Toshiba has recently introduced the Toshiba TCKE9 reusable e-fuse (electronic fuse) series, a new lineup of e-fuse ICs that can be used repeatedly, to protect power supply lines from various electrical faults like overcurrent, overvoltage, overtemperature, and short circuits. These new chips integrate various protection features into a single chip which simplifies circuit design and reduces component count compared to how a traditional protection circuit with multiple components is designed. This new line of products offers different ICs with different voltage ratings and adjustable current settings, alongside two reset modes auto-retry and latching. All these features make this e-fuse useful for applications like laptops, wearables, audio/video equipment, and industrial applications like automation systems, robotics, and many other applications. Toshiba TCKE9 reusable e-fuse Specification Input Voltage – 2.7V to 23V (Maximum – 25V) Output Current – 0 to 4.0A (Adjustable overcurrent limit – 0.5A to 4.0A via external resistor) ON Resistance […]
Toshiba M4K Group microcontrollers for motor control get expanded flash & memory capacity
Toshiba has included eight new products with 512KB/1MB flash storage capacity and four packages in its M4K Group of Arm Cortex-M4-powered microcontrollers. The M4K Group is part of Toshiba’s TXZ+ Family Advanced Class, consisting of five groups of low-power, high-performance 32-bit microcontrollers. The new microcontrollers expand code flash memory to 512KB/1MB from the 256KB maximum supported by current products, and RAM capacity to 64KB from 24KB. They retain the Arm Cortex-M4 core, integrated code flash, and 32KB data flash memory (with 100K program/erase cycles). With different motor control options such as advanced programmable motor circuits, advanced 32-bit encoders, advanced vector engine plus, and three units of high-speed, high-resolution 12-bit analog/digital converters, these class of microcontrollers are quite capable of 3-motor control, even in small scale applications (64-pin). The new products with 1MB code flash separate the memory into two distinct 512KB areas, enabling memory swap and seamless over-the-air firmware updates, […]
Toshiba “MH3 Group (2)” Arm Cortex-M3 MCU supports firmware updates without interrupting operation
Toshiba “MH3 Group (2)” Arm Cortex-M3 microcontrollers come with a 1MB flash memory partitioned into two 512KB partitions to enable firmware updates without interrupting microcontroller operation using an area swap function to rotate to the new firmware seamlessly. The new M3H Group (2) builds upon the M3H Group(1) by expanding the code flash memory up to 1MB, and the RAM capacity from 66KB to 130KB. Both are part of the “TXZ+ Family