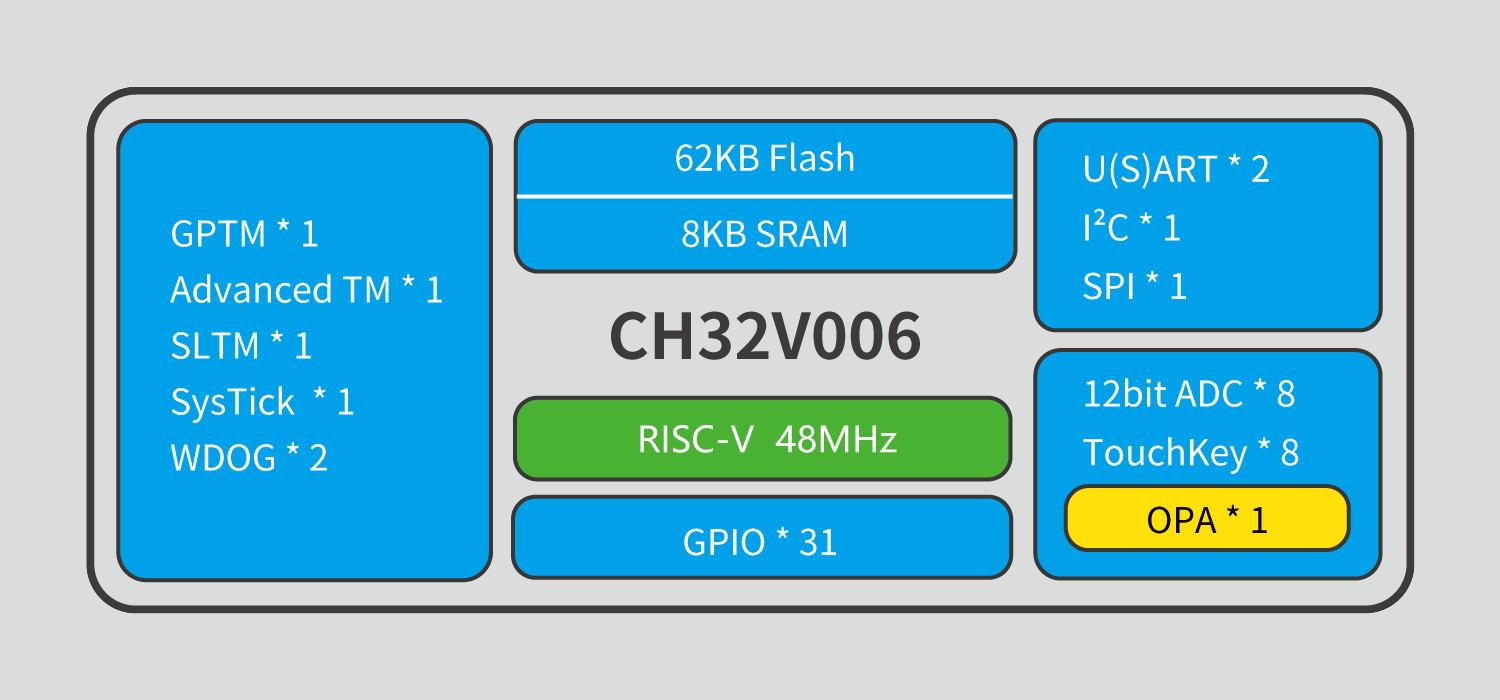
WCH CH32V006 RISC-V microcontroller is an upgrade to the 10-cent CH32V003 microcontroller with more I/Os, up to four times the memory, storage, a wider supply voltage range, the addition of a TouchKey interface, as well as a new 32-bit V2C RISC-V core instead of the V2A core found in the CH32V003. More specifically that means we went from the CH32V003 with 2KB SRAM and 8KB flash, up to 8KB SRAM and 62KB for the CH32V006, and 6KB SRAM and 32KB flash for the CH32V005, a smaller sibling of the new RISC-V microcontroller. WCH CH32V005 & CH32V006 specifications (with highlights in bold to show differences against CH32V003): CPU – 32-bit “RISC-V2C” core up to 48 MHz Memory – 6KB SRAM (CH32V005) or 8KB SRAM (CH32V006) Storage – 32KB flash (CH32V005) or 62KB flash (CH32V006) Peripherals Up to 31x GPIO with interrupt support (CH32V003 had up to 18x GPIO) 2x USART interfaces […]
Recyclable PCB created by the University of Washington is made from Vitrimers
Ludwik Leibler a Polish-born French physicist and his team from the Laboratoire Matière Molle et Chimie at ESPCI ParisTech created a new class of plastics known as “vitrimers” and material researchers at the University of Washington (UW) have leveraged the new plastics to develop a recyclable PCB (printed circuit board) known as “Vitrimers PCB” (vPCB) that can be recycled