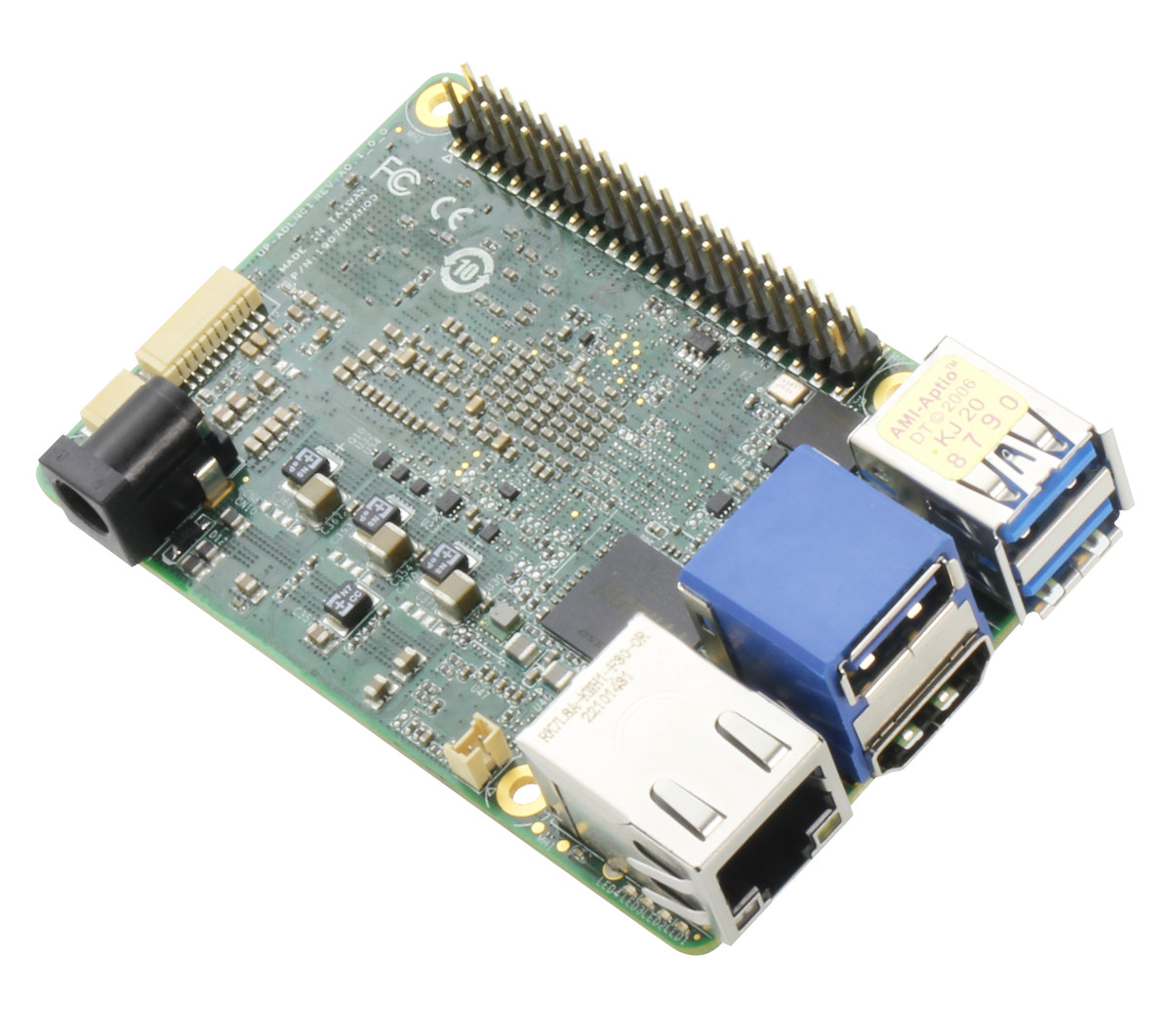
AAEON UP 7000 is an x86 single board computer with a layout similar to the Raspberry Pi 4 but based on a more powerful Intel Processor N50, N97, or N100 Alder Lake-N SoC with Gigabit Ethernet, three USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports, HDMI 1.4 video output, and a 40-pin GPIO header. Not to be confused with the larger UP Squared Pro 7000 also powered by an Alder Lake-N processor, the UP 7000 is an update to the UP 4000 SBC with an Intel Apollo Lake processor introduced just last year. The new fanless board also comes with up to 8GB LPDDR5, 64GB eMMC flash, and an onboard TPM 2.0. UP 7000 (SKU: UP-ADLN01) specifications: Alder Lake-N SoC Intel Processor N50 dual-core processor up to 3.4 GHz with 6MB cache, 16EU Intel UHD Graphics Gen 12 @ 750 MHz; TDP: 6W Intel Processor N97 quad-core processor up to 3.6 GHz with […]
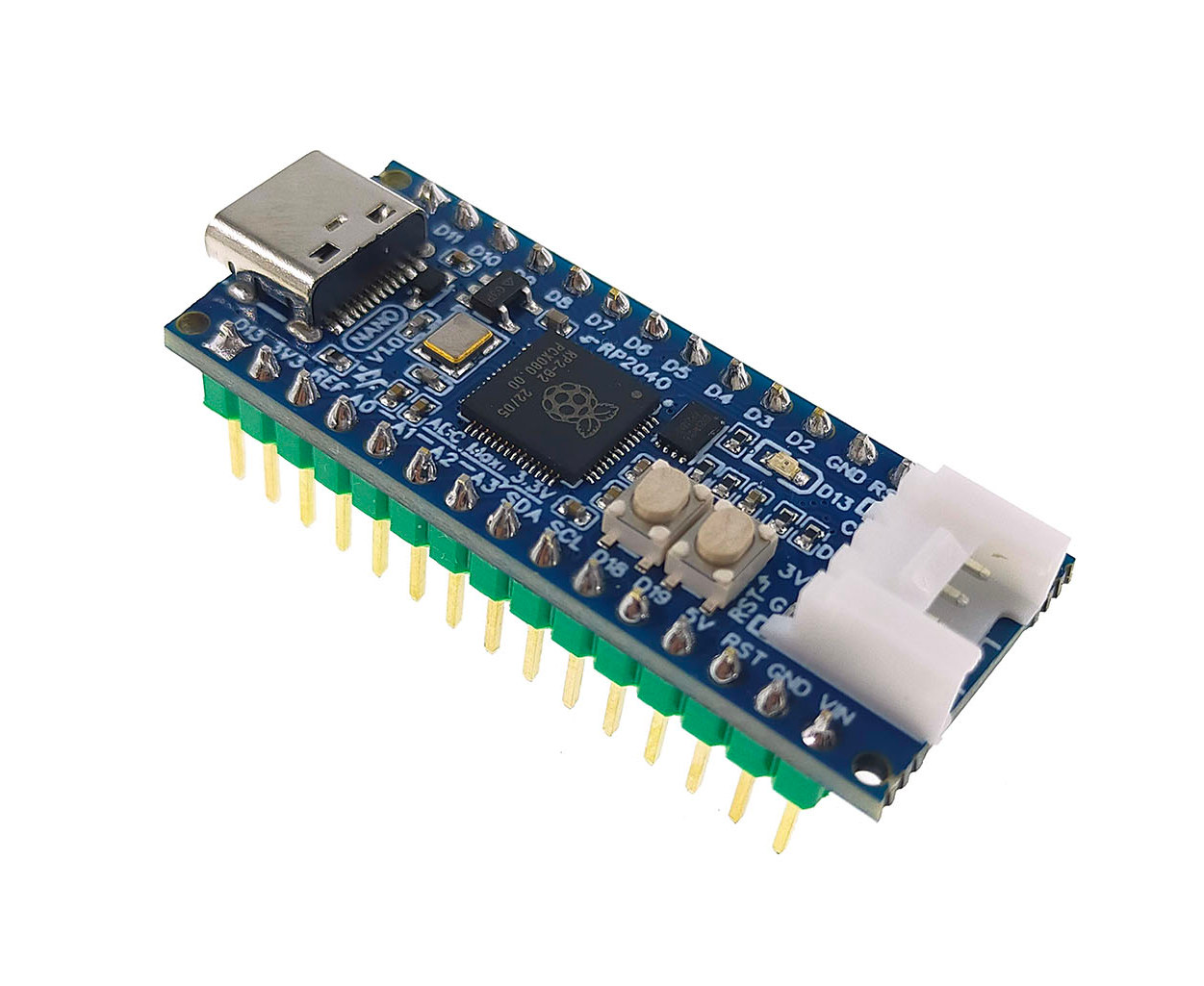
RP2 Nano is a $6.6 Raspberry Pi RP2040 board with Arduino Nano form factor