Advanced Class” manufactured with a 40nm process, and equipped with a 120 MHz Arm Cortex-M3 core as well as various interface and motor control options such as UART, I2C, Advanced Encoder Input Circuit, and Advanced Programmable Motor Control Circuit. Toshiba MH3 Group 2 key features and specifications: CPU core – Arm Cortex-M3 @ 120 MHz with memory protection unit (MPU) Internal oscillator – 10MHz (+/-1%) Internal memory Code flash memory – 512KB to 1024KB (program/erase cycles: up to […]
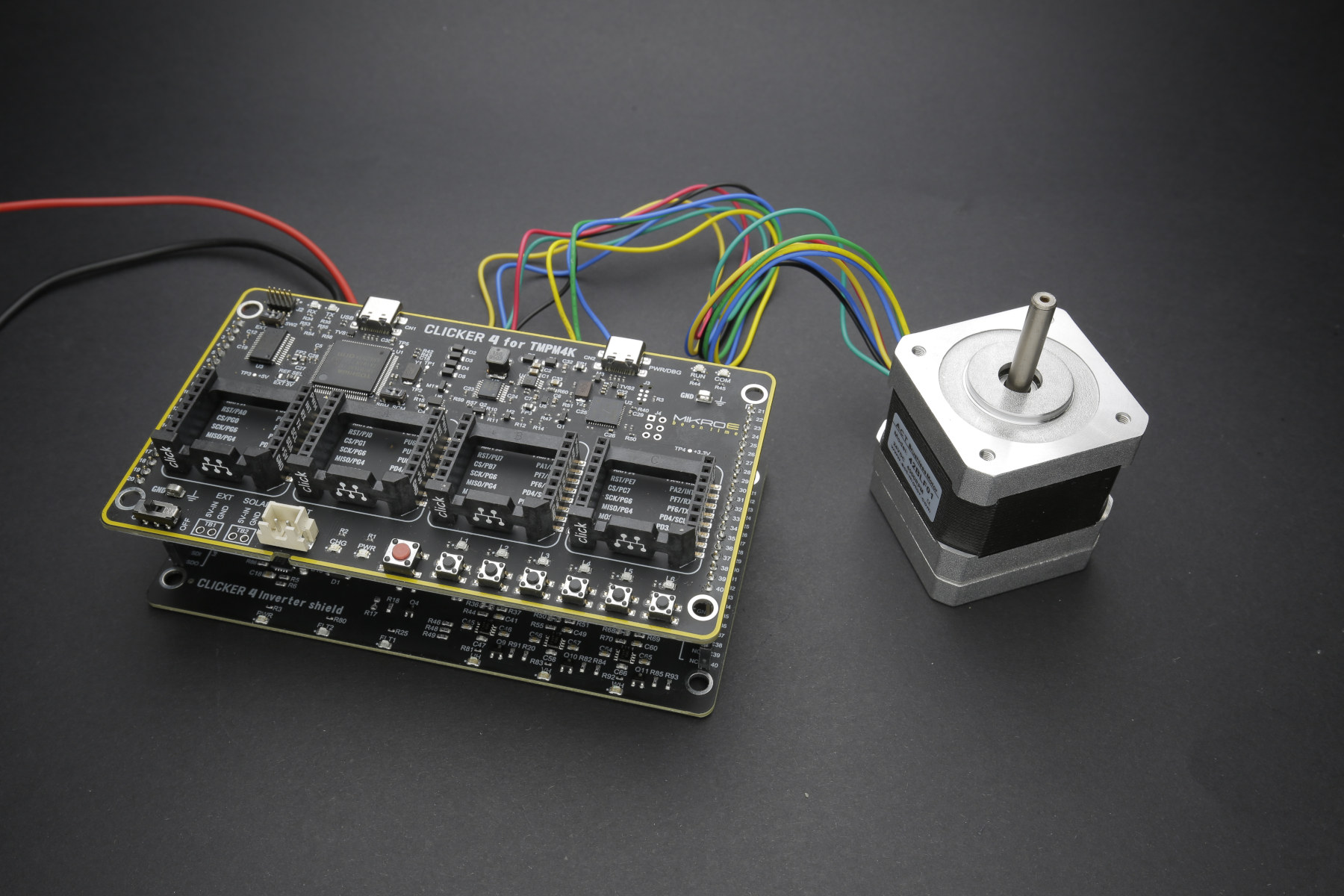
Clicker 4 for TMPM4K board targets motor control with Toshiba M4K microcontroller
Toshiba and Mikroelektronika have launched the Clicker 4 for TMPM4K development board equipped with Toshiba M4K Arm Cortex-M4 microcontroller for motor control, as well as four mikroBUS sockets for MikroE Click expansion boards. The Clicker 4 for TMPM4K board is also fitted with an on-board CMSIS-DAP compliant Debug Unit based on Toshiba’s TMPM067 MCU, extension connectors, JTAG/SWD debug ports, LED indicators and push buttons, and works best with Clicker 4 Inverter Shield with six MOSFETs for motor driving, a 48V switching power supply, and a 5V regulated power source that can power the M4K board. Clicker 4 for TMPM4K specifications: MCU – Toshiba TMPM4KNFYAFG 32-bit Arm Cortex-M4 microcontroller @ up to 160 MHz with 256KB code flash, 32KB data flash, 24KB SRAM, as well as Vector Engine (A-VE+), Encoder and Programmable Motor Driver (PMD) for brushless DC motors Expansion 4x mikroBUS sockets for adding Click board 40x connection pads with […]
Toshiba Memory to Become Kioxia
NAND flash was invented by Toshiba Memory in the early 80’s before launching commercially in 1987, and the company kept innovating over the years and introduced BiCS FLASH 3D flash memory in 2018. However Toshiba Memory is now a separated entity from Toshiba Corp as both separated in April 2017, before the former becoming a fully independent company in June 2018 after it was acquiered by a consortium led by Bain Capital, and including SK Hynix, Apple, Dell Technologies, Seagate Technology and Kingston Technology. For that reason, EETimes reports Toshiba Memory will soon change name, and from October 1, 2019 will be known as Kioxia. The name combines words from Japanese and Greek languages with respectively “kioku” translating into “memory”, and “axia” meaning “value”, which the company says “reflects the value of memory in society driven by increasing amounts of active data through 5G, IoT and cloud computing”. This does […]
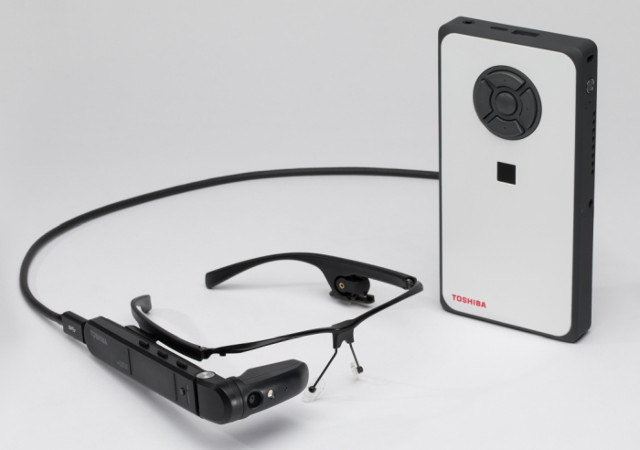
Toshiba Unveils dynaEdge AR Smart Glasses Powered by a Portable Windows Mini PC
