Last year, the SD association introduced Class A2 application performance class for SD cards designed for optimal performance when running an OS or programs from the cards thanks to fast read and write random I/O, specifically 400O IOPS minimum for read operations, 2000 IOPS minimum for write operations. Since Class A2 was announced about 18 months ago, I simply assumed Class A2 SD cards were already available, but to my surprise I was wrong, as according to AnandTech, Sandisk Extreme micro SD cards are the first of the kind soon-to-be available commercially. Sandisk Extreme micro SD card specification: Capacity – 64GB, 128GB, 256GB, or 400GB Interface – UHS-I Sequential Speeds – Read: Up to 160 MB/s; Write: Up to 90MB/s (128GB to 400GB), up to 70MB/s (64GB) Random Speeds – Read: >= 4000 IOPS; Write: >=2000 IOPS SDA Labels – C10, U3, V30, A2 Temperature Range – -25 to 80°C […]
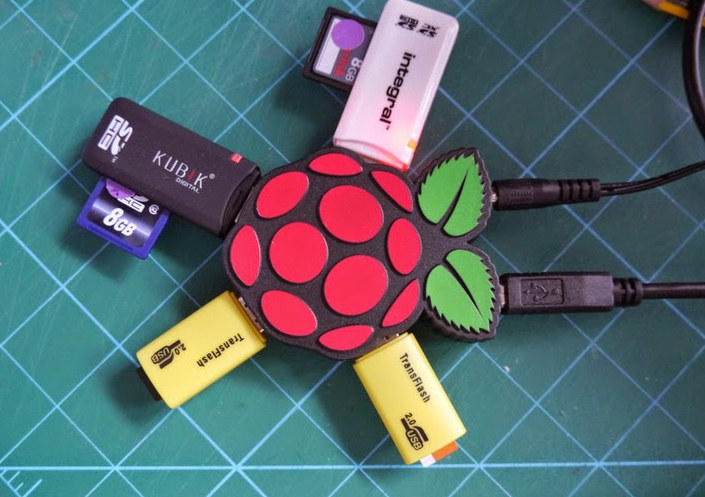
How to Make a Low Cost DIY SD Card Duplicator
If you have to duplicate many SD cards for example to boot Raspbian on multiple Raspberry Pi board, one option is buy one of those SD card duplicators, but the problem is that they are not really cheap, for example the Systor 1-to-7 cards model sells for $540. Bob Brown, a retired senior lecturer, is now teaching K-12 students how to get started with Raspberry Pi boards, and must prepare bootable SD cards for his class. In order to save time, a duplicator would have been nice, but the price is too high, so instead he went with a DIY solution. You’ll first need some hardware, including a powered USB hub with the number of cards you want to duplicate, and corresponding SD card reader, and a larger micro SD card to hold Raspbian and/or other operating systems (optional, only for Raspberry Pi based duplicator). Mr. Brown made a 10-port […]
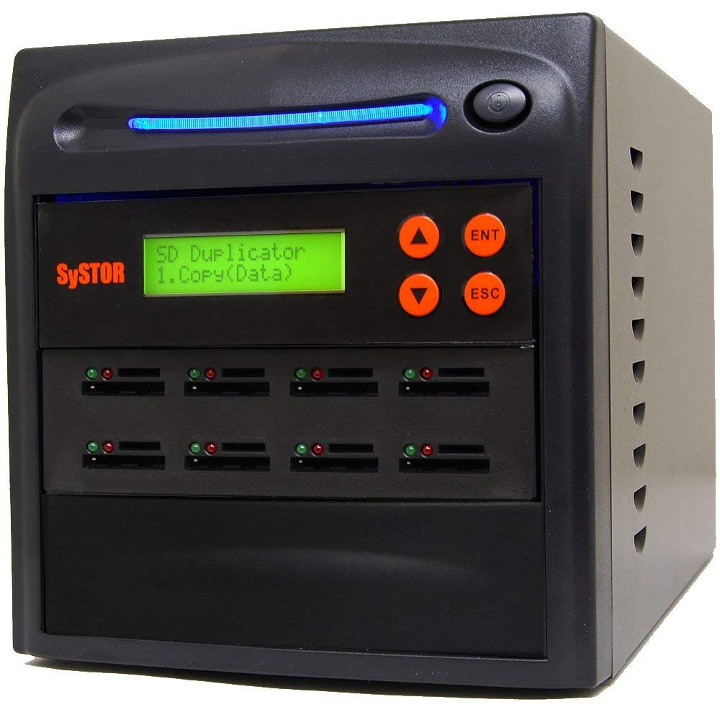
SySTOR (Micro) SD Card Duplicators Can Handle Up to 200 SD Cards
So this week-end, I started to play with ROC-RK3328-CC (Renegade) board that I received from T-Chip / Firefly-Team and as always, I used Etcher to flash the firmware images to micro SD cards. Once flashing is complete, you’ll get a screen mentioning Etcher Pro, a standalone hardware solution allowing to duplicate the content of one micro SD card to 16 other cards. That’s very interesting if you need to duplicate many cards for a project, but the only problem is that the device is not available just yet. So I thought such equipment must already exist and indeed, a company called SySTOR offers such systems able to duplicate one (micro) SD card to up to 199 other (micro) SD cards. Some of the specifications & key features of the system: Processor – Multi-core processor System Memory – 256 MB DDR3 Capacity – Various models from 4 to 200 micro SD […]
SD Express Adds PCIe and NVMe Interfaces to SD Cards for up to 985 MB/s Transfer Rates
SD cards are known for the convenience, portability, and relatively cheap prices, but not so much for their performance which can be pretty poor especially for the cheaper and lower capacity models, and when fast random I/O is needed. The SD Association have been working on helping customer buy performant cards for their needs with – for instance – the app performance class introduced in SD 5.1 specification, which defines minimum random read and write speeds in Class A1 and Class A2 micro SD cards. However, the association has gone a step further with SD Express found in SD specification 7.0 that adds PCIe and NVMe interfaces to the legacy SD card interface. SD Express will enable theoretical data transfer rate up to 985 MB/s via PCIe 3.0, as well as advanced memory access mechanisms such as Bus Mastering, Multi Queue (without locking mechanism) and Host Memory Buffer thanks to […]
