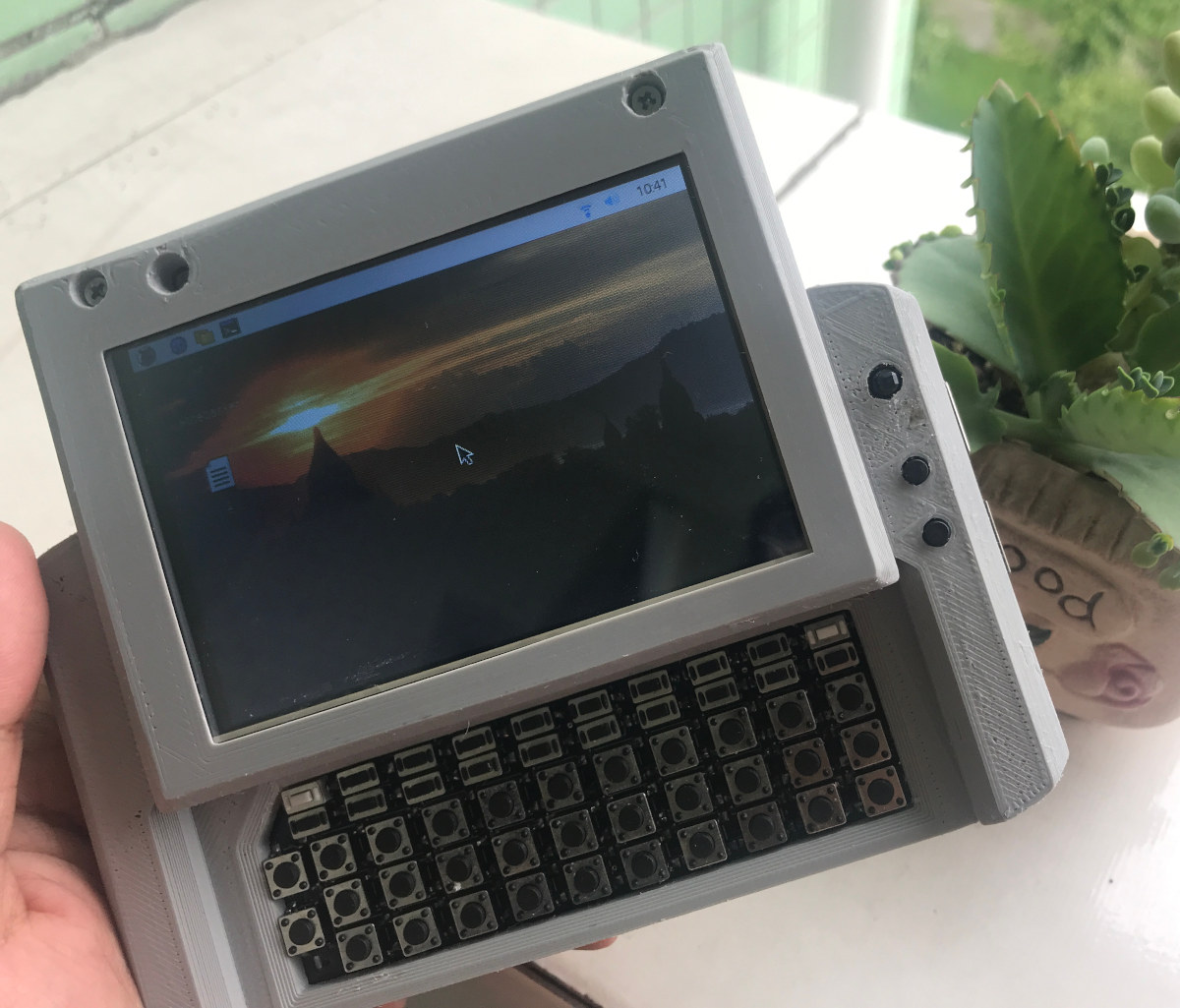
Earlier this year we wrote about Mutantc V3 DIY Raspberry PI UMPC after noticing a talk about it at FOSDEM 2021 online conference. MutantC V4 is a new version of the Raspberry Pi handheld PC that is both easier to build and cheaper. The new model replaces the Arduino Pro Micro board with a more compact ESP32-S2 module and offers a Lite version with even fewer parts (notification LED, IR blaster, IMU, etc..) to make it easier to build. The new MutantC v4 shares many of the same features of the previous versions: Supported SBCs – Raspberry Pi Zero, 2, 3, 4 and compatible. Wireless module for keyboard and other controls – Ai. Thinker ESP-12K module based on ESP32-S2 single-core WiFi microcontroller @ 240 MHz with 8MB flash Display – 2.8-inch, 3.5-inch, or 4-inch “GPIO” LCD such as AdaFruit PiTFT 480×320 display Keyboard – 56-key customizable keyboard with 2x shoulder […]
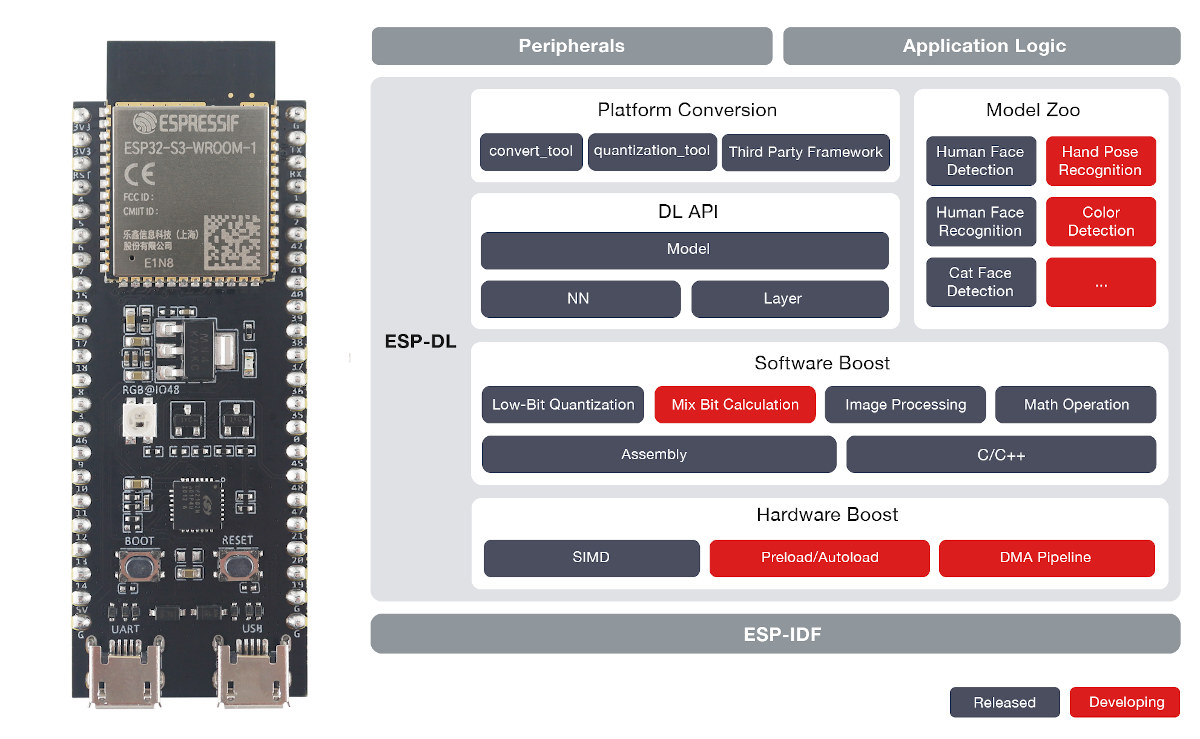
Leverage ESP32-S3 AI capabilities with the ESP-DL library
ESP32-S3 is the first Espressif wireless processor with AI instructions, and ESP-DL library for ESP-IDF allows you to easily leverage those AI instructions using boards such as the ESP32-S3-DevKitC-1. The ESP-DL library provides APIs for Neural Network (NN) Inference, Image Processing, Math Operations, and Deep Learning Models that make full use of ESP32-S3’s AI