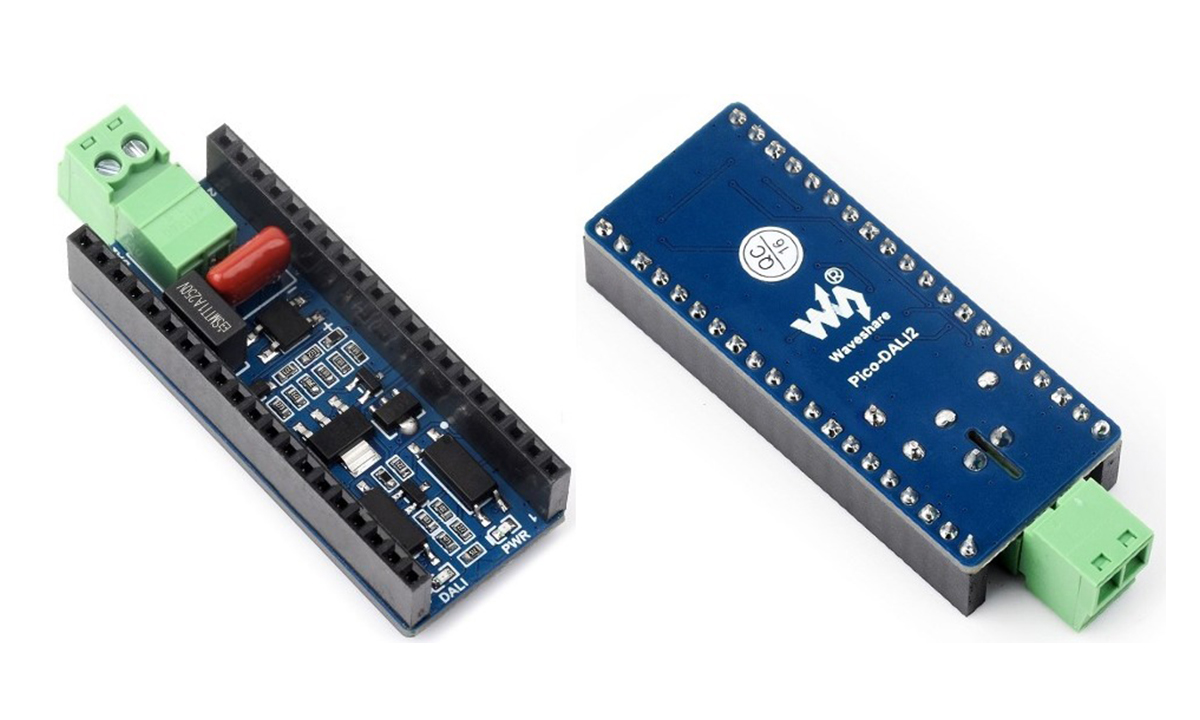
Waveshare has recently launched the Pico-DALI2 expansion module for ESP32-Pico series boards designed to enable DALI communication for customized control of multiple lighting groups. It is compatible with development boards such as the ESP32-C6-Pico and ESP32-S3-Pico and includes a DALI communication screw terminal for connecting external DALI devices. DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) is a standardized protocol used for lighting control in building automation systems. The latest version of the DALI2 protocol is better than the old one in that it offers enhanced interoperability, additional features like multi-master configurations, and better energy management capabilities. DALI2 devices can communicate bidirectionally, meaning controllers can send commands and also receive status feedback from lighting devices, allowing for more complex automation and diagnostics. We can get more information about DALI from Wikipedia. We have previously seen the uses of DALI in Texas Instruments MSPM0 Arm Cortex-M0+ microcontrollers as an interface and in Acme CM3-Home […]
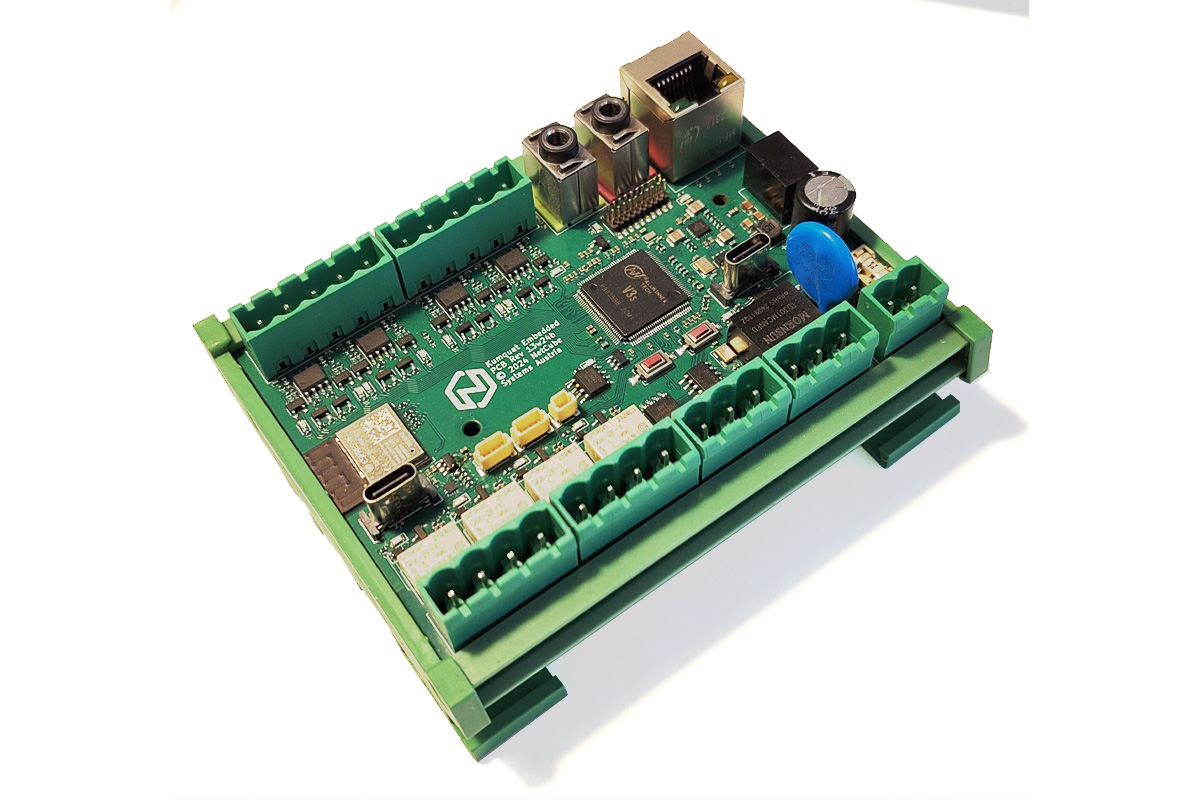
Kumquat – An Allwinner V3s embedded system board with isolated CAN, Ethernet and ESP32 for WiFi and Bluetooth
The Kumquat is an Allwinner V3s board designed for industrial automation, home automation, IoT projects, robotics, and embedded system development. The Allwinner V3s features ARM Cortex-A7 cores with 64MB DDR2 RAM and 8MB SPI flash storage. Connectivity options include Ethernet, USB-C, isolated CAN-FD, and WiFi/Bluetooth via an ESP32 module. Additionally, it has eight auto-detecting 12/24V IOs, four relays for controlling external devices, and a real-time clock