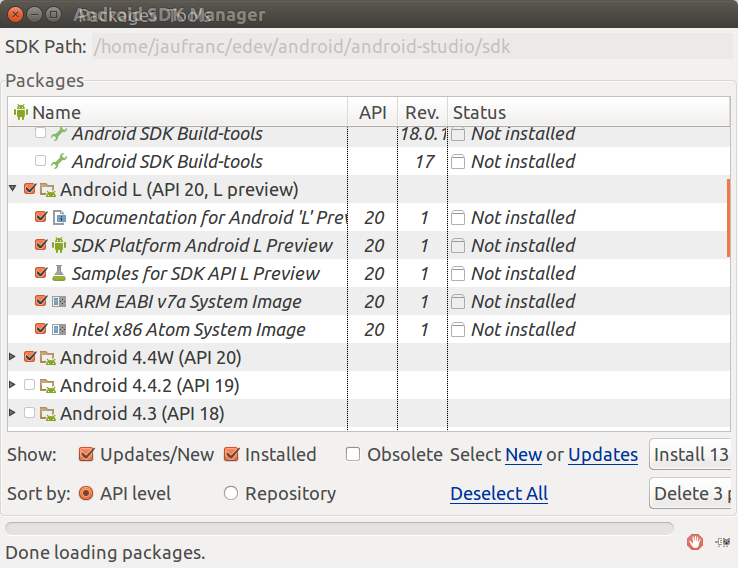
As mentioned yesterday, Android L Developer Preview was about to be released, and this is now done with images for Nexus 5 “Hammerhead” and Nexus 7 “razor” available right now. However, if you don’t have either of these devices, or you’d rather not install a beta version on the phone you use everyday, you can still give a try in the SDK emulator. I’ve tried Android L myself in Ubuntu 14.04. Here’s what you have to do: Install Android Studio IDE in Ubuntu, and Create a new Project or open an existing project (Android Studio Version is now 0.61) Click on Tools->Android->SDK Manager in the top menu, and select the Android L (API 20, L Preview) packages as shown below, and click on “Install xx Packages” button. Accept the license as required, and click Install. This step can take countless hours… Now we’ll need to create a Virtual Device for […]
Low Power Mode (Suspend to RAM) in uCLinux for Freescale Kinetis K70 MCU
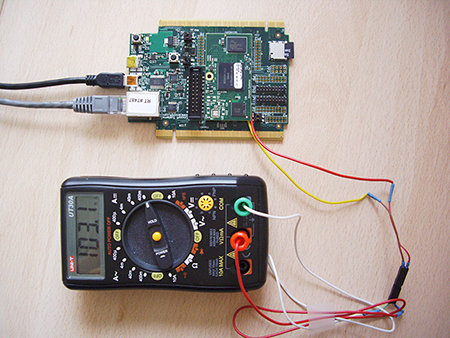
All ARM based micro-controllers and processors implement multiple power mode in order to save optimize power usage depending on the tasks. However, I’ve been told by some hobbyists/developers/makers that low power modes are not always implemented in Linux, especially for low cost systems either because of hardware limitations or the software is not implemented. EmCraft Systems has just released their latest embedded (uC-) Linux distributions for the MCU boards, and one of the features now available is “suspend to RAM” for their K70 SoM development kit, based on Freescale Kinetis K70 Cortex M4 MCU, which consume just around 600 to 700 uA @ 3.3V (2 to 2.3 mW) in this low power mode. They have connected a multimeter to measure the current drawn at different power modes. If you want to know all the details, you should probably read the company’s article on “Linux Low-Power Mode on Kinetis“, but I’ll […]
How to Upgrade Firmware for Rockchip RK3066, RK3188, RK3328, RK3288, RK3399 Devices with the Command Line in Linux
Previously I wrote an article entitled “How to Flash Rockchip RK3066 / RK3188 Firmware in Linux” explaining how to use a graphical tool called RkFlashKit to upgrade firmware on Rockchip devices using a Linux computer. This tool had some limitations, and it would just have a subset of features of RkAndroidTool (Windows), and it was not possible to flash “update.img” type of firmware which are often provided and flashed with RkBatchTool in Windows. Luckily there’s now a command line tool called upgrade_tool that allows you to flash the “update.img” firmware files directly from Linux. I’ve already shown how to use it with Radxa Rock, but it’s buried with other instructions, so I’ve decided to make a separate post. This has been tested in Ubuntu 14.04 with Radxa Rock (RK3188) and Measy U2C (RK3066). Ready? Let’s start by downloading and extracting upgrade_tool. You may want to add the installation path to […]