many times over. The team tested their vPCB for strength and electrical properties and found that they are very similar to standard FR-4 PCB material. This means Vitrimers PCBs could offer a solution to reduce landfill waste and make it easier to recycle leftover copper, maximizing resource recovery. Key Features of Vitrimers-based Recyclable PCBs: Base material – Employs vitrimer epoxy, a type of polymer that can be repeatedly cured and uncured without damage. Environmentally sustainable – Designed to reduce e-waste and offer a more circular lifecycle for electronics. Performance – Electrical […]
QEMU 9.0 released with Raspberry Pi 4 support and LoongArch KVM acceleration
QEMU 9.0 open-source emulator just came out the other day, and it brings on board major updates and improvements to Arm, RISC-V, HPPA, LoongArch, and s390x emulation. But the most notable updates are in Arm and LoongArch emulation. The QEMU 9.0 emulator now supports the Raspberry Pi 4 Model B, meaning you can run the 64-bit Raspberry Pi OS for testing applications without owning the hardware. However, QEMU 9.0 has some limitations since Ethernet and PCIe are not supported for the Raspberry Pi board. According to the developers, these features will come on board in a future release. For now, the emulator supports SPI and I2C (BSC) controllers. Still on ARM, QEMU 9.0 provides board support for the mp3-an536 (MPS3 dev board + AN536 firmware) and B-L475E-IOT01A IoT node, plus architectural feature support for Nested Virtualization, Enhanced Counter Virtualization, and Enhanced Nested Virtualization. If you develop applications for the LoongArch […]
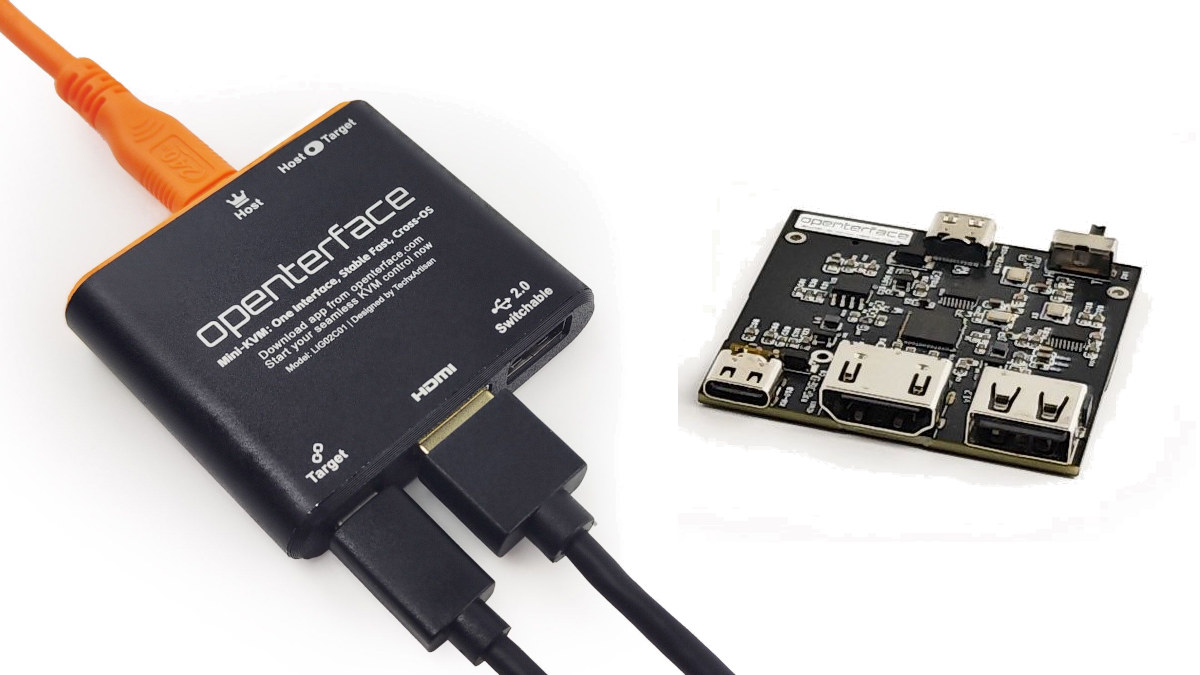
Openterface Mini-KVM is an affordable KVM-over-USB device (Crowdfunding)
Openterface Mini-KVM compact, open-source hardware KVM-over-USB device with HDMI and audio inputs which connects over a USB-C port to the host computer. We’ve seen quite a few low-cost KVM-over-IP solutions based on single board computers over the years, but the Openterface Mini-KVM is quite different (and cheaper) as a plug-and-play and network-independent KVM-over-USB device that establishes a direct HDMI and USB connection between the host computer and the target device. It supports many of the same features as KVM-over-IP solutions except for some features such as ATX support found in the PiKVM v4 Plus or the Pi-Cast KVM with an expansion board that allows the target device to be turned off and from the host device. Mini-KVM (model LIG03D01) specifications: Control method – KVM-over-USB Video capture – Up to 1920×1080 @ 30 Hz with under 140ms latency through HDMI or VGA (the latter requires an add-on VGA-to-HDMI cable) Audio capture […]
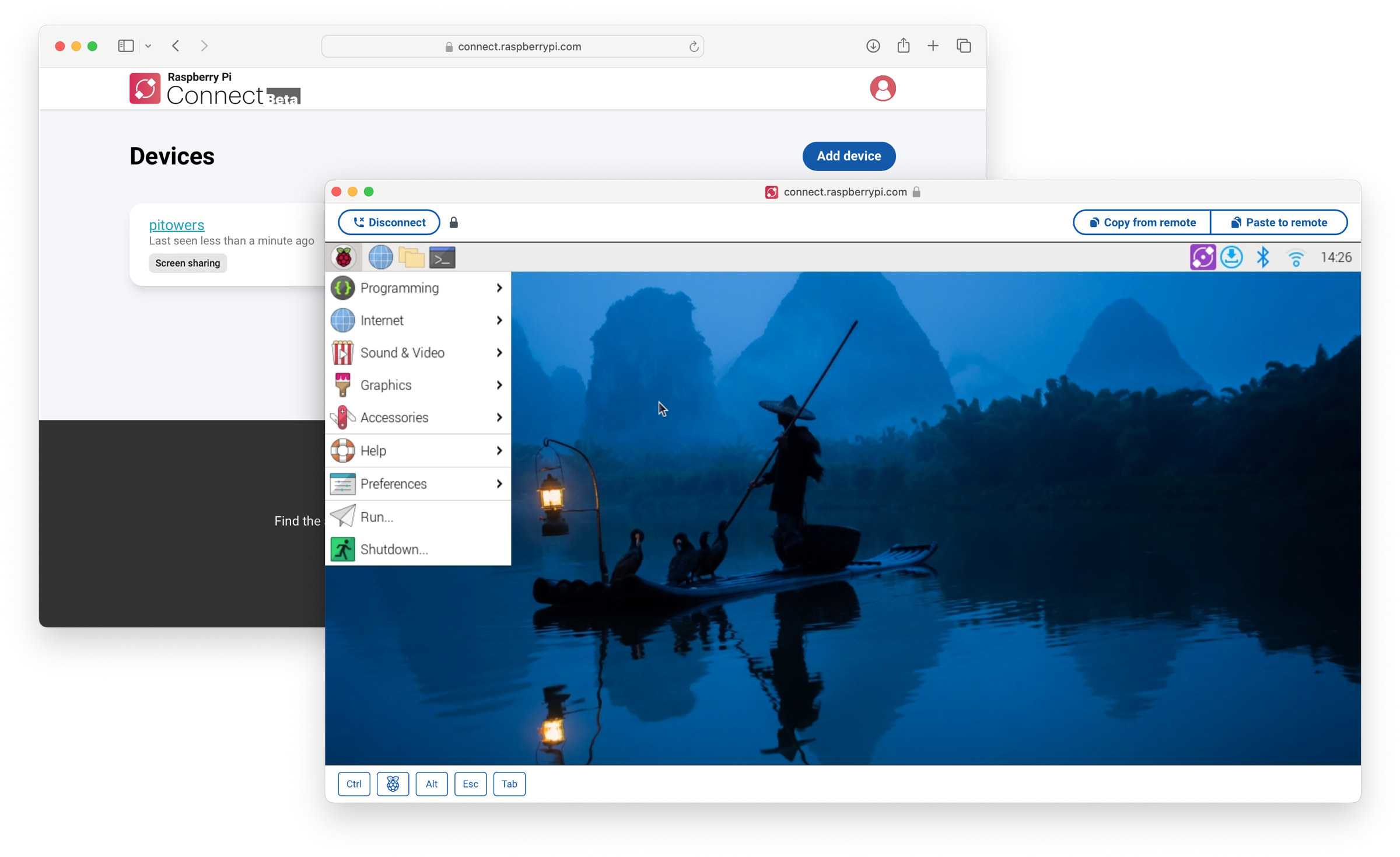