ArtronShop RP2 Nano board features the Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller in the Arduino Nano form factor in a way that’s much cheaper than the official Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect board. That’s possible because Thailand-based AtronShop did not include all the bells and whistles such as WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity, sensors, and used a smaller flash. So the RP2 Nano basically offers the same I/Os and features as the Arduino Nano, but the Microchip ATmega328 8-bit AVR microcontroller gives place to the more powerful Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Cortex-M0+ MCU plus 2MB flash, and the board also adds an extra Grove connector for expansion. RP2 Nano specifications: MCU – Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Cortex M0+ microcontroller @ 133 MHz with 264 kB of embedded SRAM Storage – 2MB SPI flash USB – 1x USB Type-C OTG port for power, data, and programming Expansion Arduino Nano headers (2x 15-pin headers) Up to […]
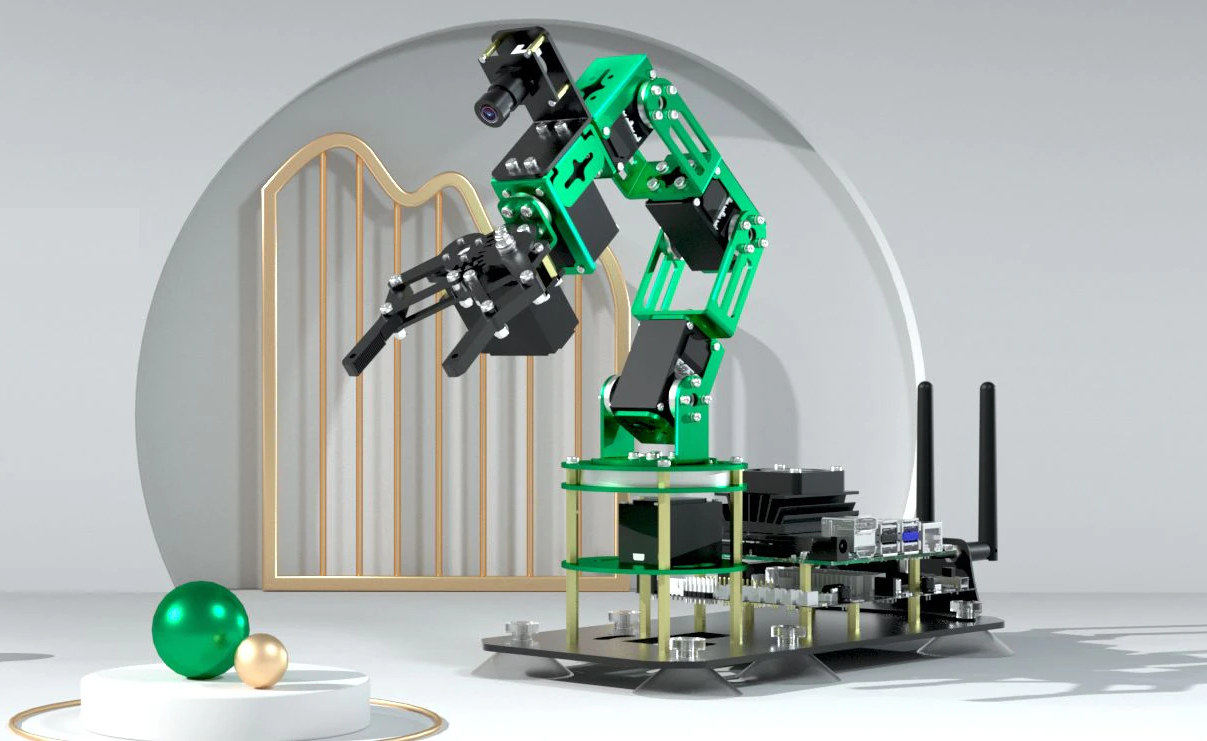
