NXP has just unveiled the NXP i.MX 91 single-core Cortex-A55 processor following the introduction of the i.MX 93 in 2021, and designed for cost-optimized edge devices running Linux. The NXP i.MX 93 processor comes with up to two Cortex-A55 cores, a Cortex-M33 real-time core, and an Ethos U65 microNPU, but targeting entry-level Linux systems, the NXP i.MX 91 processor does without the real-time core and the AI acceleration, while still integrating NXP EdgeLock Secure Enclave, and the company highlights support for multiple wireless connectivity options through companion chips such as the IW612 that supports Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.2, 802.15.4, and the new Matter protocol. NXP i.MX 91 specifications: CPU – Arm Cortex-A55 running at up to 1.4GHz with 256KB L2 cache System Memory – Up to 2.4GT/s x16 LPDDR4 with Inline ECC Storage 3x SD 3.0, SDIO 3.0, eMMC 5.1 1x Octal SPI including support for SPI NOR and SPI […]
Snagboot is an open-source cross-vendor recovery tool for embedded targets
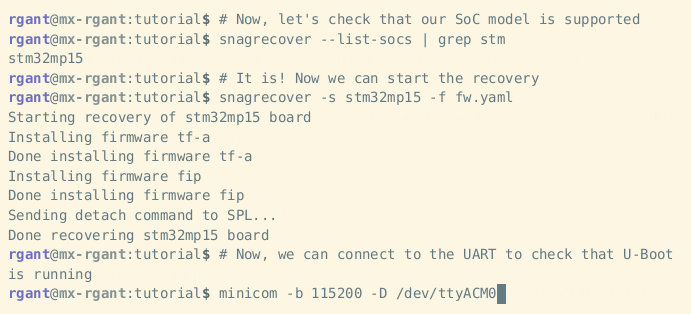
Bootlin has just released the Snagboot open-source recovery tool for embedded platforms designed to work with multiple vendors, and currently STMicro STM32MP1, Microchip SAMA5, NXP i.MX6/7/8, Texas Instruments AM335x and AM62x, and Allwinner “sunxi” processors are supported. Silicon vendors usually provide firmware flashing tools, some closed-source binaries, that only work with their hardware. So if you work on STM32MP1 you’d use STM32CubeProgrammer, while SAM-BA is the tool for Microchip processors, NXP i.MX SoC relies on UUU, and if you’ve ever worked on Allwinner processors you’re probably family with sunxi-fel. Bootlin aims to replace all those with the Snagboot recovery tool. The Python tool is comprised of two parts: snagrecover using vendor-specific ROM code mechanisms to initialize external RAM and run the bootloader (typically U-Boot) without modifying any non-volatile memories. snagflash communicates with the bootloader over USB to flash system images to non-volatile memories, using either DFU, USB Mass Storage, or […]