Raspberry Pi Connect software makes remote access to Raspberry Pi boards easier
Raspberry Pi Connect software, currently in beta, aims to make remote access to the Raspberry Pi boards even easier and more secure by using a web browser and minimal configuration needed. It’s been possible to access Raspberry Pi boards remotely through VNC forever, and the X protocol used to be an option before the switch to Wayland, but both can be somewhat hard to configure especially when wanting to access the machine on a different local network or from the internet. Raspberry Pi Connect aims to change that. Under the hood, we’re told the web browser and the Raspberry Pi device established a secure peer-to-peer connection with the same WebRTC communication technology found in programs such as Zoom, Google Meet, or Microsoft Teams. The Raspberry Pi runs the “rpi-connect” daemon that listens to screen-sharing requests from the Raspberry Pi Connect website and establishes a secure, low-latency VNC instance directly between […]
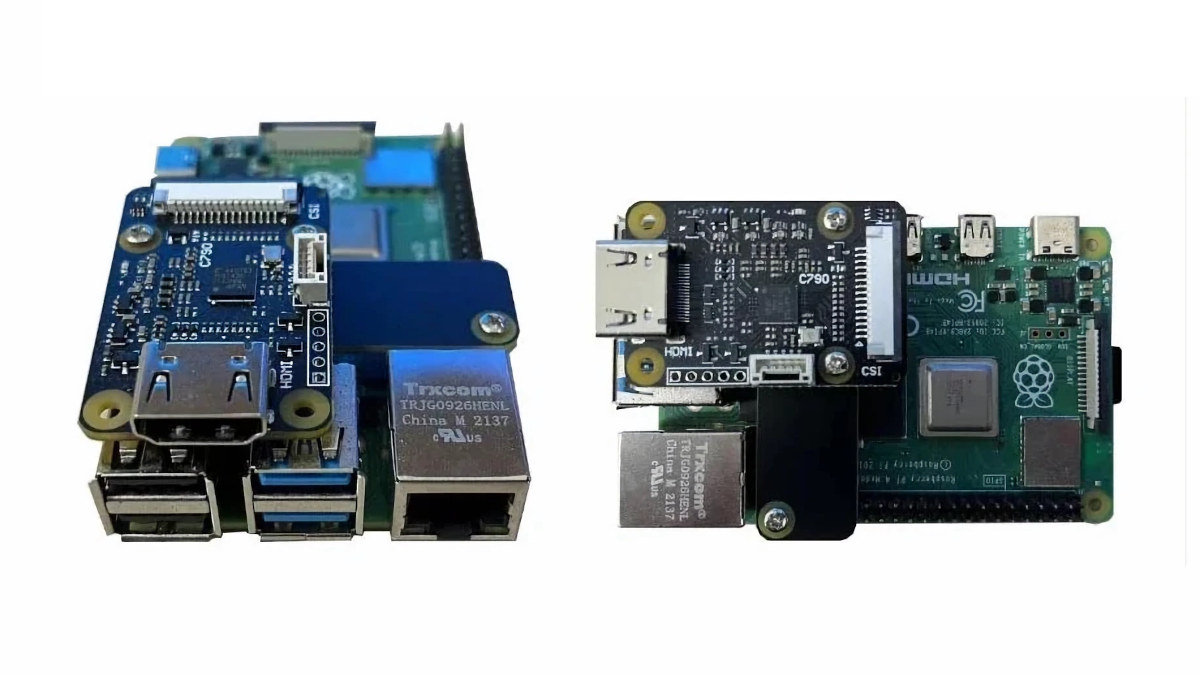
$23 C790 HDMI to MIPI CSI adapter adds HDMI and audio input to Raspberry Pi SBCs
C790 is an HDMI to MIPI CSI-2 board compatible with Raspberry Pi single board computers featuring a 40-pin GPIO header that adds both HDMI input up to 1080p60 and I2S audio input to the popular Arm SBC. The solution can be