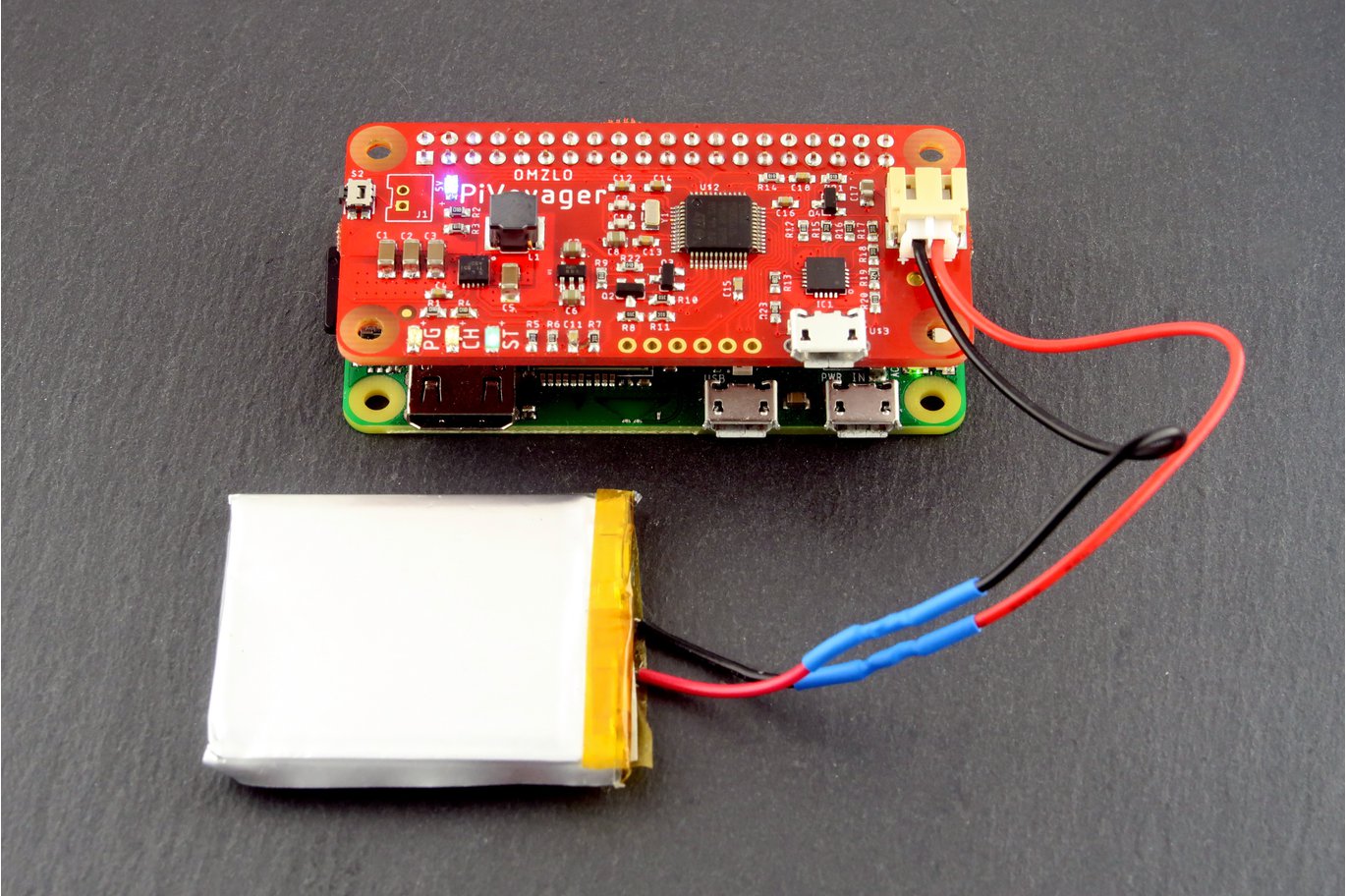
The Raspberry Pi is a powerful SBC (Single Board Computer), and aside from being used for everyday computing stuff, the Raspberry Pi can be embedded as the brain of various projects. Using the Raspberry Pi for standalone projects do create some concerns about power. How do I power the Pi? Should I get a power bank? Or maybe I need a longer wired connector. If powering your Raspberry Pi based project has always being a concern to you, then you don’t have to worry about it again with the introduction of the PiVoyager. The PiVoyager is an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) for the Raspberry Pi specially designed to work with standard Li-Ion or LiPo batteries. It is shaped in the form a Pi Zero HaT making it fully compatible with PiZero form factor, but nevertheless, it will still work with any Raspberry-PI having the conventional 40-pin header found in the Pi […]
Somu Tiny Open Source FIDO2 Security Key Enables Passwordless Login & Two-factor Authentication (Crowdfunding)
Tomu is a tiny, open source USB connector-sized board powered by a Silicon Labs Happy Gecko Cortex-M0+ MCU that adds two keys to your computer and can work as a Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) token to support two-factor authentication (2FA). But the board is not secure enough for FIDO2 support, and Tomu’s developer worked on a secure USB key called Solokey, and shrank it to Tomu form factor. Meet Somu open-source and secure key with FIDO2 support for compatibility with your Google, Twitter, and GitHub accounts for two-factor authentication, or your Microsoft account passwordless login. Somu hardware specifications: Secure MCU – STMicro STM32L432KC Arm Cortex-M4 microcontroller with TRNG, security isolation for keys, two levels of locked flash Crypto Algorithms – ECC P256 (as per FIDO2 standard) Supported Protocols – FIDO2, U2F Host Interface – USB type-A port Misc – Two touch buttons ( in FIDO2 firmware the two buttons behave […]