MicroPython 1.20 released with Raspberry Pi Pico W support, mip package manager, smaller footprint
Damien George has recently announced the release of MicroPython 1.20 with support for the Raspberry Pi Pico W board., a new lightweight package manager called mip, a smaller footprint thanks to the use of compressed type structs, and many other changes. mip package manager The new mip package manager uses a custom protocol optimized for embedded systems to query and install packages, and intends to replace upip for installing packages from micropython-lib or any URL. Mip can be run directly on a device, as long as it has network connectivity, or via mpremote from a host computer. Damien explains all pure-Python drivers have been moved from the micropython repository to the micropython-lib repository as part of the change in order to make it easier to install the packages needed for a given project. MicroPython is getting smaller The MicroPython binary size has been reduced by many kilobytes for all ports […]
Linux 6.3 release – Notable changes, Arm, RISC-V and MIPS architectures
Linux Torvalds has just announced the release of Linux 6.3 on the Linux Kernel Mailing List (LKML): It’s been a calm release this time around, and the last week was really no different. So here we are, right on schedule, with the 6.3 release out and ready for your enjoyment. That doesn’t mean that something nasty couldn’t have been lurking all these weeks, of course, but let’s just take things at face value and hope it all means that everything is fine, and it really was a nice controlled release cycle. It happens. This also obviously means the merge window for 6.4 will open tomorrow. I already have two dozen pull requests waiting for me to start doing my pulls, and I appreciate it. I expect I’ll have even more when I wake up tomorrow. But in the meantime, let’s enjoy (and test) the 6.3 release. As always, the shortlog […]
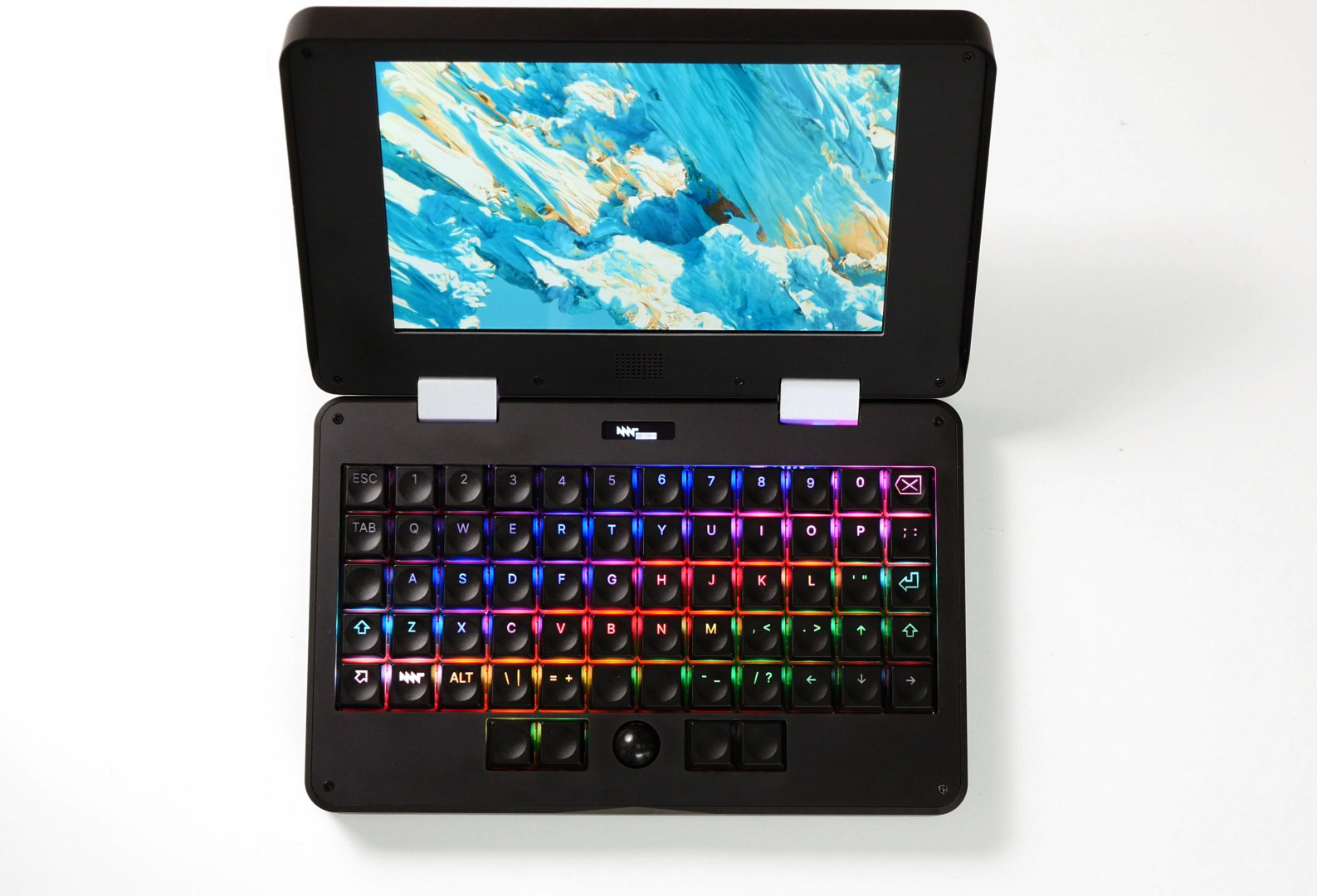