useful for IP KVM solutions as we’ve seen with the PiKVM v3 and PiCast portable KVM switch, or to capture video and audio from a camera that outputs HDMI with audio through the board’s MIPI CSI camera interface and I2S input signals on the GPIO header. C790 specifications: Supported SBC’s – Raspberry Pi Zero, 3B, 3B+, 4B, CM3, CM4 with MIPI CSI-2 input port (Note: Raspberry Pi 4 is limited to 1080p50 due to 2-lane MIPI CSI-2, CM4 supports 1080p60) Main chip – Toshiba TC358743XBG HDMI to CSI-2 bridge chip up to 1920×1080, 60 FPS Video and audio input – HDMI port up to 1080p60 Video Output – 2-lane […]
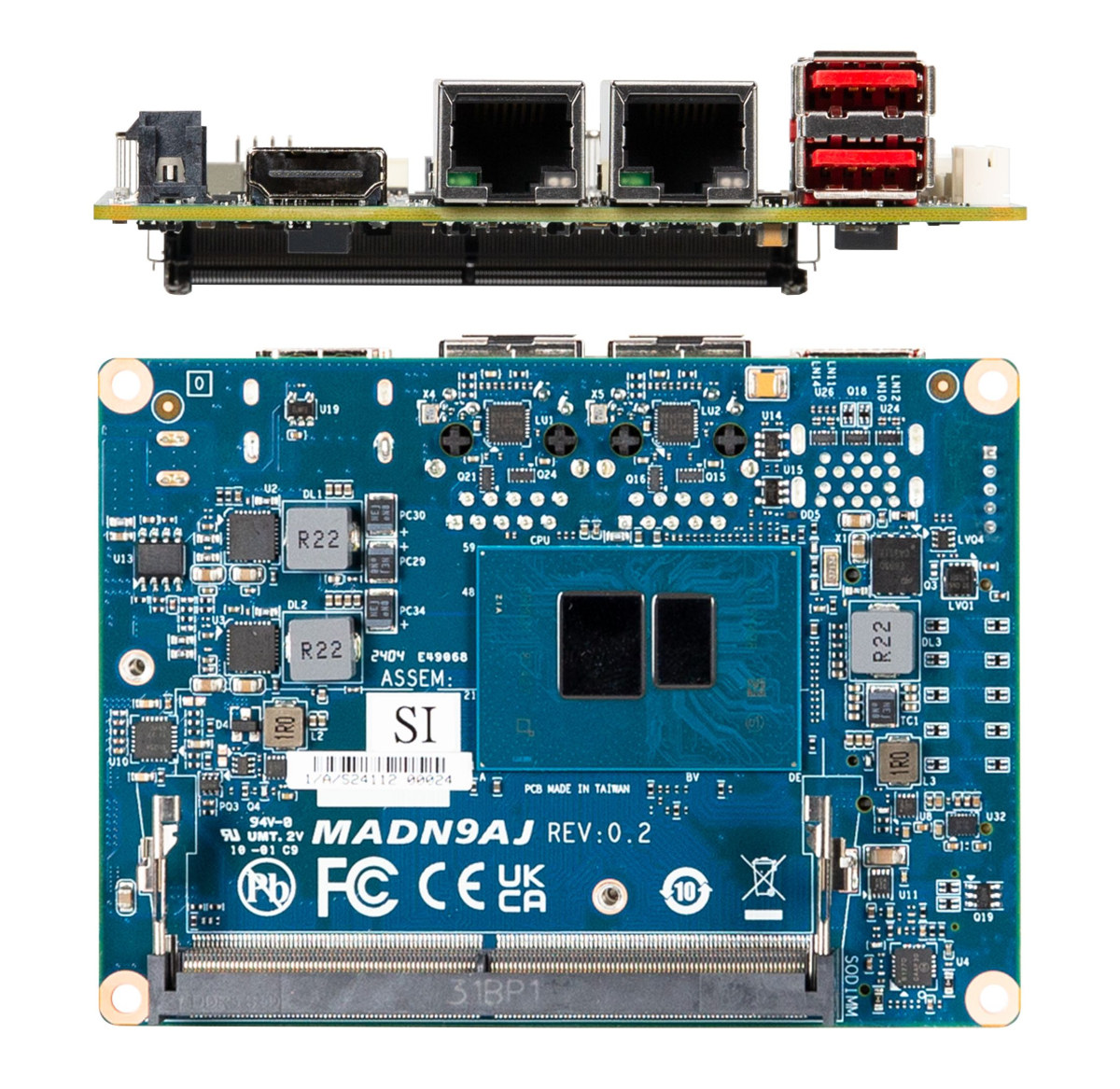
GIGAIPC PICO-N97A is a Pico-ITX SBC powered by an Intel Processor N97 CPU
GIGAIPC PICO-N97A Pico-ITX SBC features an Intel Processor N97 quad-core Alder Lake-N processor coupled with up to 16GB DDR5 SO-DIMM memory and M.2 SATA or NVMe storage designed for passively cooled and enclosed systems for Industry 4.0 applications in the smart cities, retail, and healthcare sectors. The single board computer supports up to two independent displays via HDMI and LVDS interfaces. It also provides dual Gigabit Ethernet, two USB 3.1 ports, an additional M.2 Key-B socket for wireless, and various headers for RS232/RS422/RS485, GPIO, USB 2.0, and more. GIGAIPC PICO-N97A specifications: SoC – Intel Processor N97 CPU – Alder Lake-N