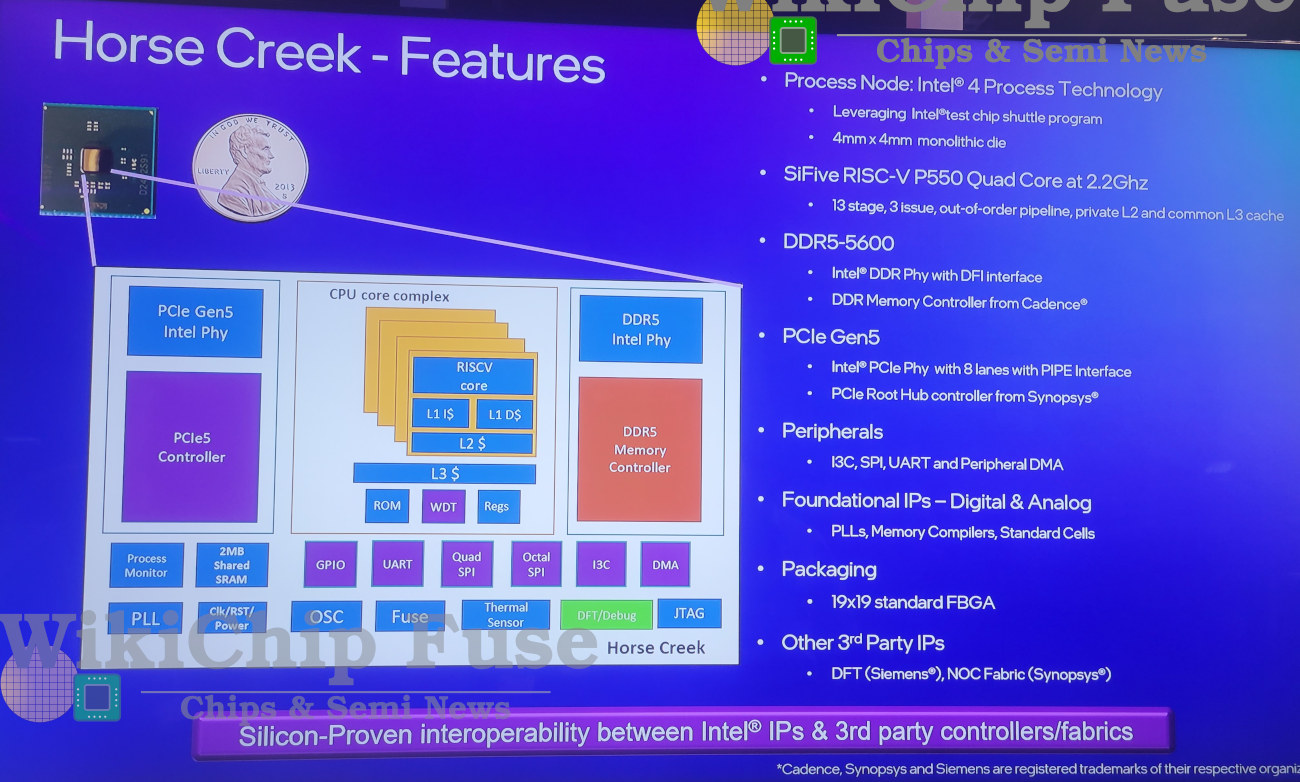
When SiFive introduced its Performance P550 64-bit RISC-V processor in 2021, we were told that Intel would use it in the Horse Creek platform with “leading-edge interface IP such as DDR and PCIe” and manufactured with Intel’s 7nm process. We now have more details about the Horse Creek platform, as a development board was showcased for the first time in public at the Intel Innovation 2022 Developer Conference, and according to a report by Wikichip, the Cortex-A75 class quad-core RISC-V processor runs at up to 2.2 GHz, supports DDR5-5600 memory and eight PCIe 5.0 lanes, and was taped out with Intel 4 process. Horse Creek platform specifications: CPU – SiFive P500 quad-core RISC-V processor @ up to 2.2 GHz with a 13-stage, 3-issue, out-of-order (OoO) pipeline, private L2 cache, and common L3 cache Memory – DDR5-5600 interface PCIe – PCIe Gen5 through Intel’s PCIe PHY with 8 lanes, Synopsys PCIe […]
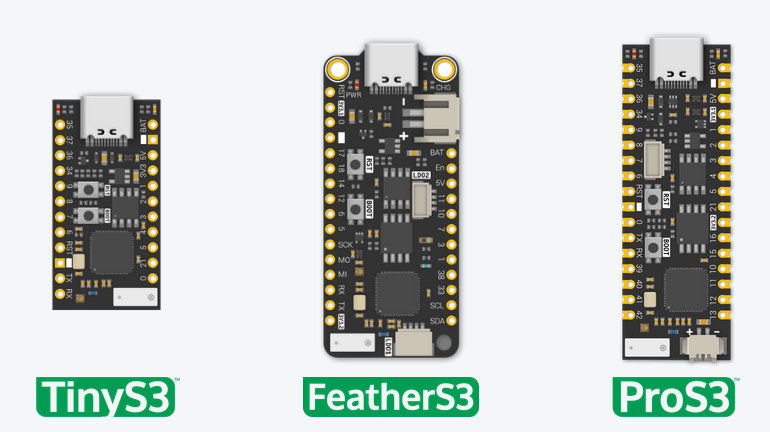
Unexpected Maker TinyS3, FeatherS3 and ProS3 boards feature ESP32-S3 dual-core wireless MCU
Seon Rozenblum, better known as Unexpected Maker, has launched upgrades to its ESP32-S2 boards such as the TinyS2 with ESP32-S3 variants, namely TinyS3, FeatherS3, and ProS3 boards. The new boards share the same form factors as the TinyS2, FeatherS2, and ProS2, but they get a more powerful dual-core microcontroller with AI instructions and 512kB SRAM. The microcontroller also adds Bluetooth 5.0 Low Energy (BLE) connectivity with Bluetooth Mesh support, instead of just WiFi 4 connectivity found in the earlier boards. TinyS3, FeatherS3, and ProS3 boards share the following