Smart glasses have never really gained traction in the consumer space, but they can still be useful in the workplace, especially with augmented reality, where relevant data can be overlaid on top of the user’s view. Toshiba has launched one of those products with dynaEdge AR smart glasses, but instead of having the battery and electronics on the glasses themselves, a portable mini PC running Windows takes care of the heavy lifting and the battery. This should make the glasses lighter – provided proper cable management -, and offer longer battery life. dynaEdge AR100 head mounted display (HMD) specifications: Display – 0.26″ with 640 x 360 resolution (equivalent to 4.1″ display about 35cm away); angle adjustment Audio – Dual microphone with noise cancellation, speaker USB – USB type C port to connect to mini PC Sensors – Ambient light, compass, gyroscope, proximity Location – GPS support Built-in Camera Misc – […]
Ubuntu 17.10 May Corrupt the BIOS on Some Lenovo, Acer, Dell, and Other Laptops
Canonical has decided to temporarily remove the download link to Ubuntu 17.10 due leaving a notice reading: The download of Ubuntu 17.10 is currently discouraged due to an issue on certain Lenovo laptops. Once fixed this download will be enabled again. The issue that many user are reported being unable to save BIOS settings or boot with USB in several Lenovo Laptops with many topics about this issue on Lenovo Forums. The installed operating system still boots normally, so many affected people may not have even noticed. Based on the bug report it seems to be related to the enablement of intel-spi-* drivers (Intel Serial Flash drive) in the kernel (CONFIG_SPI_INTEL_SPI_PCI option), and this could also affect Ubuntu 16.04 with HWE kernels. The fix is to disable the driver in the kernel, and Canonical will soon release images. The downside of not using the driver are likely null or minimal, […]
Embedded Linux Conference 2015 Schedule – IoT, Cars, and Drones
Embedded Linux Conference 2015 will take place in San Jose, California, on March 23 – 25, 2015, and will focus on Drones, Things and Automobiles. The schedule has been published, and whether you’ll attend or not, it’s always interested to have a look at what will be talked about to have a peak into the future of Embedded Linux, or simply keep abreast with the progress in the field. So as usual, I’ve gone through the schedule, and made my own virtual program with talks that I find interesting. Monday 23rd 9:00 – 9:30 – Driving standards and Open Source to Grow the Internet of Things by Mark Skarpness, Director of Systems Engineering at Intel Billions of devices are beginning to come online, and many of these devices, large and small, are running open source software. To fuel this innovation, it’s more important than ever for these devices to use […]