Yahboom DOFBOT 6 DoF AI Vision robotic arm for Jetson Nano sells for $289 and up
Robotic arms can be expensive especially if you want one with AI Vision support, but Yahboom DOFBOT robotic arm designed for NVIDIA Jetson Nano offers a lower cost alternative as the 6 DoF robot arm sells for about $289 with a VGA camera, or $481 with the Jetson Nano SBC included. We previously published a review of the myCobot 280 Pi robotic arm from Elephant Robotics, and while it’s working well, supports computer vision through the Raspberry Pi, and is nicely packaged, it sells for around $800 and up depending on the accessories, and one reader complained the “price tag is still way too high for exploration“. The DOFBOT robotic arm is looking more like a DIY build, but its price may make it more suitable for education and hobbyists. DOFBOT robotic arm main components and specifications: SBC – NVIDIA Jetson Nano B01 developer kit recommended, but Raspberry Pi, Arduino, […]
Review of SunFounder Raspberry Pi UPS Power Supply
SunFounder’s Raspberry Pi UPS Power Supply is a complete UPS kit for the Raspberry Pi 3/4 Model B/B+ with a PiPower board, a 2,000 mAh battery, and all accessories requires for the assembly. It also works with other Raspberry Pi-sized boards that support 5V DC input such as Banana Pi BPI-M5, Libre Computer ROC-RK3328-CC, and other similar SBCs. Many years ago, I bought a Raspberry Pi battery pack for review hoping that it would also work as a UPS, but it was not perfect as the board would sometime reboot during power failure simulations. Since then, there have been many UPS kits launched to the market, but I didn’t try any so far, so when SunFounder contacted CNX Software to review their “Raspberry Pi UPS Power Supply”, I took the opportunity, and I will report my finding in this review. Raspberry Pi UPS Power Supply key features UPS module output […]
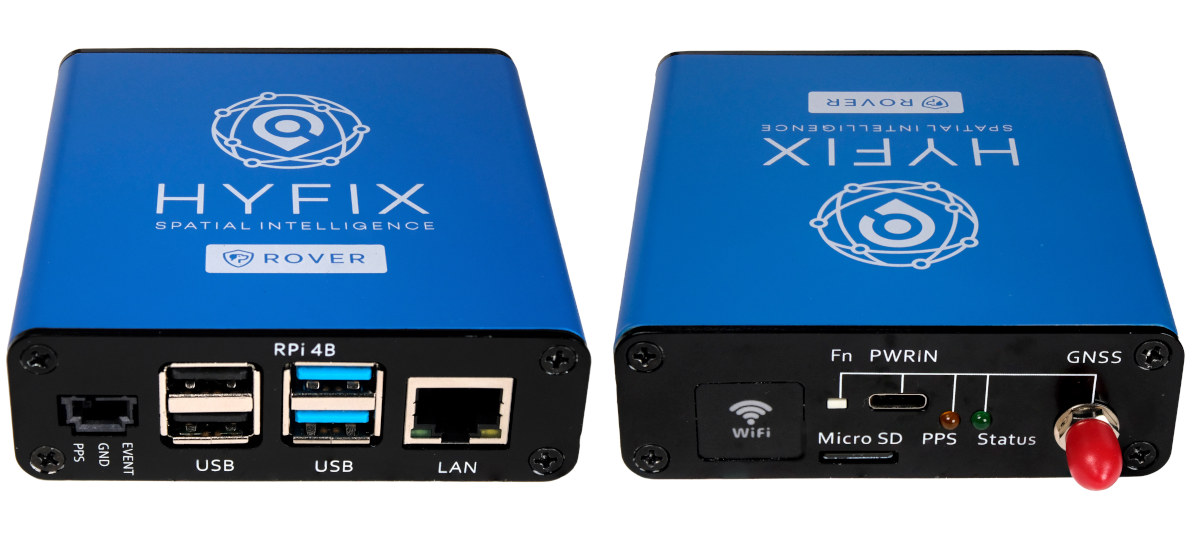
Affordable RTK GNSS receiver supports USB or/and Ethernet interfaces (Crowdfunding)