features: SoC – Espressif Systems’ ESP32-S3 with Dual-core 32bit Xtensa LX7 microcontroller up to 240MHz RISC-V ULP Co-processor 512KB SRAM 2.4GHz Wifi 4 (802.11b/g/n) Bluetooth 5.0 BLE + Mesh Memory – 8MB QSPI PSRAM Flash – 8MB to 16MB depending on the model. USB – 1x USB Type-C connector with reverse back-feed protection for power and programming Antenna – 3D high gain […]
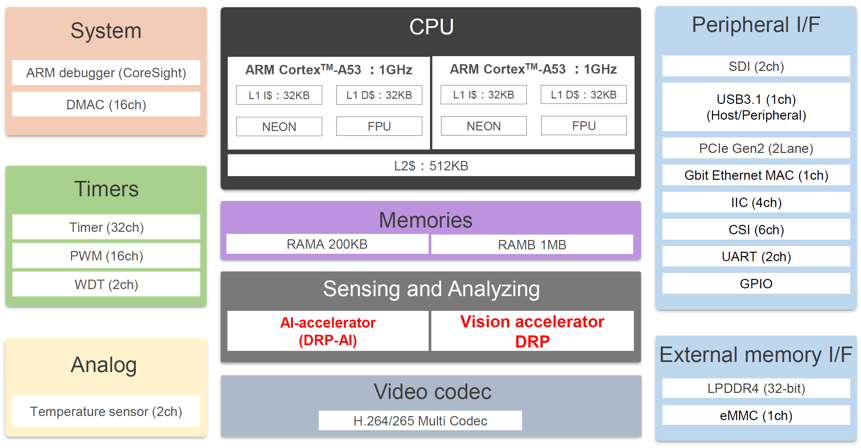
Renesas RZ/V2MA microprocessor embeds AI & OpenCV accelerators for image processing
Renesas has launched the RZ/V2MA dual-core Arm Cortex-A53 microprocessor with a low-power (1TOPS/W) DRP-AI accelerator and one OpenCV accelerator for rule-based image processing enabling vision AI applications. The MPU also supports H.265 and H.264 video decoding and encoding, offers LPDDR4 memory and eMMC flash interfaces, as well as Gigabit Ethernet, a USB 3.1 interface, PCIe Gen 2, and more. The RZ/V2MA microprocessor targets applications ranging from AI-equipped gateways to video servers, security gates, POS terminals, and robotic arms. Renesas RZ/V2MA specifications: CPU – 2x Arm Cortex-A53 up to 1.0GHz Memory – 32-bit LPDDR4-3200 Storage – 1x eMMC 4.5.1 flash interface Vision and Artificial Intelligence accelerator DRP-AI at 1.0 TOPS/W class OpenCV Accelerator (DRP) Video H.265/H.264 Multi Codec Encoding: h.265 up to 2160p, h.264 up to 1080p Decoding: h.265 up to 2160p, h.264 up to 1080p Networking – 1x Gigabit Ethernet USB – 1x USB 3.1 Gen1 host/peripheral up to 5 […]
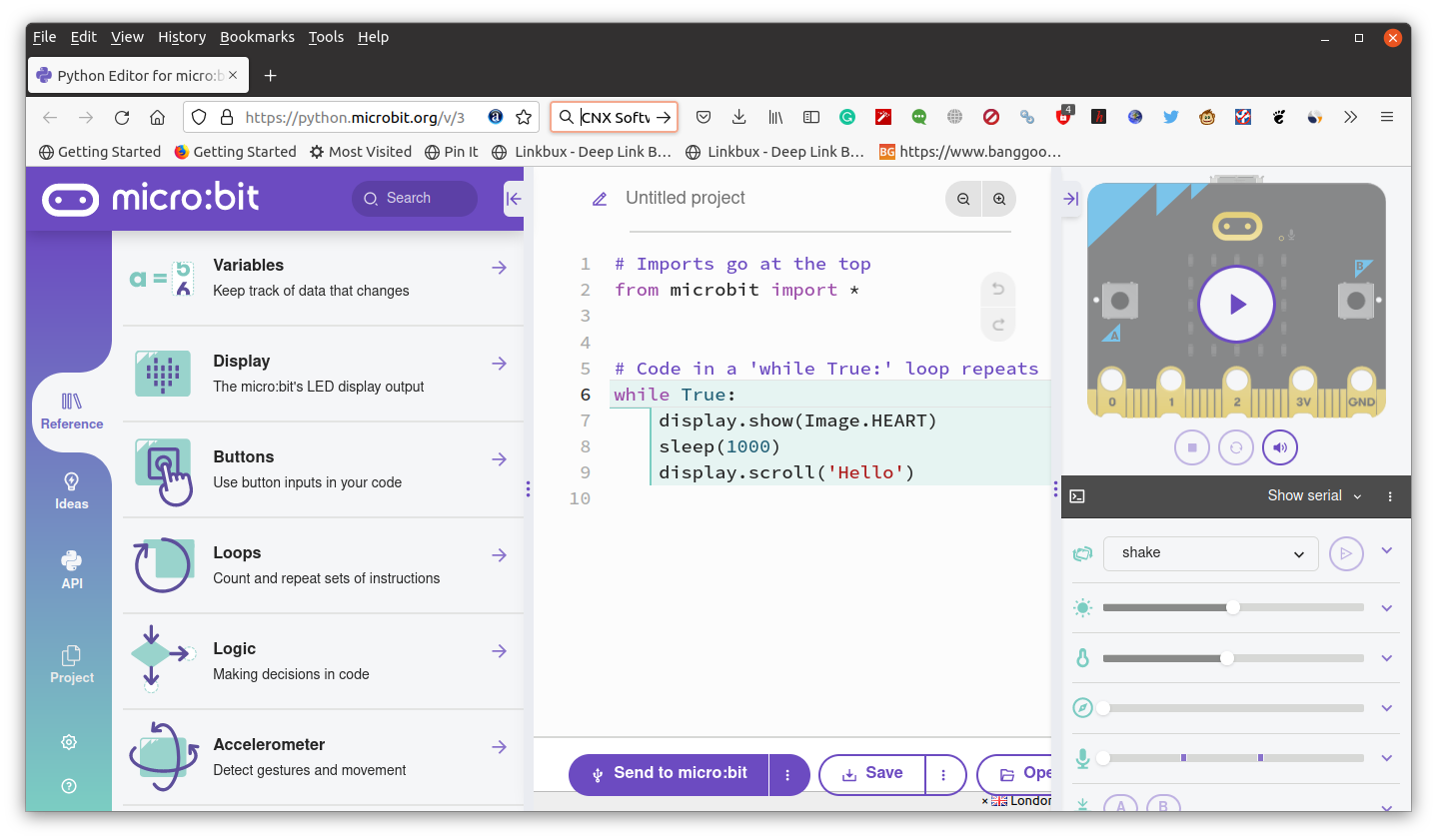
The BBC has released a new web-based Python editor for the micro:bit board