with battery backup. The Kumquat runs on Buildroot Linux with a mainline kernel and can be programmed with various programming languages making it a great alternative to traditional PLCs. Kumquat board specification SoC – Allwinner V3s CPU – ARM Cortex-A7 @ up to 1.2 GHz Memory – Integrated 64MB DDR2 DRAM clocked at 400MHz @ 1.5 V Video engine Storage 8MB SPI Flash for bootloader and user code I2C EEPROM for MAC addresses and user data SDIO Connector for eMMC or SD card Connectivity […]
D-Robotics RDK X3 Development Board features Sunrise X3 quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 SoC with a 5TOPS “Bernoulli” BPU
The D-Robotics RDK X3 development board is designed for edge AI applications and features a Sunrise X3 quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 processor running at 1.5GHz with a dual-core BPU (Brain Processing Unit) with 5 TOPS of edge inference capability. The board includes a 40-pin GPIO interface, ensuring compatibility with Raspberry Pi 4B accessories for versatile project development. The RDK X3 offers 2GB or 4GB of LPDDR4 RAM and includes a MicroSD card slot for storage expansion. Designed for real-time applications like robot control and intelligent monitoring, its 5 TOPS inference capability makes it ideal for computer vision workloads such as object detection, body segmentation, scene parsing, etc… Previously, we covered the Horizon X3 AI development board, which uses the same Horizon Robotics Sunrise X3 processor. We’ve also written about several other edge AI development boards, including the Synaptics Astra Platform SL1680, SagireEdge AI 600, and MYiR Tech’s MYC-LR3568. Feel free to […]
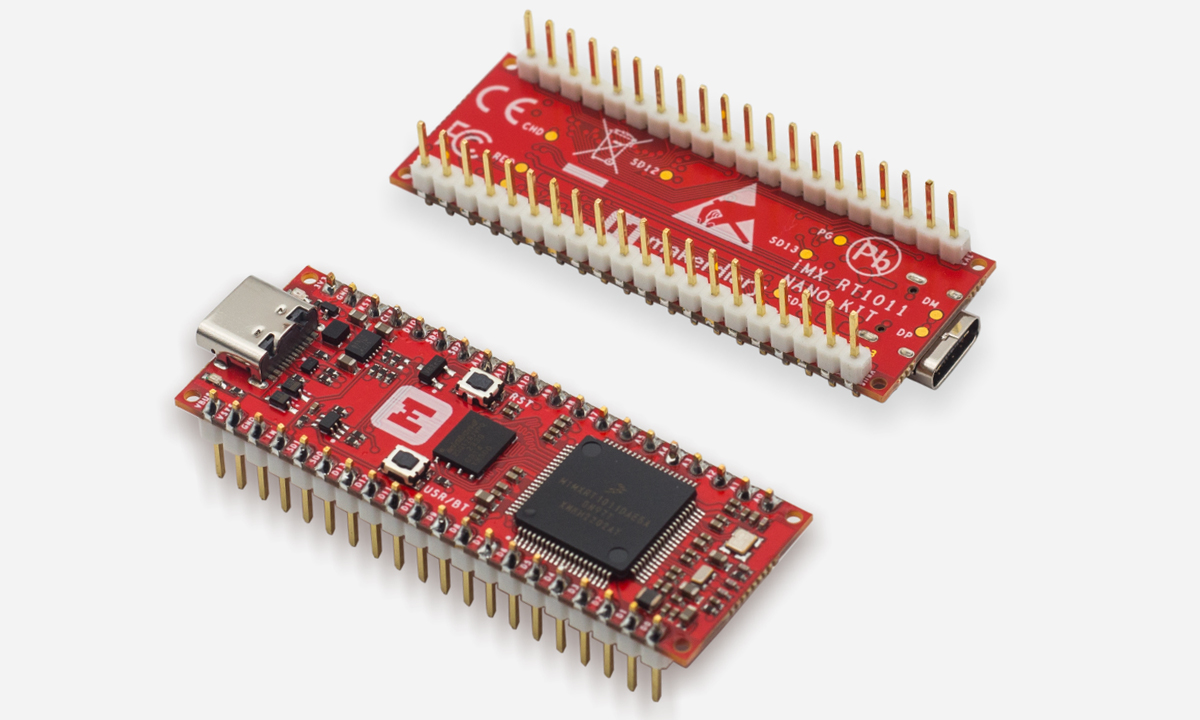
$15 Makerdiary iMX RT1011 Nano Kit runs Zephyr RTOS on 500 MHz NXP iMX RT1011 crossover MCU