HYFIX’s RTK Rover is an affordable, centimeter-accurate RTK (Real-time Kinematic) GNSS receiver with either a USB interface or/and Ethernet connectivity with the latter relying on a Raspberry Pi 4 SBC. As a reminder, RTK relies on traditional GNSS networks like GPS and works with a Base station at a fixed location and a Rover station that can be fitted to a drone or mobile robot in order to determine the position with up to one-centimeter accuracy. The RTK Rover from HYFIX is equipped with a dual-band LC29H GNSS module from Quectel and an onboard IMU sensor that tracks position through dead reckoning when GNSS connectivity is lost. RTK Rover specifications: MiniPCIe card with Dual-Band L1/L5 RTK Receiver (Quectel LC29H) Antenna – External antenna (6x5x2 cm) connected to SMA connector Sensor – IMU Interfaces USB Type-C port for power and serial Interface Ethernet Rover Kit only – Gigabit Ethernet and USB ports […]
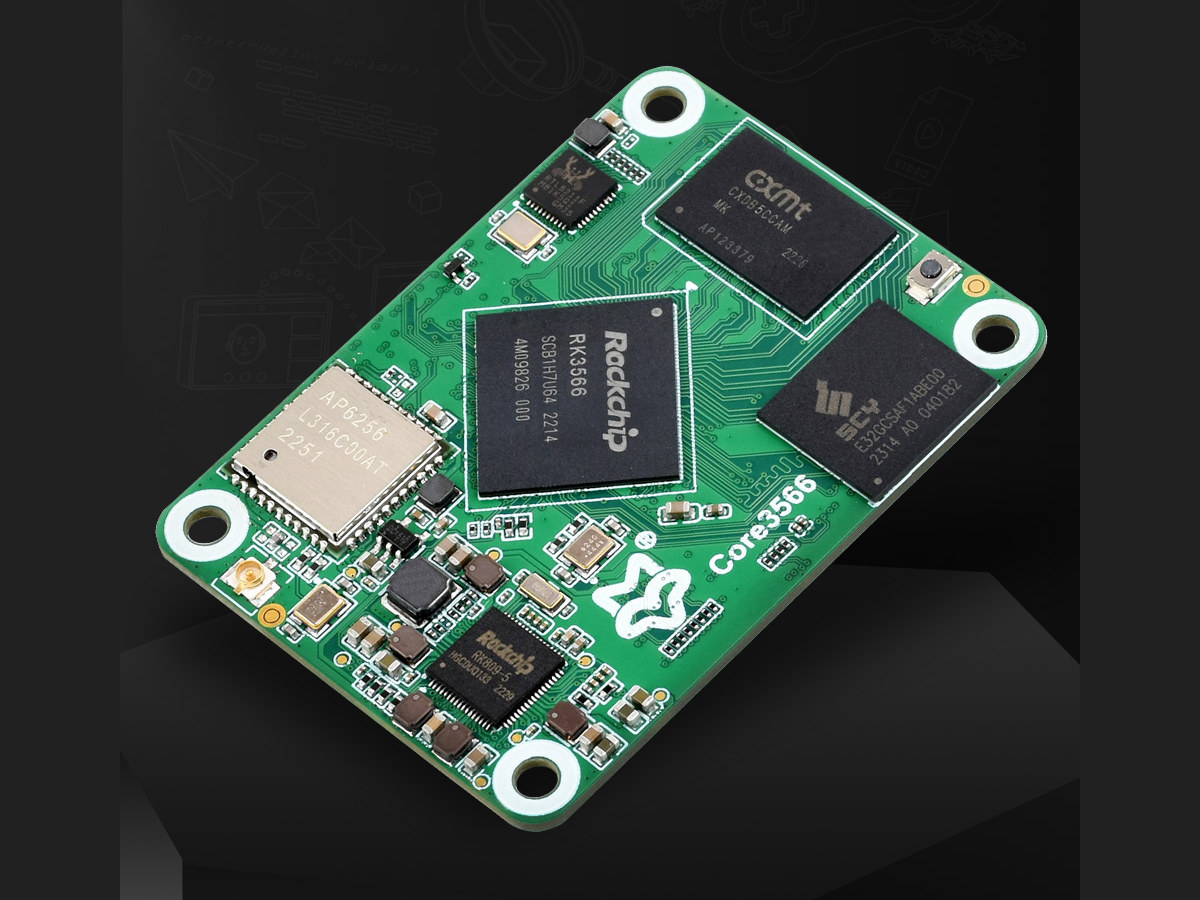
LuckFox Core3566 – A Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 alternative that sells for $24 and up