MNT Pocket Reform open-source 7-inch modular laptop launched on Crowd Supply
The MNT Pocket Reform, a smaller version of the MNT Reform laptop, with a 7-inch display has just launched on Crowd Supply with an NXP i.MX8M Plus system-on-module, but also compatible with an NXP Layerscape LS1028A module, Raspberry Pi CM4, Pine64 SOQuartz, and an AMD Kintex-7 FGPA module. The open-source modular laptop also comes with a 128GB eMMC flash, 8GB RAM, WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 5.0 connectivity on-module, an optional 1TB NVMe SSD, a backlit 60-key mechanical keyboard with an optical trackball and four buttons, a micro HDMI port to connect an external display, a few USB ports, and Ethernet through an ix industrial connector. MNT Pocket Reform specifications: SoM – Boundary Devices Nitrogem8M Plus system-on-module with SoC – NXP i.MX 8M Plus quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 @ 1.8GHz with Cortex-M7 real-time core, Vivante GC7000UL GPU, 2.3 TOPS NPU with open drivers, H.264/H.265 Video Decoder with open drivers (Hantro), and HiFi4 […]
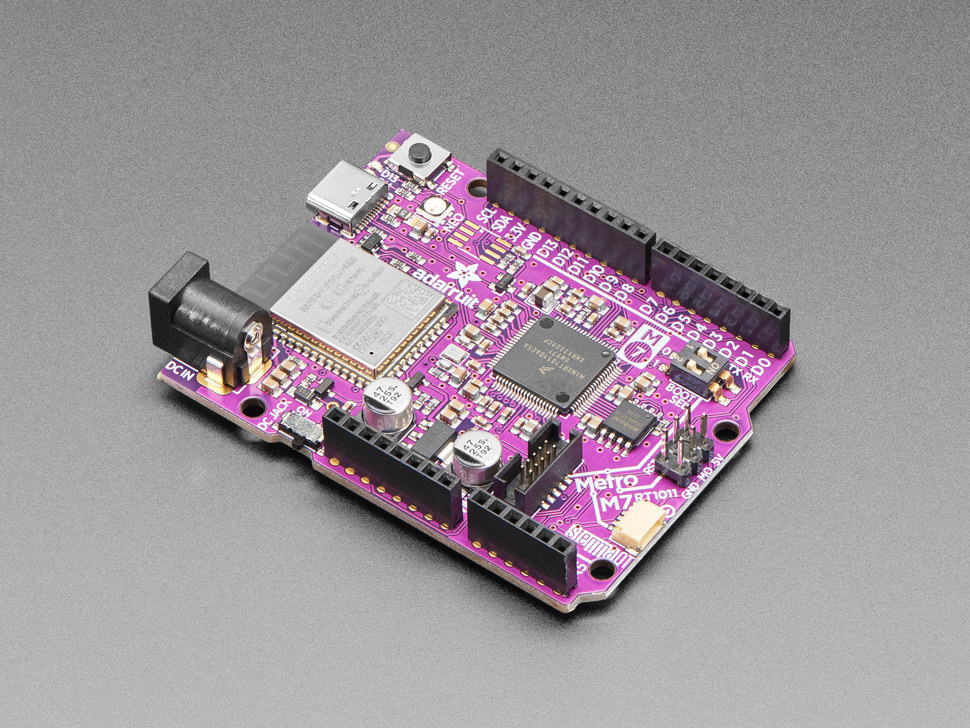
Arduino UNO compatible Adafruit Metro M7 features 500 MHz NXP i.MX RT1011 Cortex-M7 SoC
Adafruit Metro M7 is a development board based on a 500 MHz NXP i.MX RT1011 Arm Cortex-M7 crossover MCU that follows Arduino UNO form factor and integrates the ESP32-based “AirLift” WiFi module for wireless connectivity. The board also comes with 4MB QSPI storage, a few LEDs and buttons, a Qwiic connector for additional expansion beyond Arduino Shields, and an SWD connector for debugging. The board takes 6V to 12V DC input via a power barrel jack, but can also be powered through its USB Type-C port. Adafruit Metro M7 specifications: SoC – NXP iMX RT1011 crossover microcontroller with an Arm Cortex-M7 clocked at 500 MHz and 128KB SRAM/TCM Storage – 4MB of QSPI XIP Flash Wireless – AirLift WiFi co-processor with TLS/SSL support (better known as ESP32-WROOM-32) USB – 1x USB Type-C port for power and programming Expansion Arduino UNO headers for Arduino shields compatibility STEMMA QT connector for I2C […]