There are already Python editors such as Thonny, but the BBC thought those were not good enough and released a new web-based Python editor specifically designed for the micro:bit education board targeting 11 to 14 years old pupils. The micro:bit Python editor includes drag and drop code examples, code structure & error highlighting, auto-complete feature, a simulator to test the code before uploading it to the micro:bit board, and a Quick ideas section to help pupils get started with projects. The BBC’s micro:bit Python editor works with both the micro:bit V1 and V2, but note the simulator shows a micro:bit V2, so if you are using the previous generation micro:bit, some code may work on the simulator but not on your micro:bit V2 board. For that reason, the BBC marked the code that only works on a micro:bit V2 with ‘V2’ in the Reference section. While the BCC is a […]
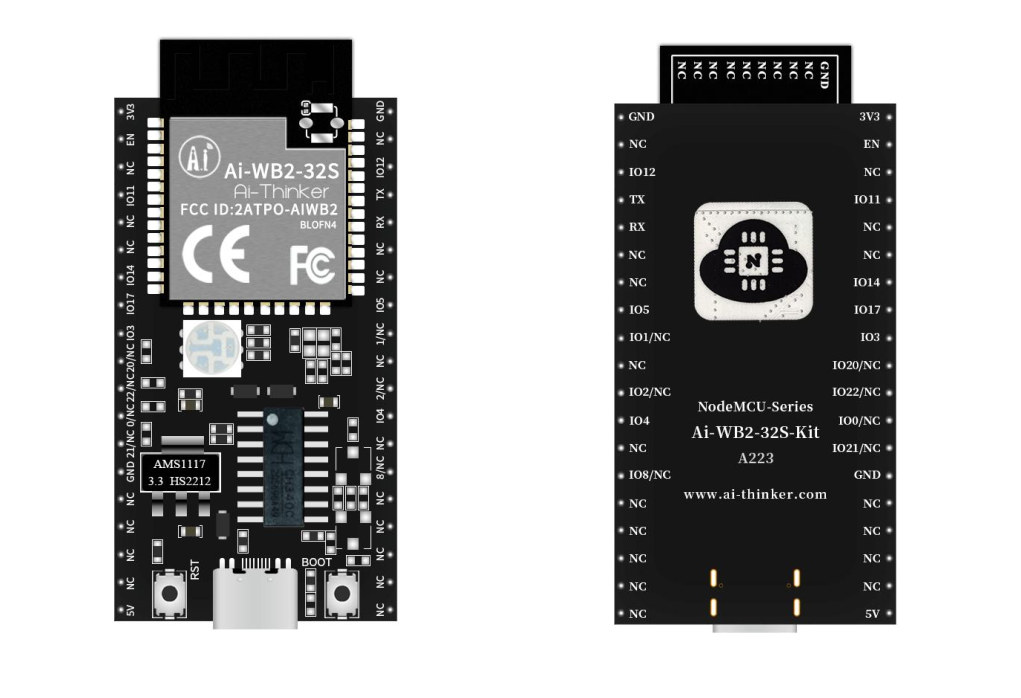
AI Thinker Ai-WB2 modules feature BL602 RISC-V MCU with WiFi and BLE connectivity
AI Thinker has just introduced a new family of wireless IoT modules with the Ai-WB2 equipped with Bouffalo Lab BL602 RISC-V microcontroller offering both 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE connectivity. There are ten different modules to choose from, probably to keep mechanical and electrical compatibility with ESP8266 and ESP32 modules, and the company expects customers to integrate those into Internet of Things (IoT) products, mobile devices, wearables, Smart Home appliances, and more. Ai-WB2 modules share the following specifications: Wireless MCU – Bouffalo Lab BL602 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller @ up to 192 MHz with 276KB