promotion Plan” earlier, I noticed a new open-source operating system called HybridOS described as “totally new” and designed for “smart IoT devices and cloud computing environment”. It’s actually more of an ecosystem than an operating system, as it offers three main components with a device side running on devices running Linux kernel or another POSIX-compatible kernel, a server side running on servers in the cloud, and a client side to manage the cloud and devices from Windows, Linux distributions, iOS, or Android. HybridOS Device Side relies on several open-source projects including: hiWebKit, the HybridOS derivative of WebKit: hiACEJS, the HybridOS derivative of OpenHarmony ACELite hiViewRenders, the renderers for hiview tag of hiWebKit hiShell, the app running environment (the shell) Various Graphics stacks including hiMesa, the HybridOS derivative of Mesa hiCairo, the HybridOS derivative of Cairo: hiDRMDrivers, DRM Drivers for HybridOS […]
Summer 2021 of Open Source Promotion Plan is China’s alternative to Google Summer of Code
China has now an alternative to the Google Summer of Code, an international annual program in which Google awards stipends to students who successfully complete a free and open-source software coding project during the summer. China’s alternative is called “Summer 2021 of Open Source Promotion Plan”, also known as “summer 2021” for short, and is organized by the Institute of Software Chinese Academy of Sciences and the openEuler community. It’s a global program open to college students around the world who want to participate in the development and maintenance of open-source software. There’s only one specific requirement to be able to apply: be at least 18 years old at the time of registration. Selected students will be paid according to the complexity of the project with 12000 RMB ($1,867), 9000 RMB ($1,400), or 6000 RMB ($933) “bonuses” to be distributed at the end of the project. Other stakeholders include the […]
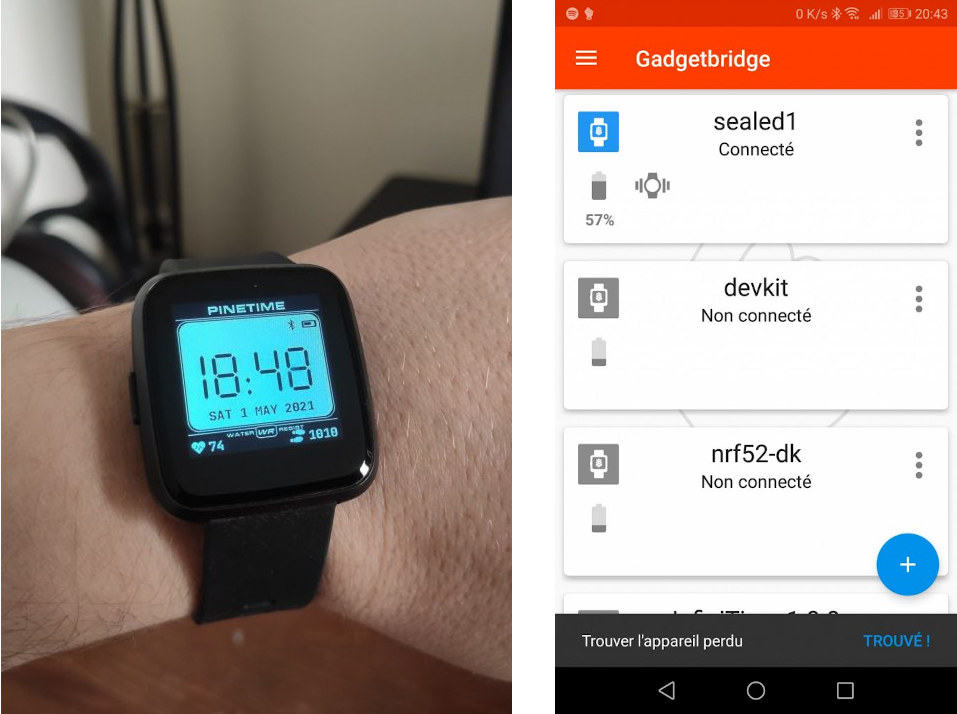
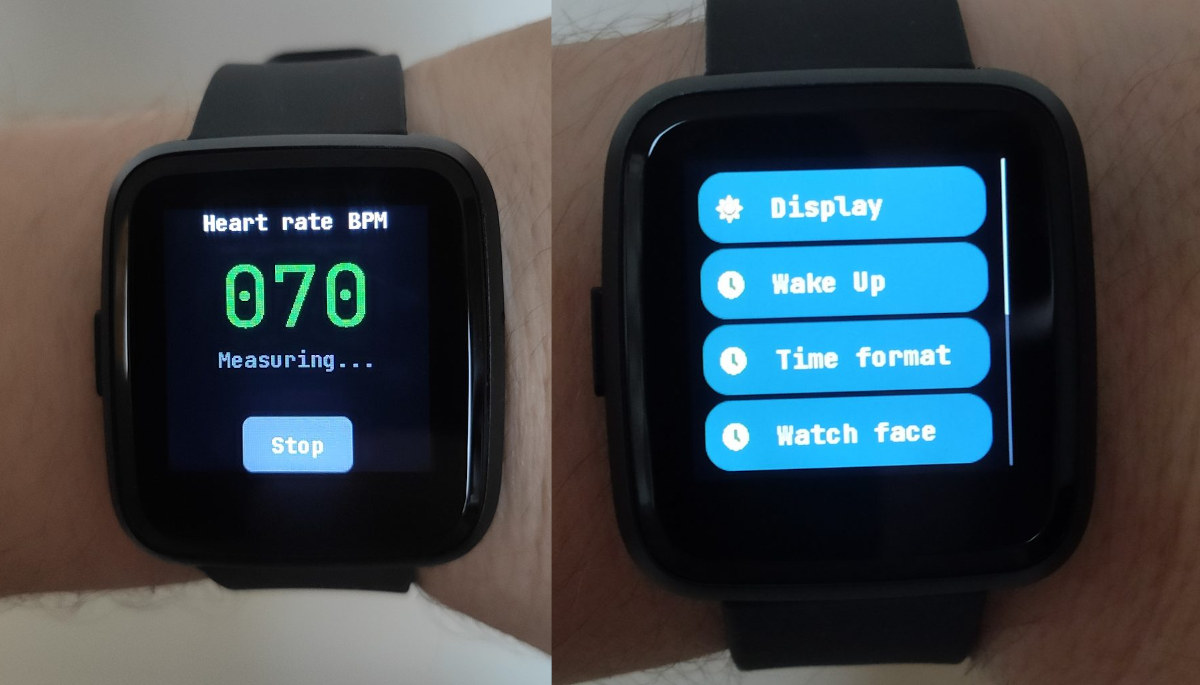
InfiniTime 1.0 firmware released for PineTime smartwatch
The PineTime smartwatch was unveiled and first launched in 2019, as a low-cost, open-source wearables development kit/platform for developers wanting to work on firmware development for the Nordic nRF52 powered device. Progress was made on various solutions such as ATCwatch Arduino firmware, and as time passed, the PineTime slowly became more like an “enthusiast-grade” end-user product. This is basically what it has become with the first stable