We’ve already seen Rockchip RK3566 system-on-modules that follow the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 with the likes of Pine64 SOQuartz and Radxa CM3. But there’s at least one more Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 alternative based on the RK3566 SoC with the LuckFox Core3566 going for as little as $23.99. I found out about the new module after checking out the upcoming Orange Pi Compute Module 4 (another CM4 alternative based on RK3566), and the LuckFox Core3566 is offered with 2GB or 4GB RAM, an optional 32GB eMMC flash, and an optional WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 5.0 module. LuckFox Core3566 specifications: SoC – Rockchip RK3566 quad-core Cortex-A55 processor up to 1.8 GHz with a 32-bit RISC-V MCU, an Arm Mali-G52 GPU supporting OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0/3.2, OpenCL 2.0, Vulkan 1.1, a 0.8 TOPS NPU for AI acceleration System Memory – 2GB to 4GB LPDDR4 Storage – Optional 32GB eMMC module Wireless module […]
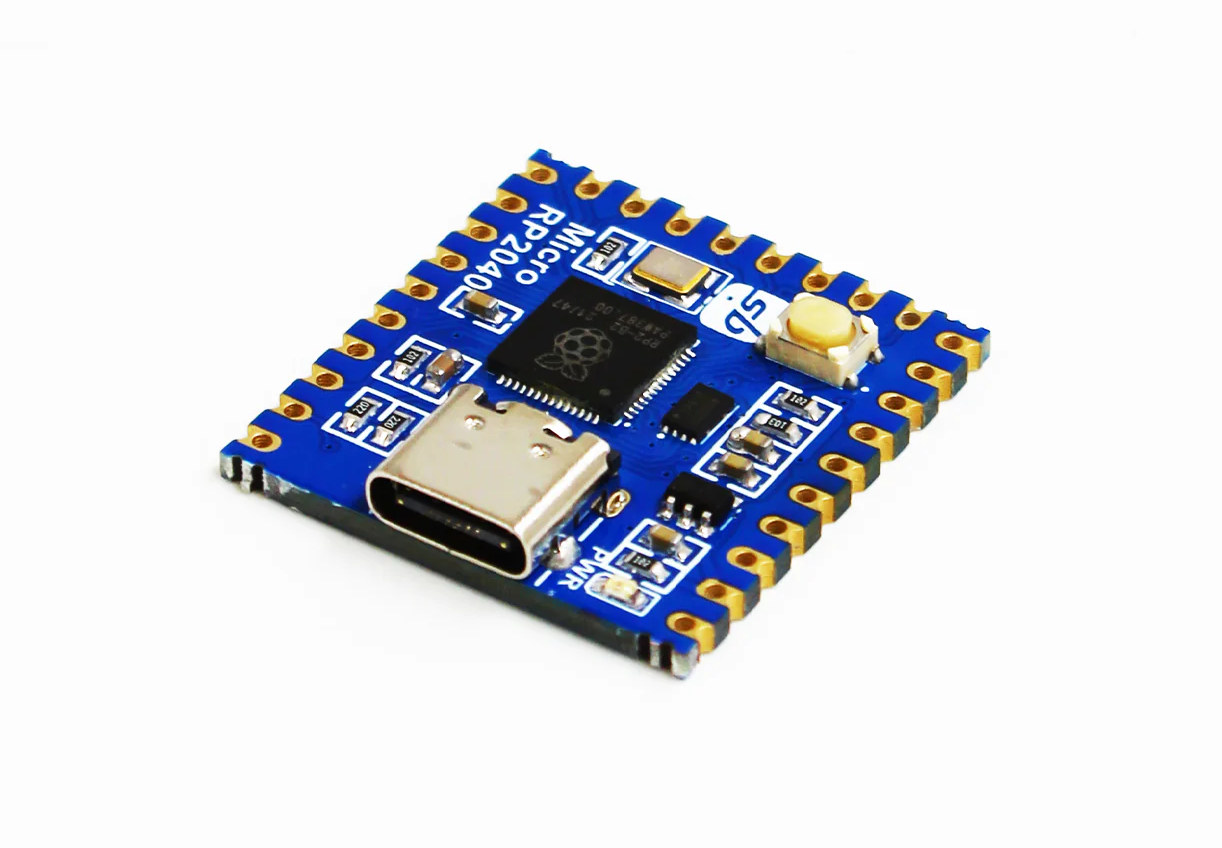
Micro RP2040 is a tiny Raspberry Pi RP2040 module with a USB Type-C port, 28 castellated & through holes
