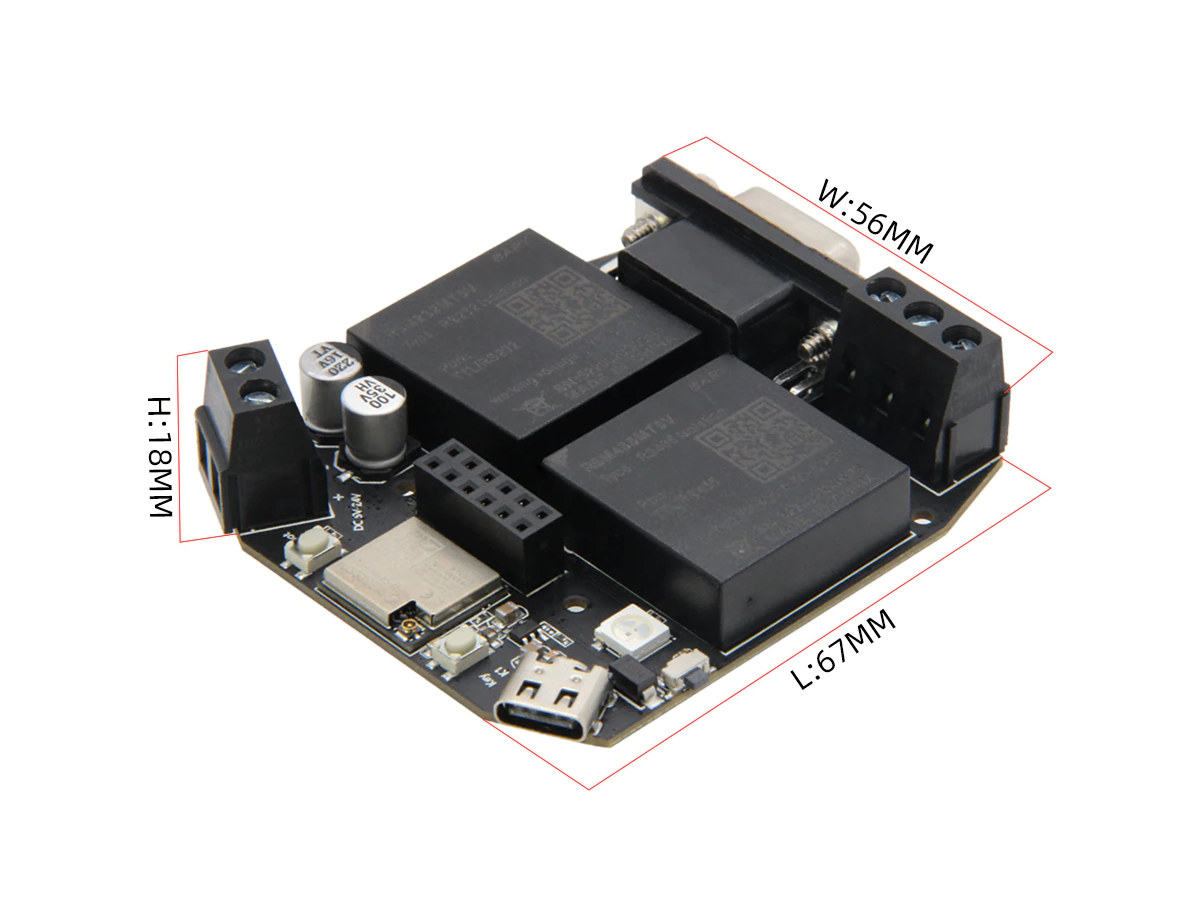
LILYGO T-RSC3 is a relatively compact ESP32-C3 board with WiFi 4 and Bluetooth LE 5.0 connectivity, support for RS232 and RS485 communication protocols through a DB9 connector and a terminal connector respectively, and a wide 5V to 24V DC power input. LILYGO had already made an ESP32 board with CAN Bus and RS485 interfaces called the T-CAN485, but without any isolation. The new T-RSC3 offers both RS232 and RS485 interfaces, but no CAN Bus, protected by isolated transceiver modules that should make it safer to use in industrial environments. LILYGO T-RSC3 board specifications: Wireless module – Espressif Systems ESP32-C3-MINI-1U module with ESP32-C3 RISC-V microcontroller @ 160 MHz with 400 KB SRAM, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4, Bluetooth 5.0 LE & Mesh, 4MB flash, and a u.FL antenna connector Industrial control interfaces RS232 via DB9 connector, RSM232MT5V isolated transceiver with 3000V isolation, 4.75~5.25V input, 5V/50mA output, baud rate from 1200 to 256,000 […]
Espressif ESP32-P4 – A 400 MHz general-purpose dual-core RISC-V microcontroller
Espressif ESP32-P4 is a general-purpose dual-core RISC-V microcontroller clocked at up to 400 MHz with AI instructions extension, numerous I/Os, and security features. It also happens to be the first microcontroller from Espressif Systems without wireless connectivity, and as such, it should probably be seen as an alternative to STM32F7/H7 or NXP i.RT Arm Cortex-M7 microcontrollers/crossover processors, and likely offered at a significantly lower cost. It should also offer lower power consumption than other ESP32 chips thanks in part to a third RISC-V core clocked at 40 MHz that can keep the system running while the other two high-performance cores are down. ESP32-P4 key features and specifications: MCU subsystems Dual-core RISC-V HP (High-performance) CPU @ up to 400 MHz with AI instructions extension and single-precision FPU, 768KB of on-chip SRAM Single-RISC-V LP (Low-power) MCU core @ up to 40 MHz with 8KB of zero-wait TCM RAM Memory & Storage I/F […]