SRAM, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE connectivity Storage – 2MB or 4MB SPI flash WiFi range – Up to about 500 meters (typical) I/Os – SDIO, SPI, UART, I2C, IR receiver, PWM, ADC, DAC, and GPIO (except Ai-WB2-01S with just UART/PWM/GPIO/ADC) Power Supply – 2.7V to 3.6V > 500mA Power […]
Linux 6.0 release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V, and MIPS architectures
Linux 6.0 has just been released by Linus Torvalds: So, as is hopefully clear to everybody, the major version number change is more about me running out of fingers and toes than it is about any big fundamental changes. But of course there’s a lot of various changes in 6.0 – we’ve got over 15k non-merge commits in there in total, after all, and as such 6.0 is one of the bigger releases at least in numbers of commits in a while. The shortlog of changes below is only the last week since 6.0-rc7. A little bit of everything, although the diffstat is dominated by drm (mostly amd new chip support) and networking drivers. And this obviously means that tomorrow I’ll open the merge window for 6.1. Which – unlike 6.0 – has a number of fairly core new things lined up. But for now, please do give this most […]
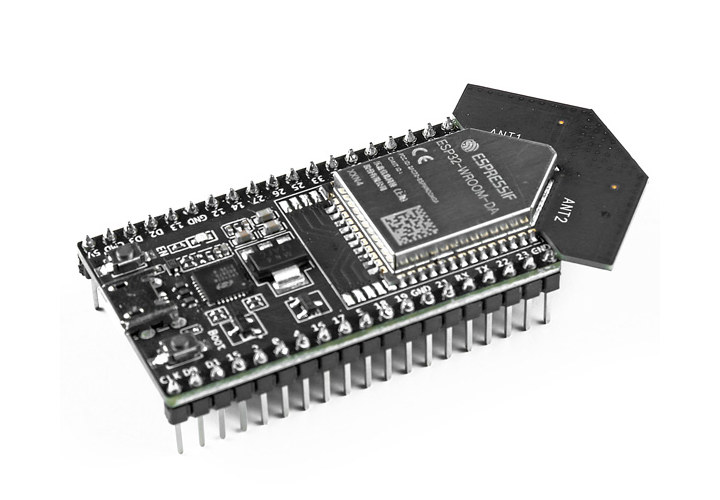
ESP32 DevKitC V4 IoT development board ships with ESP32-WROOM-DA dual antenna module
The ESP32 DevKitC V4 is now selling with the ESP32-WROOM-DA module with two PCB antennas that was introduced last year in order to offer a longer WiFi range and better reliability. The development kit is exactly the same as the other ESP32 DevKitC V4 models, and the only difference is the dual antenna design. When running a recent version of the