SB Components’ Micro RP2040 is a tiny module based on the Raspberry Pi RP2040 Arm microcontroller with up to 23 GPIOs and a USB Type-C port for easy powering and programming. Ever since the Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Arm Cortex-M0+ microcontroller was released, companies have been making tiny modules based on it. Some come with a USB Type-C port such as the Pimoroni Tiny 2040 and the Adafruit QT Py RP2040 boards, while others focused on providing a smaller form factor for soldering only with design such as the RP2040 Stamp or the minuscule 12x12mm Femto module. The Micro RP2040 module comes with a USB-C port and more I/Os than competing modules thanks to a slightly larger 25 x 24.95mm design. Micro RP2040 specifications: MCU – Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Cortex-M0+ microcontroller @ up to 133 MHz with 264kB of SRAM Storage – 2MB QSPI flash USB – USB Type-C […]
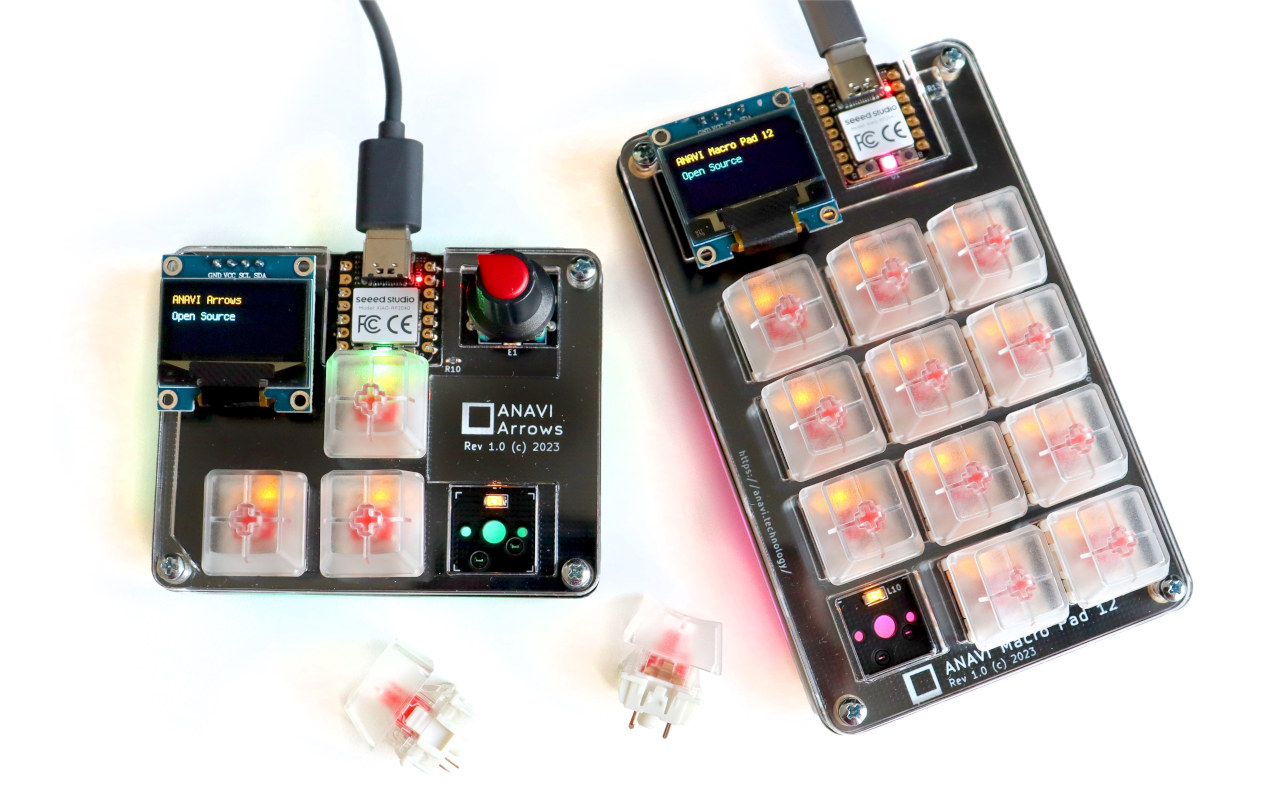
ANAVI launches CircuitPython-programmable Macro Pad 12 & Arrows mechanical keyboards (Crowdfunding)
ANAVI Technology has launched two more open-source hardware mechanical keyboards based on the Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller, equipped with an OLED display, and programmable with CircuitPython: the ANAVI Macro Pad 12 with 12 keys and the ANAVI Arrows with four keys and a rotatory encoder. The new mechanical keyboards follow ANAVI Macro Pad 10 & Knobs input devices equipped with the same Seeed Studio XIAO RP2040 MCU module running the KMK firmware written with CircuitPython, but with different form factors and features. ANAVI Macro Pad 12 specifications: MCU module – Seeed Studio XIAO RP2040 with Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Cortex-M0+ microcontroller @ up to 133 Mhz with 264KB SRAM, 2MB SPI flash, USB Type-C port Keys – 12x Gateron red, linear, non-clicky mechanical switches and transparent keycaps with yellow LED backlighting Display – OLED display connected to I2C slot (can be replaced with another I2C module) Host interface – USB […]