Year 2022 in review – Top 10 posts and statistics
It’s the last day of the year and the time to look at some of the highlights of 2022, some traffic statistics from CNX Software website, and speculate on what 2023 may bring us. The semiconductors shortage continued in 2022, but things are looking brighter in 2023 with the full reopening of the world mixed with forecasts of difficult economic times that should keep the demand/supply equation in check. On the Arm processor front the biggest news of the year, at least in this corner of the Internet, was the launch of the Rockchip RK3588 octa-core Cortex-A76/A55 processor together with interesting single board computers that we’ll discuss below. Announced last year, the Amlogic A311D2 octa-core Cortex-A73/A53 was finally made available in a few SBC’s, and we finally got some news about the Amlogic S928X Cortex-A76/A55 SoC showcased in 8K TV boxes, but we have yet to see it in action. […]
Pinecil V2 Bluetooth LE soldering iron gets a web interface
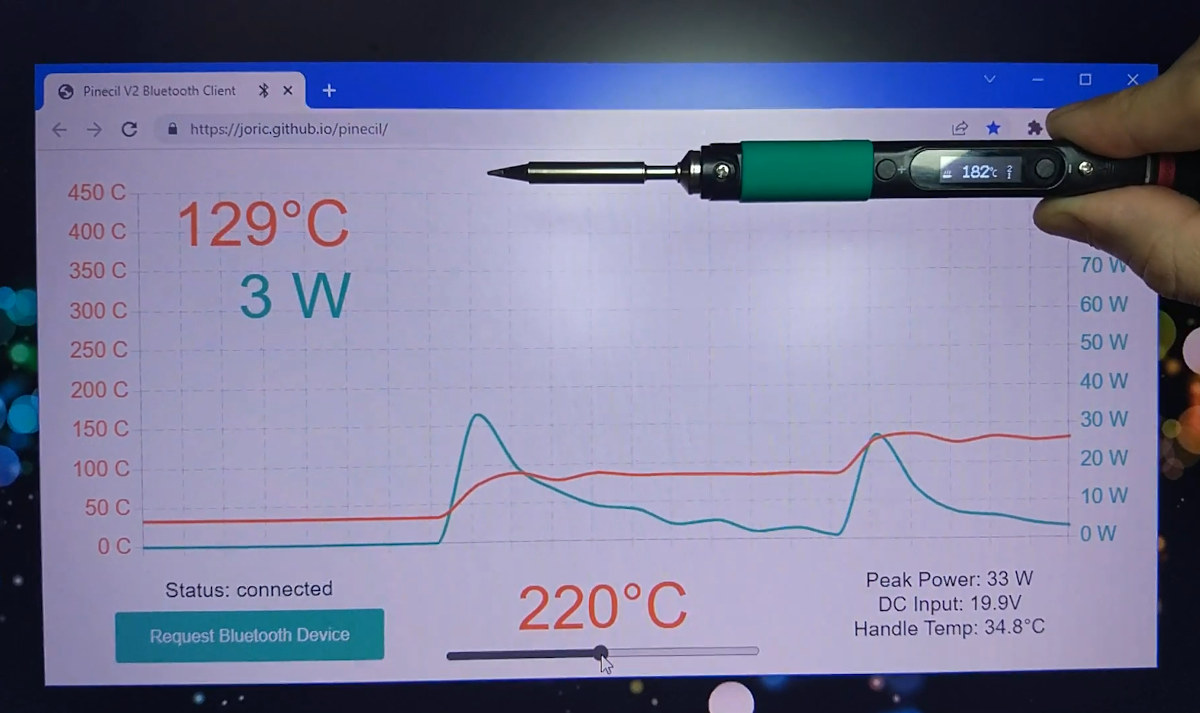
It’s now possible to make use of the Pinecil V2 soldering iron‘s Bluetooth LE connectivity through a web-based interface used to monitor and/or set the temperature and power of the RISC-V soldering iron. When the Pinecil V2 soldering iron was launched with a Bouffalo Lab BL706 RISC-V Bluetooth microcontroller last summer, we were told there were main potential cases to make use of the Bluetooth LE features: OTA firmware upgrade and remote telemetry and control. The latter is now being taken care of by Joric who has written a web application to visualize telemetry data and even control the temperature of the soldering iron. To be able to use the Bluetooth features, you’ll first need to install the latest Pinecil V2 firmware with blisp flashing utility before going to https://joric.github.io/pinecil to pair your soldering iron as explained in the wiki. Note the implementation relies on the Web Bluetooth API which […]