Ubuntu 14.04 and Slitaz on Radxa Rock
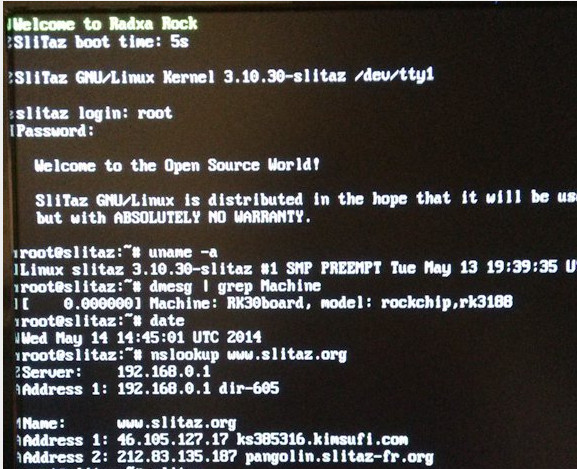
Various Android and Linux images are available on Radxa Rock download page, but if you’d like to get newer images or other options, two developers have provided binaries and posted instructions to get Ubuntu 14.04 and Slitaz operating systems, the later currently booting with Linux kernel 3.10. Naoki FUKAUMI has published a miniroot how-to install a Ubuntu 14.04 Core (minimal headless installation) on Radxa Rock and Radxa Rock Lite. Installation should be relatively easy as he provide the update.img for both board so your can use the usual method in Windows (RkBatchTool) or upgrade_tool in Linux. If you don’t have serial console, you’ll have need to flash the parameter file requiring RkAndroidTool in Windows, and the same upgrade_tool in Linux. If once the installation and configuration is complete, you want a desktop environment,you can always run “apt-get install lubuntu-desktop” to install LXDE. SliTaz is a lightweight Linux distribution. I previously […]
How to Boot a Headless Linux Image on Amlogic S802 TV Boxes (Tronsmart Vega S89 Elite)
As some of you already know, I’ve been playing around with Tronsmart Vega S89 Elite, an Android TV Box powered by Amlogic S802 quad-core ARM Cortex A9r4 processor at 2 GHz. Today, I’ll show how to boot a headless Linux image on any Amlogic-based S802 TV Box from the network. The instructions can mainly be used as a starting point for developers, as it requires access to a serial terminal via UART, but if you’ve never done it before, the instructions should be easy enough to follow. Everything is loaded from the network, the kernel (via boot.img) is loaded via TFTP, and the rootfs (Linaro ALIP image) is mounted via NFS, so it’s nearly impossible to brick your device using the method provided. Linaro ALIP rootfs comes with LXDE, but at this stage, the desktop environment is not showing, even though my HDMI TV is properly detected by the drivers. […]
How to Extract a Device Tree File from Android Firmware Files