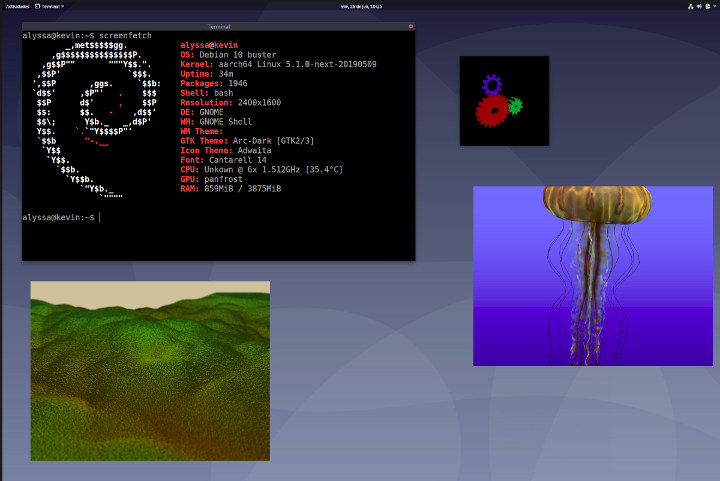
Rock Pi 4 SBC Runs GNOME & KDE Plasma using Panfrost Open Source GPU Driver & Wayland
One of the highlights of Linux 5.2 release was support for two new Arm Mali GPU open-source drivers, namely Lima for Mali-4xx GPU, and Panfrost for the Midgard Mali-T6xx/7xx/8xx series, and the more recent Bifrost Mali-Gxx GPUs. Collabora worked on the release and was donated a few Rock Pi 4 boards from Radxa directly to work on the project. For those who are not familiar, Rock Pi 4 board is powered by a Rockchip RK3399 processor with a Mali-T860MP4 GPU that is supported by Panfrost open source GPU driver. The company managed to have Debian 10 Buster running on Rock Pi 4 using 3D graphics acceleration thanks to Panfrost drivers on both GNOME and KDE Plasma desktop environment, as well as Weston Wayland compositer. The good news is that you can build Rock Pi 4 images by yourself using Debos with the following commands:
|
1 2 3 |
git clone https://gitlab.collabora.com/rockpi/rockpi4 cd rockpi4 docker run --rm --interactive --tty --device /dev/kvm --workdir /recipes --mount "type=bind,source=$(pwd),destination=/recipes" --security-opt label=disable godebos/debos --scratchsize=8G rockpi4.yml |
Alternatively, you could directly download […]
easySwitchBox is a LoRa Wall Switch Powered by Coin Cell Batteries and Arduino (Crowdfunding)