Sipeed LM4A – T-Head TH1520 RISC-V module to power Raspberry Pi 4 competitor and cluster board
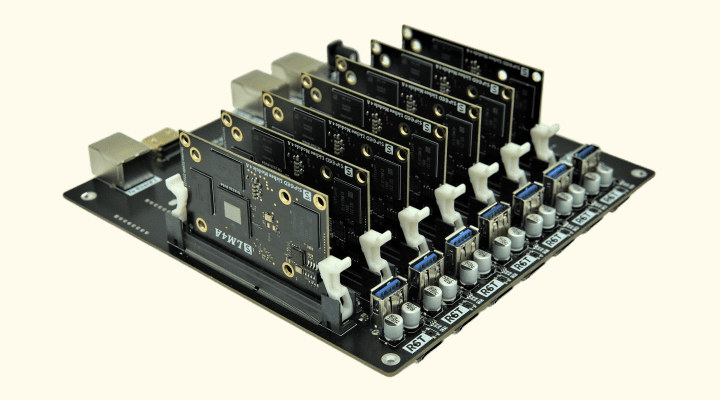
Sipeed LM4A is a quad-core RISC-V system-on-module based on the T-Head TH1520 SoC found in the ROMA laptop and destinated to be found in a Raspberry Pi SBC competitor as well as a cluster board. The LM4A, which stands for Lichee Module 4 Model A, comes with 4GB to 16GB RAM, and up to 64GB flash, and connects to the carrier board through a 260-pin SO-DIMM connector. The TH1520 is one of the rare RISC-V SoCs with a 3D GPU, and the SBC based on LM4A has been shown to outperform the Raspberry Pi 4 in benchmarks as we’ll see below. Sipeed LM4A specifications: SoC – Alibaba T-Head TH1520 quad-core RISC-V Xuantie C910 (RV64GCV) processor @ 2.5 GHz, Xuantie C906 audio DSP @ 800 MHz, low power Xuantie E902 core, 50 GFLOPS Imagination 3D GPU, and 4 TOPS NPU System Memory – 4GB, 8GB, or 16GB RAM Storage – Optional […]
Linux 6.1 LTS release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V and MIPS architectures
Linus Torvalds announced the release of Linux 6.1, likely to be an LTS kernel, last Sunday: So here we are, a week late, but last week was nice and slow, and I’m much happier about the state of 6.1 than I was a couple of weeks ago when things didn’t seem to be slowing down. Of course, that means that now we have the merge window from hell, just before the holidays, with me having some pre-holiday travel coming up too. So while delaying things for a week was the right thing to do, it does make the timing for the 6.2 merge window awkward. That said, I’m happy to report that people seem to have taken that to heart, and I already have two dozen pull requests pending for tomorrow in my inbox. And hopefully I’ll get another batch overnight, so that I can try to really get as […]
Armbian 22.11 released with 64-bit RISC-V UEFI, ultra minimal images support