release of InfiniTime firmware, which was selected as the default firmware in September 2020. The main features of InfiniTime 1.0 firmware include: Two clock faces – digital and analog Apps – Stopwatch, music control, navigation, heart rate, as well as Paddle and 2048 games User settings – Display timeout, time format, wake up conditions OTA upgrades via an open-source bootloader based on MCUBoot Heart rate monitoring and step counting Between 3 and 5 days of battery life depending on usage Firmware based on […]
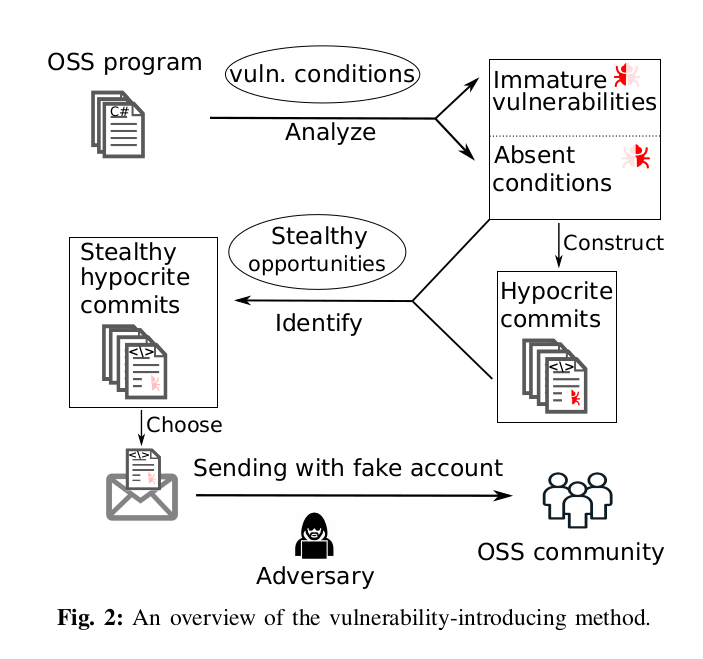
PhD students willfully committed known malicious changes to mainline Linux
We just reported about the Linux 5.12 changelog with a focus on Arm, MIPS and RISC-V targets on Tuesday, and at the time, the expectation was a delay of about one week after Linux 5.12-rc8 was outed on Sunday, April 18. But Linux 5.12 could be further delayed due to shenanigans from two Ph.D. students doing a research project on open-source vulnerability at the University of Minnesota. This was announced by Greg Kroah-Hartman on the Linux kernel mailing list. Commits from @umn.edu addresses have been found to be submitted in “bad faith” to try to test the kernel community’s ability to review “known malicious” changes. The result of these submissions can be found in a paper published at the 42nd IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy entitled, “Open Source Insecurity: Stealthily Introducing Vulnerabilities via Hypocrite Commits” So their work at to be reverted with 190 reversions so far. It also […]
RK3566 & RK3568 processors to get Linux mainline support soon
Rockchip RK3566 & RK3568 processors were just officially announced at the end of the year, and soon followed with announcements of related such as Core-3568J AI Core system-on-module, some Android 11 TV boxes, Station P2 mini PC, and RK3566/RK3568 development boards. But it did not take long, as RK3566/RK3568 are about the get support for mainline Linux, with engineers from Collabora and Rockchip having recently committed preliminary support for RK356x platforms, notably using Pine64 Quartz64 SBC for testing. The most recent commits target power management, networking, and the PCI host controller. It’s not clear when code will be merged to mainline, but Collabora said “Pine64 Quartz64 SBC out-of-the-box support is right around the corner” in a recent tweet. In any case, it’s good news there’s active development for mainline Linux on the new Rockchip processors, as that means it will be possible to run the latest version of Linux on […]