instructions with a 16-bit face recognition model running 6.25 faster, while the 8-bit model is 2.5 times faster than without acceleration. The ESP-DL library can be used as a project component. For instance, it can be used as a submodule of ESP-WHO computer vision framework, by simply copying it to the esp-who/components/ directory. The Model Zoo contains several pre-trained models for (human) face detection & recognition, and cat face detection, with more being developed including color detection and hand-pose detection. Espressif Systems also provides tools to use your own models, and a convention tool allowing you […]
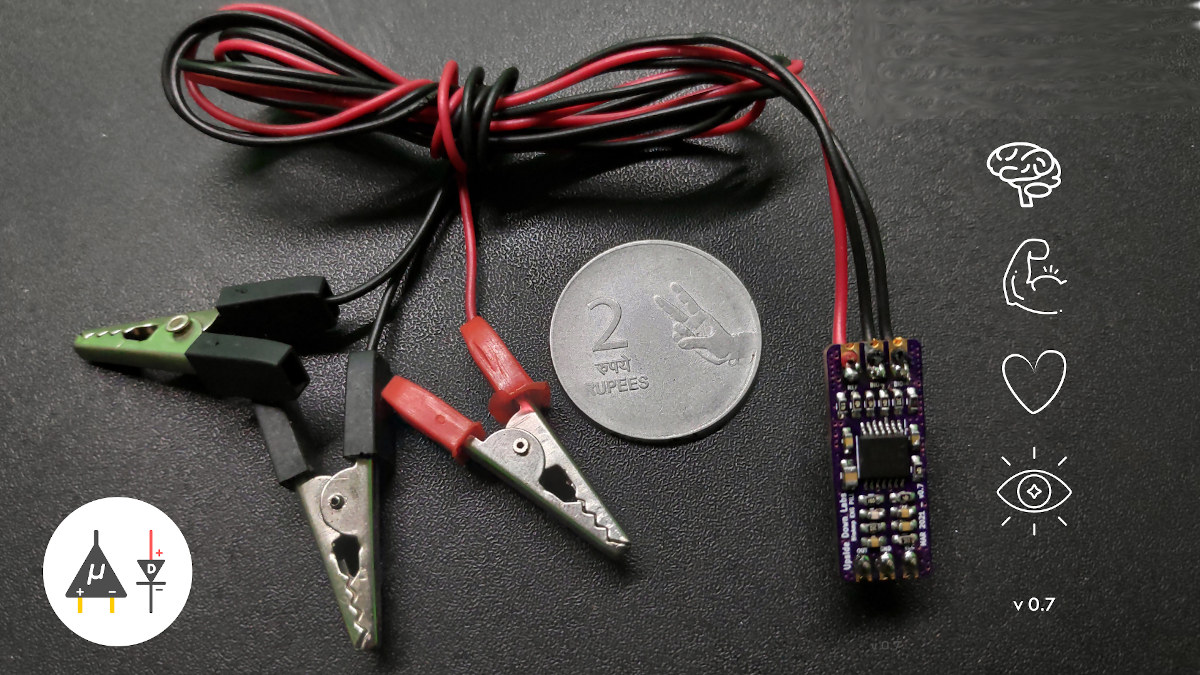
BioAmp EXG Pill board enables ECG, EMG, EOG, and EEG biosensing (Crowdfunding)
BioAmp EXG Pill is a small Analog Front End (AFE) biopotential signal-acquisition board designed to be interfaced to any 5V MCU board with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) such as most Arduino boards, or through a dedicated 5V ADC like the Texas Instruments ADS1115. The board can record biopotential signals like ECG (electrocardiogram), EMG (electromyography), EOG (electrooculography), and EEG (electroencephalogram), or in more simple terms, biosignals from the heart, muscles, eyes, or brain activity. BioAmp EXG Pill key features and specifications: Compatible with any 5V MCU with an ADC Biopotentials: ECG, EOG, EMG, and