Makerdiary’s iMX RT1011 Nano Kit is a prototyping board featuring the NXP iMX RT1011 Cortex-M7 Crossover MCU running Zephyr RTOS. It offers 128 KB of on-chip RAM, configurable as TCM or general-purpose memory, and supports high-speed USB, UART, SPI, I2C, SAI, PWM, GPIO, and ADC, making it suitable for a variety of embedded applications. The board also includes a 128 Mbit external QSPI flash with XIP support, flexible power management, a programmable LED and Button, and a USB-C connector. It features a dual-row 40-pin layout (DIP/SMT) with up to 33 multi-function GPIO pins, 15 of which can be used as ADC inputs, along with a Serial Wire Debug (SWD) port. Optional pre-soldered headers are available for added flexibility. We previously covered other iMX RT1011-based development boards, such as the Olimex RT1010-Py running MicroPython and Adafruit Metro M7 with CircuitPython firmware. Be sure to check them out if you’re interested. Makerdiary’s […]
Google Pigweed SDK now supports Raspberry Pi RP2350 microcontroller
Google Pigweed, a collection of open-source libraries for embedded software development, now supports the Raspberry Pi RP2350 MCU and comes as a software development kit (Google Pigweed SDK). These libraries, also called modules, are building blocks that make embedded software development faster and more reliable. It targets tiny 32-bit microcontrollers such as STMicro STM32L452, Nordic Semi nRF52832, and the Raspberry Pi Pico line of microcontrollers. The library components have shipped in Google Pixels, Nest thermostats, robots, satellites, and drones. On August 8, the Pigweed project was released as a software development kit (SDK) in developer preview with official support