Up to now, all our cheap Android devices were based on older Linux kernel (3.0.x, 3.4.x) that still used board files (arch/arm/board, but we’ve recently seen companies like Amlogic and Rockchip release source code with Linux kernel 3.10.x. One of the key differences between these version are the move from board files to flattened device tree and multi-platform support. If it is fully implemented, a single kernel image should be able to boot multiple hardware platforms, and all low level configuration handled by the device tree file. Since I’ve connected the serial port of Tronsmart Vega S89 for debugging, and it’s a slow news day, I thought I might try to boot the Linux kernel I compiled myself, but one of the challenge was to get the device tree file. I’ll show how to extract it from the firmware. It should also be possible to get it directly from the […]
Imperas Releases ARM Cortex A53 & A57 Open Source Models for OVPsim
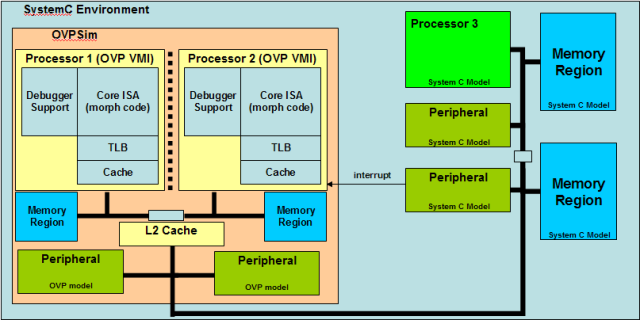
Since the end of 2012, it has been possible to use ARM 64-bit Fast models to run code compiled for the new ARMv8 architecture by emulating a 64-bit ARM processor inside an Intel / AMD processor. ARM fast models are not the only “free” option anymore, as Imperas has released OVPsim 20140430 with open source models for ARM Cortex A53 and Cortex A57 cores. OVPsim is a virtual platform that’s available free of charge for personal usage. The simulator itself (OVPsim) is closed source, but processor, peripheral and platform models are released under the Apache License version 2.0. OVP models of the ARM Cortex-A53 and Cortex-A57 are fully instruction accurate models, and you can use them for personal with an additional free license key, but if you want to make use of advanced features such as TrustZone and hardware virtualization you’ll need to purchase a commercial version (Imperas Developer or […]
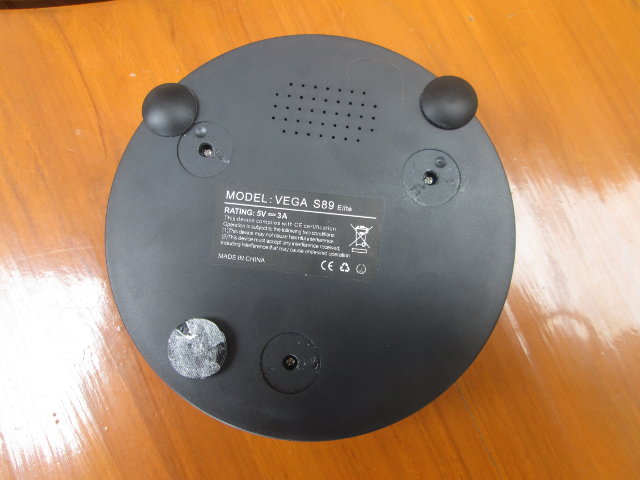
How to Open Tronsmart Vega S89 (Elite) and Access the Serial Console
Tronsmart Vega S89 (Elite) is an Android TV based on Amlogic S802 quad core ARM Cortex A9 processor @ 2GHz, and is one of the fastest Chinese ARM box on the device, at least until Rockchip RK3288 and AllWinner A80 devices come to market. In my unboxing post, I mentioned the UART pins were available, and sometimes in March Amlogic released U-boot and Linux source code for M802/S808, so it’s likely some developers will play around, and eventually run Linux (Ubuntu, Debian, …) on the platform. So today, I’ve done some preliminary work by connecting a USB to serial debug board to my device. The steps to follow are straightforward, and should work on Beelink M8/S82, Jesurun S82, MBOX-S82, IdeaStar S82, etc… which are basically the same box with different names. Before accessing the serial port, we’ll need to open the box. Start by removing the 3 sticky pads at […]