EEG (configurable) No. of channels: 1 Electrodes: 2 or 3 (configurable) Input Voltage – 5 – 40 V Input Impedance: > 35 MΩ Dimensions – 25.4 x 10 mm OSHWA certifications – IN000026 The board is open-source hardware and you’ll find KiCAD hardware design files like schematics and Gerber files on Github where you’ll also find several […]
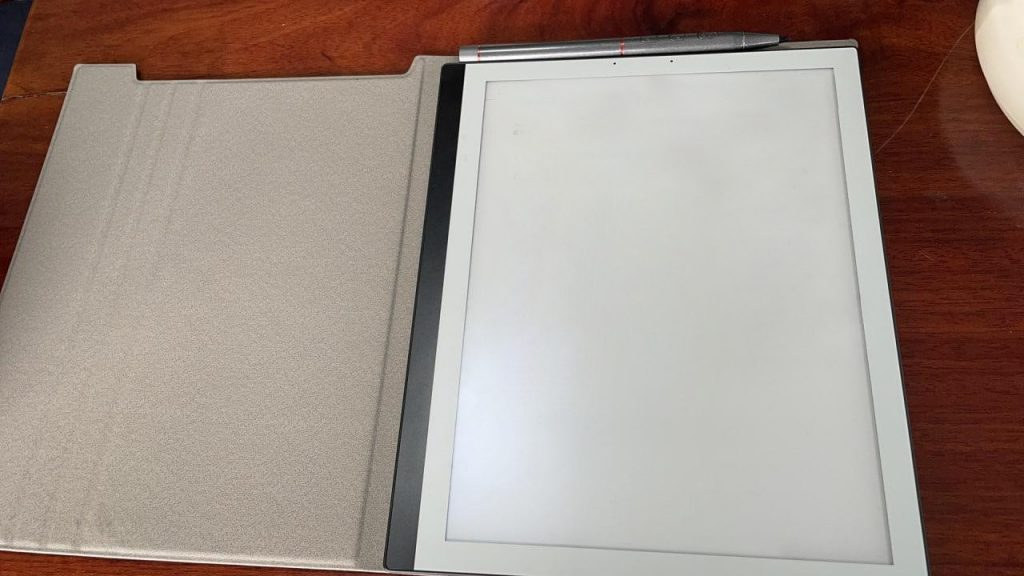
PineNote is a community supported 10.3-inch e-Reader based on Rockchip RK3566 SoC
We’ve covered several e-readers in the past, but the PineNote 10.3-inch e-reader will be a bit different, as the hardware & software will be entirely developed by the community like other Pine64 platforms such as Pinebook Pro, PineCone, Rock64 single board computer, etc… Based on the Rockchip RK3566 quad-core Cortex-A55 processor, PineNote will be one of the fastest e-readers on the market, and leverage the code already written for Quartz64 single board computer, including mainline Linux support. PineNote (preliminary) specifications: SoC – Rockchip RK3566 quad-core A55 processor with Mali-G52 EE GPU, 0.8 TOPS NPU (AI accelerator) System Memory – 4GB of LPDDR4 RAM Storage – 128GB eMMC flash Display – 10.3-inch panel with 1404×1872 resolution (227 DPI), 16 levels of grayscale, front light with cool (white) to warm (amber) light adjustment, capacitive glass layer for finger touch-based input, and a Wacom electromagnetic resonance layer (EMR) for EMR pen input. There’s […]