for Raspberry Pi RP2350 and the associated Pico 2 development board. The new release uses the Bazel build system – a feature upstreamed into the Pico SDK by the Google Pigweed team – and a complete, open-source Clang/LLVM toolchain. The Google Pigweed SDK includes sample code, modules, and a comprehensive tutorial […]
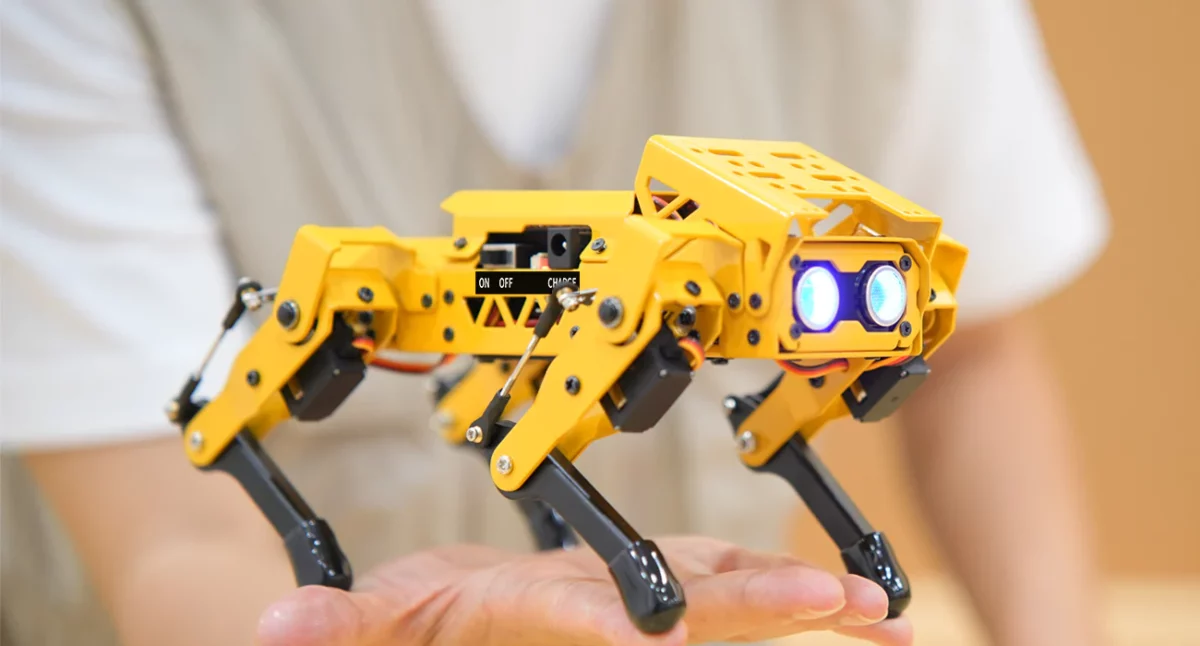
MechDog AI Robot Dog features ESP32-S3 controller, supports Scratch, Python, and Arduino programming
Hiwonder’s MechDog is a compact AI robot dog powered by an ESP32-S3 controller that drives eight high-speed coreless servos. It features built-in inverse kinematics for precise and agile movements and has ports for various I2C sensors such as ultrasonic and IMU sensors. The robot is equipped with a durable aluminum alloy frame and a removable 7.4V 1,500mAh lithium battery for power. MechDog integrates with the ESP32-S3 AI vision module, supporting dual-mode network communication either AP Hotspot Direct Connection Mode or STA LAN Mode so that users can access a designated URL webpage via an app or PC for real-time monitoring using a high-definition camera. Also, this robot dog supports various sensor modules, including a touch sensor, light sensor, dot matrix display, and programmable MP3 module, allowing for secondary development and expansion, offering extensive creative possibilities. Previously, we wrote about the Waveshare UGV AI Rover, which features a 2mm thick aluminum […]
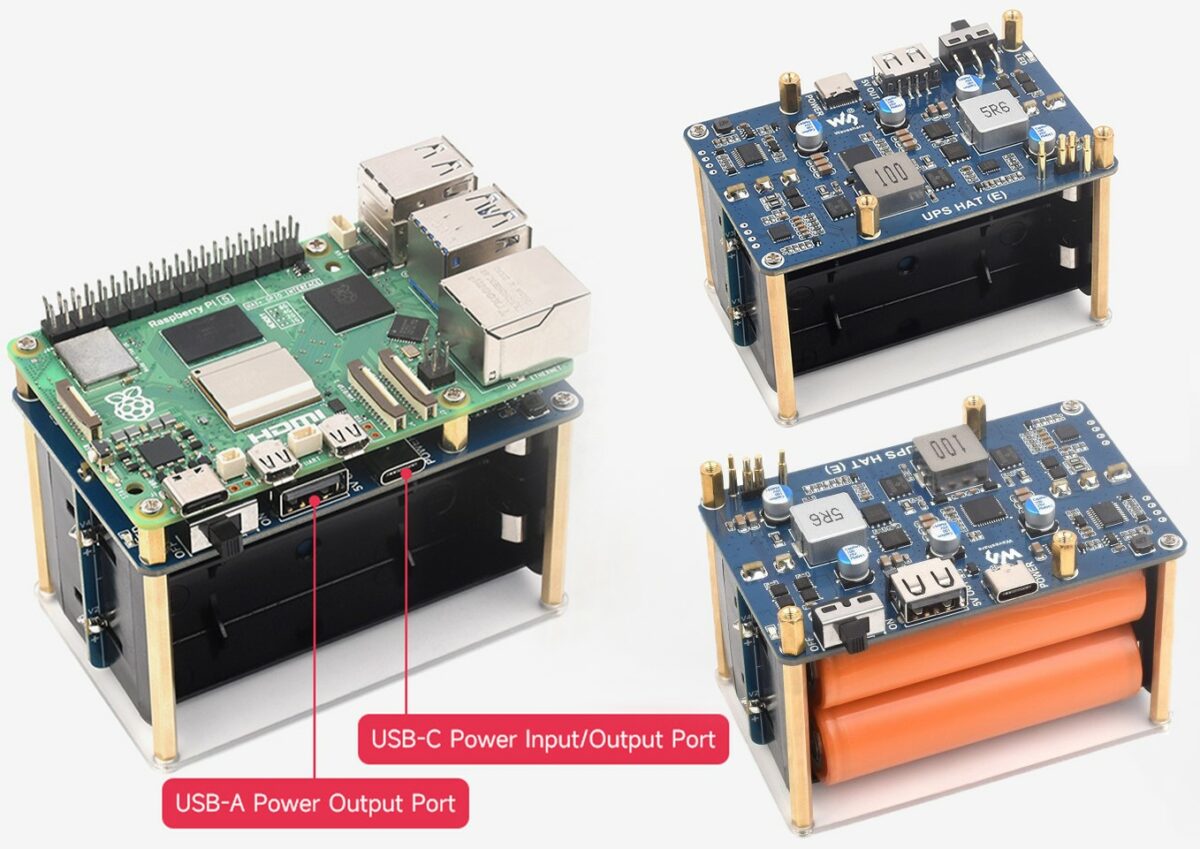
Waveshare UPS HAT (E) for Raspberry Pi 5/4/3B+ takes four 21700 Lithium batteries, supports USB PD 3.0