Linux 6.2 release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V, and MIPS architectures
Linux 6.2 has just been released with Linus Torvalds making the announcement on LKML as usual: So here we are, right on (the extended) schedule, with 6.2 out. Nothing unexpected happened last week, with just a random selection of small fixes spread all over, with nothing really standing out. The shortlog is tiny and appended below, you can scroll through it if you’re bored. Wed have a couple of small things that Thorsten was tracking on the regression side, but I wasn’t going to apply any last-minute patches that weren’t actively pushed by maintainers, so they will have to show up for stable. Nothing seemed even remotely worth trying to delay things for. And this obviously means that the 6.3 merge window will open tomorrow, and I already have 30+ pull requests queued up, which I really appreciate. I like how people have started to take the whole “ready for […]
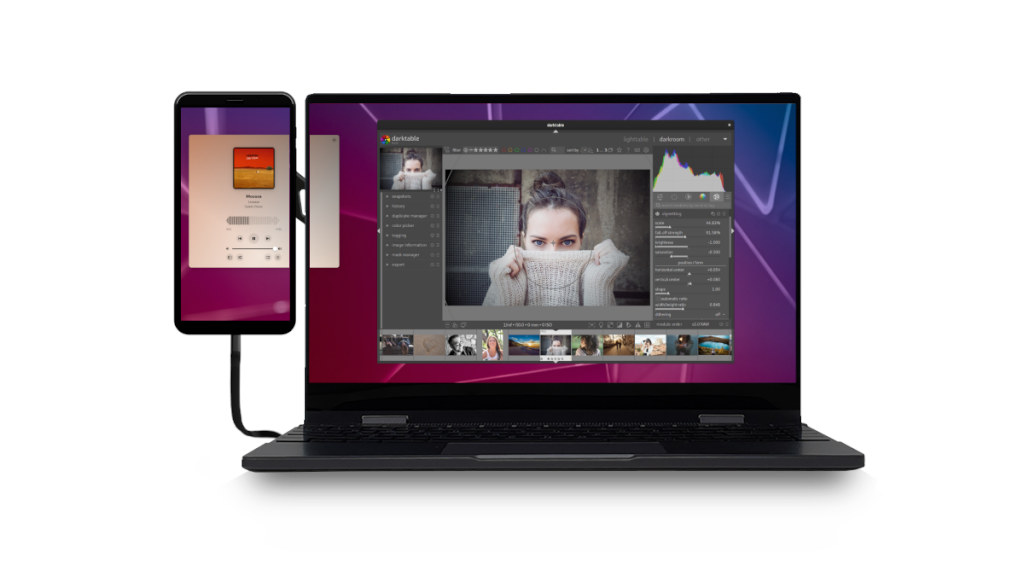
Purism Lapdock kit converts the Librem 5 Linux smartphone into a laptop
Purism has just announced the Lapdock kit to turn their Librem 5 Linux smartphone into a laptop with a 13.3-inch touchscreen display thanks to the NexDock 360 laptop dock. I was a big believer in mobile desktop convergence around 10 years ago, expected to be soon able to use my phone as a computer or laptop with a dock, and it looked like it might have become a reality when Canonical launched the Ubuntu Edge smartphone crowdfunding campaign in 2013. But it turns out demand was not sufficient, and Canonical eventually ended their convergence efforts focusing on profitable IoT and cloud segments instead. But that does not mean there isn’t a niche market and Purism’s Lapdock kit addresses it to some extent. The Lapdock kit is comprised of three parts namely the NexDock 360 laptop dock, a magnetic mount to attach the Librem 5 to the side of the NexDock […]