Debian 11 “BullsEye” released with Panfrost & Lima GPU drivers, exFAT support, driverless printing
Debian 11 “BullsEye” has been released with Panfrost & Lima open-source drivers for Arm GPUs, in-kernel exFAT file system, driverless printing, and many more updates, plus a 5-year support window. Debian’s release is significant as the Linux operating system serves as the base for Ubuntu and derivatives, Raspberry Pi OS, and together with Ubuntu, is one of the operating systems supported by Armbian which offers images for a range of Arm-based single board computers. Arm Mali GPU support in Debian 11 I remember a few years ago 3D graphics acceleration on Arm boards was news, as it was quite a challenge to get it working due to binary blobs. But Debian 11 now comes with Mesa 20.3 framework which includes Panfrost and Lima open-source Mali GPU drivers by default, as well as the Vulkan 1.0 conformant V3DV driver for Raspberry Pi 4. As noted in the documentation that means the […]
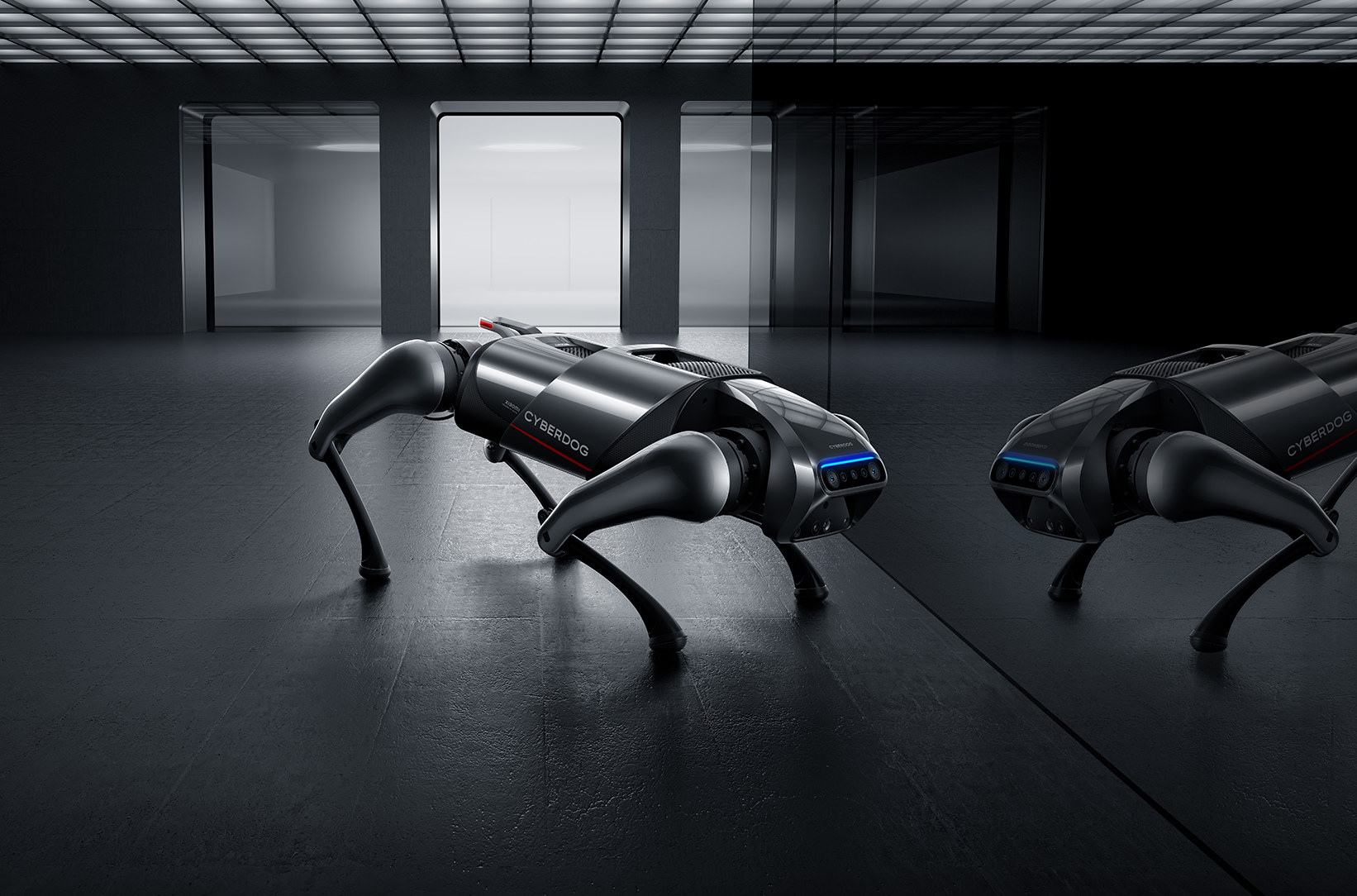
Xiaomi CyberDog quadruped robot is based on NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX
We’ve previously written about consumer-grade smart robotic dogs selling for several hundred dollars with Petoi Bittle equipped with Arduino & Raspberry Pi, as well as XGO Mini Pro with Kendryte K210/K510 AI processor. Xiaomi has now launched its own quadruped robot that looks like a dog with the Xiaomi CyberDog equipped with a more powerful NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX system-on-module (SoM), a larger and heavier body than competing consumer models, and a price tag of a little over $1,500. Xiaomi CyberDog specifications and key features: SoM – NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NXwith an hexa-core NVIDIA Carmel 64-bit Arm processor, a 384-core NVIDIA Volta GPU with 48 Tensor Cores, 2x NVDLA deep learning accelerators delivering a total of 21 TOPS at 15 Watts, 8GB RAM. Storage – 128GB “near” industrial-grade SSD Xiaomi’s in-house developed servo motors offering Maximum torque – Up to 32N·m Rotation speed – Up to 220Rpm Maximum speed – […]
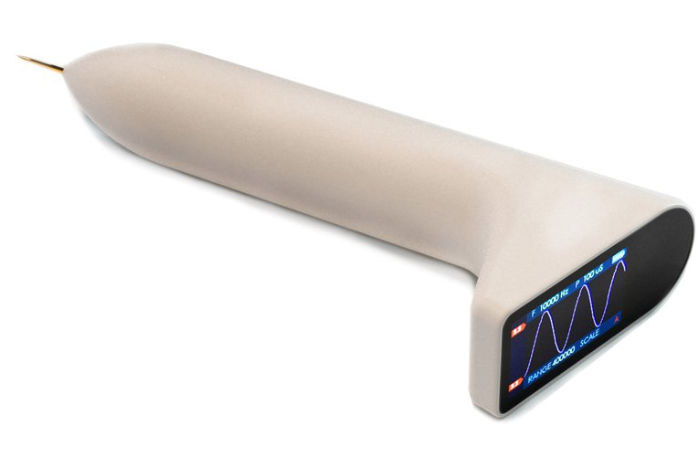
Arduino programmable wireless multitool offers color display, touch controls (Crowdfunding)
QUARK may look like the perfect weapon to hijack a plane, but instead, it’s an open-source, Arduino-based wireless multitool for hardware engineers equipped with a full-color screen and touch-based controls. Based on ESP32 WiFI & Bluetooth wireless SoC, Mulin Group’s QUARK is an ultra-portable multimeter, signal generator and oscilloscope, a bit like IkaScope WiFi Pen-Oscilloscope, except having a laptop or phone to visualize measurements is only optional. The