quad-core/quad-thread processor @ up to 3.6 GHz Cache – 6MB cache GPU – 24 EU Intel UHD graphics @ up to 1.20 GHz TDP: 12W System Memory – Up to 16GB DDR5-4800 via a single SO-DIMM socket Storage – SATA or NVMe SSD via M.2 M-Key socket (See expansion) Video […]
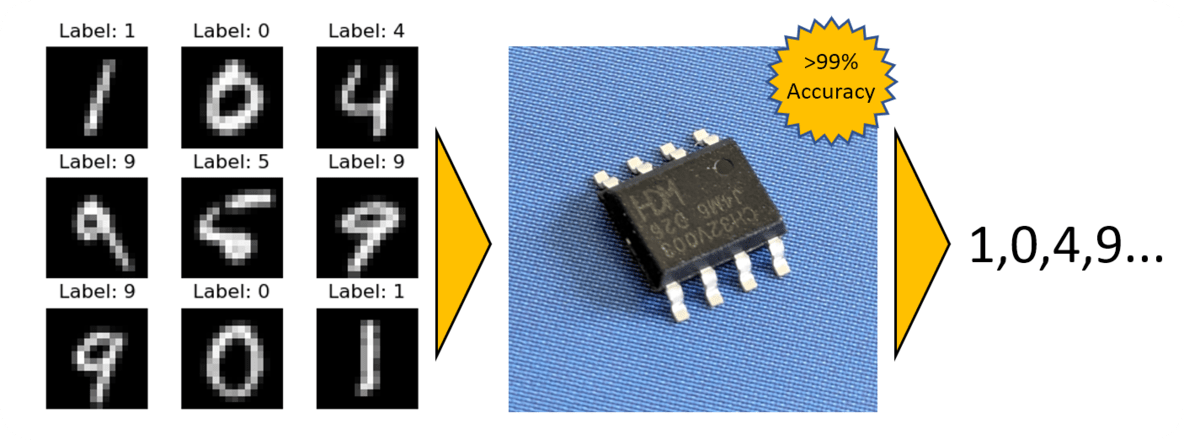
BitNetMCU project enables Machine Learning on CH32V003 RISC-V MCU
Neural networks and other machine learning processes are often associated with powerful processors and GPUs. However, as we’ve seen on the page, AI is also moving to the very edge, and the BitNetMCU open-source project further showcases that it is possible to train and run low-bit quantized neural networks using low-end RISC-V microcontrollers such as the inexpensive CH32V003. As a reminder, the CH32V003 is based on the QingKe 32-bit RISC-V2A processor, which supports two levels of interrupt nesting. It is a compact, low-power, general-purpose 48MHz microcontroller that has 2KB SRAM with 16KB flash. The chip comes in a TSSOP20, QFN20, SOP16, or SOP8 package. To run machine learning on the CH32V003 microcontroller, the BitNetMCU project does Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and fine-tunes the inference code and model structure, which makes it possible to surpass 99% test accuracy on a 16×16 MNIST dataset without using any multiplication instructions. This performance is […]