Armbian 22.11 has just been released with three new SBCs, support for 64-bit RISC-V UEFI, a new ultra-minimal image optimized for software development, and various improvements. Armbian was born as a framework to build better OS images, usually Debian or Ubuntu, for Arm-based single board computers from Orange Pi, Hardkernel (ODROID), FriendlyElec, Banana Pi, and others, but now with the release of Armbian 22.11, support for the RISC-V architecture has started since the system can now generate 64-bit RISC-V UEFI images. Some other highlights of Armbian 22.11 include: Added support for Banana Pi BPI-M5 (Amlogic S905X3), ODROID-M1 (Rockchip RK3568), and Rock Pi 4C Plus (Rockchip RK3399-T) Enabled community images with a weekly release cycle Added ultra minimal images optimized for software deployment Improved support for the Rock Pi S (Rockchip RK3308) Kernel upgrade is frozen by default to improve stability I could not find details about the new “Minimal” images, […]
$6 Pine64 Ox64 SBC features BL808 64-bit/32-bit RISC-V multi-protocol WiSoC with 64MB RAM
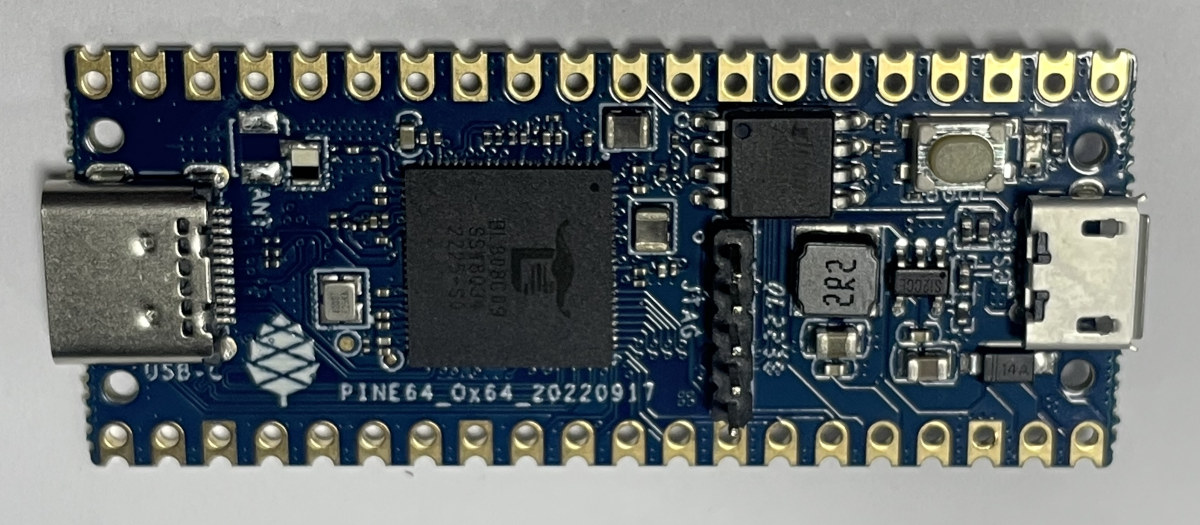
Pine64 Ox64 is a single board computer powered by Bouffalo Lab BL808 dual-core 64-bit/32-bit RISC-V processor with up to 64MB embedded RAM, multiple radios for WiFi 4, Bluetooth 5.0, and 802.15.4 (Zigbee), as well as an AI accelerator. The board also features up to 16MB XSPI NOR flash, a MicroSD card socket, a USB 2.0 OTG port with support for a 2-lane MIPI CSI camera module, and two 20-pin GPIO headers for expansion. It measures just 51 x 21mm, or in other words, is about the size of a Raspberry Pi Pico W. Pine64 Ox64 specifications: SoC – Bouffalo Lab BL808 with: CPU Alibaba T-head C906 64-bit RISC-V core @ 480MHz Alibaba T-head E907 32-bit RISC-V core @ 320MHz Alibaba T-head E902 32-bit RISC-V @ 150MHz Memory – 728KB SRAM, 64MB embedded DRAM AI accelerator – NPU BLAI-100 (Bouffalo Lab AI engine) for video/audio detection/recognition Wireless 2.4 GHz 802.11 b/g/n […]