company also compares it to DT71 smart tweezers which do not have an oscilloscope function due to the tiny display. QUARK features & specifications: WiSoC – ESP32 dual-core processor with WiFI & Bluetooth connectivity Display – 240 x 134 IPS display Measurements Voltage – 0 to 26 V Current – 0 to 3.2 A Resistance from 0 to 2 MΩ Capacitance from 2 pf to 1000 uF Inductance up to 1 H Sampling rate for oscilloscope function – 400 ksps Features – […]
TTGO T-Motion USB adapter offers LoRa and GPS for under $30
USB adapters are one of the easiest ways to add new features to existing hardware, and if you’d like to add LoRa connectivity and GPS tracking to any device or board with a USB board TTGO T-Motion USB adapter offers just that. Manufactured by LilyGO, the USB dongle is based on AcSiP S76G system-in-package that integrates an STM32 MCU with a Semtech SX1276 LoRa transceiver and GPS into a single. The GPS antenna is placed on the board inside the enclosure, while the external LoRa antenna is connected through an SMA connector. TTGO T-motion specifications: SiP – AcSiP S76G system-in-package with STMicro STM32L073x Arm Cortex M0+ MCU with up to 192 KB of Flash memory and 20 KB of RAM, Semtech SX1276 supporting global 868 MHz or 915 MHz ISM-Bands, Sony CXD5603GF GNSS receiver. Antenna Internal GPS antenna External LoRa antenna Host interface – USB 2.0 male port Misc – […]