Arduino Core for the ESP32 (2.0.3 or greater), the ESP32 will automatically switch to the antenna with the strongest signal in order to deliver the best connectivity possible. ESP32 DevKitC V4 specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-WROOM-DA (PDF datasheet) with SoC – Espressif Systems ESP32-D0WD-V3 dual-core LX6 microprocessor with 520 KB SRAM, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 4.1 connectivity Storage – 4MB SPI flash Two PCB antennas (ANT1 and ANT2) USB – 1x Micro USB port for power, programming, and debugging through USB-to-UART bridge up to 3 Mbps Expansion […]
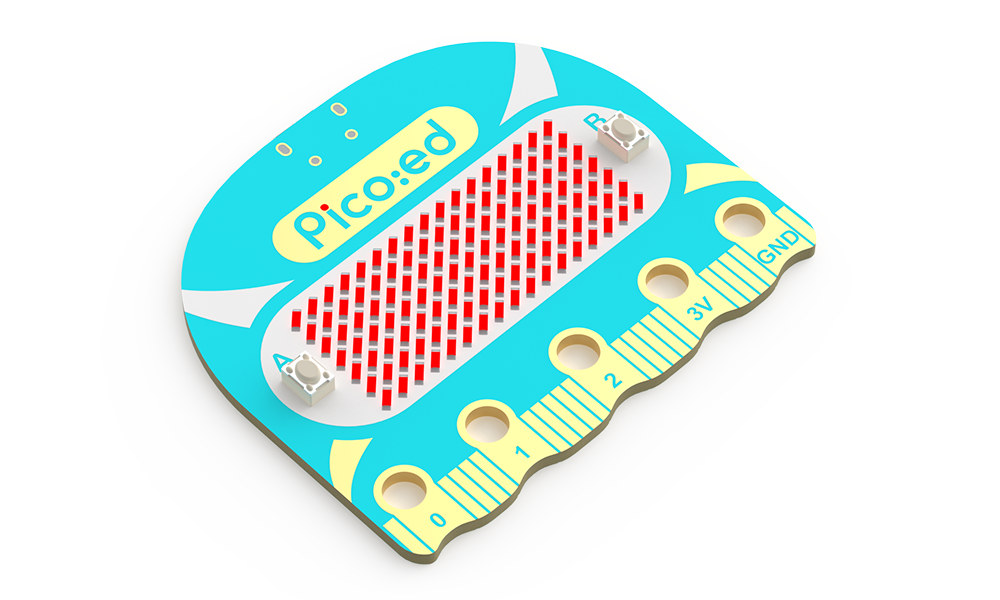
Raspberry Pi RP2040 gets into BBC Micro:bit lookalike board
ELECFREAKS Pico:ed V2 is a Raspberry Pi RP2040 board heavily inspired by the BBC Micro:bit with an edge connector exposing rings suitable for crocodile clips, a 17×7 LED matrix display, and designed for the classroom. We’ve seen several BBC Micro:bit clones – or rather adaptations – over the years with boards such as the SiFive Learn Inventor, Elecrow Mbits, and HiHope “Big Brother” board. The Pico:ed V2 adds to the list, and the main differences are that it is based on the Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller instead, and does not come with wireless connectivity relying on a USB interface only. ELECFREAKS Pico:ed V2 specifications: MCU – Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Cortex-M0+ microcontroller @ up to 133Mhz with 264kB of SRAM Storage – 2MB QSPI flash Display – 17×7 dot-matrix display USB – 1x micro USB 1.1 port for power, data, and programming I/Os 25-pin notched “Wavy” connector with up to […]