Linux 4.16 Release – Main Changes, Arm and MIPS Architectures
Linus Torvalds has just released Linux 4.16: So the take from final week of the 4.16 release looks a lot like rc7, in that about half of it is networking. If it wasn’t for that, it would all be very small and calm. We had a number of fixes and cleanups elsewhere, but none of it made me go “uhhuh, better let this soak for another week”. And davem didn’t think the networking was a reason to delay the release, so I’m not. End result: 4.16 is out, and the merge window for 4.17 is open and I’ll start doing pull requests tomorrow. Outside of networking, most of the last week was various arch fixlets (powerpc, arm, x86, arm64), some driver fixes (mainly scsi and rdma) and misc other noise (documentation, vm, perf). The appended shortlog gives an overview of the details (again, this is only the small stuff in […]
SD Association Introduces Class A2 Application Performance Class, and UHS-III Standard Supporting Up to 624 MB/s
Users of development boards booting from (micro) SD cards have often missed random I/O performance information to determine whether the device would performance well to run an operating system, but now that Google has implemented “adoptable storage” to let consumer run app from their micro SD cards, it has become an important differentiating factor for manufacturers, and the SD association announced A1 App performance class with minimum random I/O read/write performance and at least 10MB/s sequential write speed last year. The SD association has now unveiled Class A2 with better I/O performance with minimum requirements of 4000 IOPS for random reads, and 2000 IOPS for random writes, with the same 10 MB/s minimum sequential write speed. That means the application performance table now looks as shown below. Note that Class A2 is not available right now, and test requirements will be explained in SD 6.1 part 1 physical specification to […]
SD Specifications 5.1 to Introduce App Performance Class (for Random I/O) & Logo
SD cards used to store media data only, for example photos and videos in your camera or smartphone, but with the introduction of “Adoptable Storage” in Android 6.0 you can now run apps directly on a micro SD card, and many development boards rely on (micro) SD card to run the full operating system. The difference is important, as with media storage, the raw sequential read and write speeds are the most important, as large files are created and accessed, but for apps and operating systems many small read and write operations such as databases access take place on the card, so random IO performance becomes much more important. So far, the SD card specifications would only report sequential performance with different classes, and for example for are often recommended to use “Class 10” SD cards on Raspberry Pi, which does not clearly indicates the random IO performance. SD Specifications […]
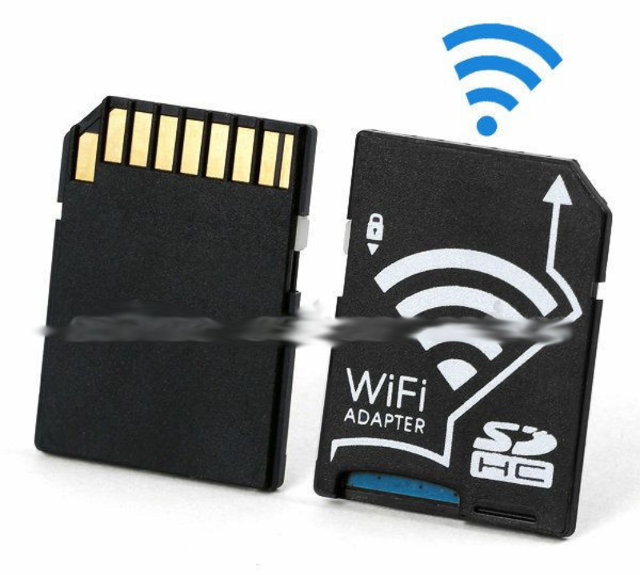
Wi-Fi SD Card Adapter for micro SD Cards Sells for $15 and Up
Wi-Fi SD cards are mostly used with camera in order to wirelessly transfer photos or/and videos to your computer or mobile device without having to take out the card or transfer them via a micro USB cable. I first discovered this type of card with Toshiba FlashAir in 2011, but now EyeFi seems to be the most popular brand, and comes in different sizes with the 8GB Wi-FI SD card selling for $44 on Amazon US. There are cheaper alternatives with some Wi-Fi SD card adapters accepting micro SD card selling for about $15 and up on Aliexpress or Buyincoins, and DX calls it CY EP-027, but sells it for $23. It does not come with storage but since a 8GB class 10 SD card now costs about $8, it’s still nearly 50% cheaper compared to the 8GB EyeFi SD card. Some features of the card: Max micro SD card […]