The Waveshare UPS HAT (E) is a UPS expansion board for Raspberry Pi 5/4B/3B+ that supports four 21700 Lithium batteries and includes a battery fuel gauge IC for monitoring voltage, current, and capacity. The USB Type-C port is compliant with the PD 3.0 standard and allows for 40W fast bi-directional charging, and a high-power buck chip provides a 5V/6A output. Additionally, it supports I2C for real-time status updates. Previously, we wrote about the wider SupTronics Raspberry Pi 5 UPS HAT, which supports four 18650 batteries and delivers up to 5V with a higher current output of 5A. This HAT has no Type-C support and uses a DC jack and XH2.54 connector for 6V-18V input. Feel free to check it out if you’re interested in this product. Waveshare UPS HAT (E) specifications: Compatibility – Raspberry Pi 5 / 4B / 3B+ USB Interfaces USB Type-C Input/Output – Supports multiple voltage levels […]
Adeept Robot HAT for Raspberry Pi is designed for DIY projects and educational needs
The Adeept Robot HAT V3.0 is a motor and sensor driver HAT that supports Raspberry Pi 5, Pi 4, and Pi 3 models. The board features a bunch of headers that give access to sensor and motor controllers including sixteen servo motor ports, a three-channel line tracking sensor, an ultrasonic sensor, IR receivers, WS2812 RGB LEDs, and more. Additionally, the board features an integrated 8.4V battery charger with a Type-C port for charging. All these features make it easy to build DIY robotics and smart car projects with this HAT. Previously we have written about similar educational robot kits including the Arduino Alvik educational robot, the XGO-Rider self-balancing robot, the Waveshare UGV Rover, SunFounder GalaxyRVR, and much more. Feel free to check that out if you are interested in those topics. Adeept Robot HAT V3.0 specifications HAT Name – Adeept Robot HAT V3.0 Host controller (one or the other) Raspberry Pi […]