easySwitchBox is a simple actuator that does one basic thing – To send an on/off signals that can be used to control anything wirelessly. Whatever you intend on doing with the signal sent is left to you. easySwitchBox is the brainchild of easySensors, the Belarus based creators of DIY Arduino focused hardware products. easySwtichBox combines an Arduino based chip and a LoRa radio to be able to send a signal for long-range distances. On the surface, easySwitchBox looks like another wall switch you have seen around, but there is more to it. Powered by the famous Atmega 328P microcontroller, easySwitchBox is more than a wall switch, and you can reprogram it to be an intelligent one indeed or anything else you want. The power supply comes from two attached coin cell battery, making it possible to move the device around and not be confined by location or space. easySwitchBox […]
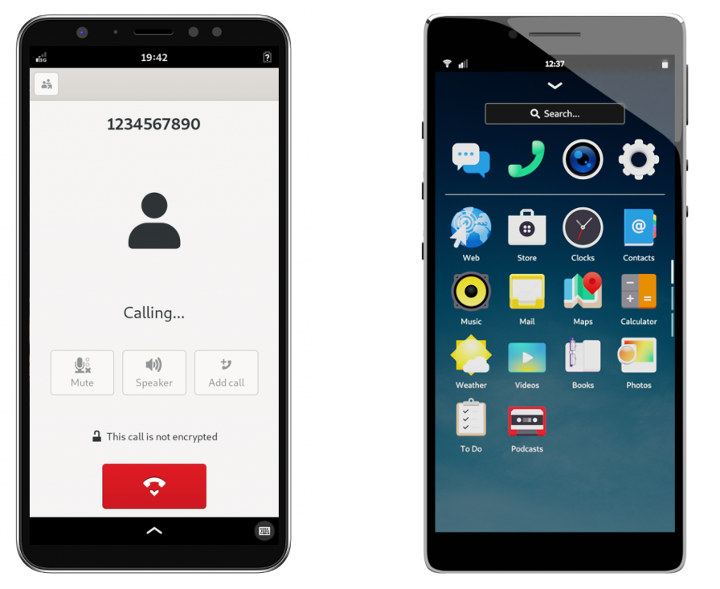
Librem 5 Linux Smartphone Specifications Finalized
If you were interested in purchasing, or more exactly pre-ordering, a privacy-focused, open source Linux smartphone with clearly defined hardware specifications, Purism Librem 5 was not quite for you. Until today that is, as while the company did not commit to exact specifications at the beginning of the project, Purism has now revealed the full specifications of Librem 5 Linux smartphone. Librem 5 specifications: SoC – NXP i.MX8M quad-core Cortex A53 @ up to 1.5GHz, Cortex-M4 real-time core, 3G GPU with OpenGL/ES 3.1, Vulkan, OpenCL 1.2 support System Memory – 3GB RAM Storage – 32GB eMMC flash, MicroSD slot up to 2 TB Display- 5.7″ IPS TFT touchscreen with 1440×720 resolution Connectivity Cellular Option 1 – Gemalto PLS8 3G/4G modem w/ single sim on replaceable M.2 card Option 2 – Broadmobi BM818 (made in China) nanoSIM tray Dual-band 802.11a/b/g/n WiFi 4, Bluetooth 4.0 GPS – Teseo LIV3F GNSS Cameras – […]
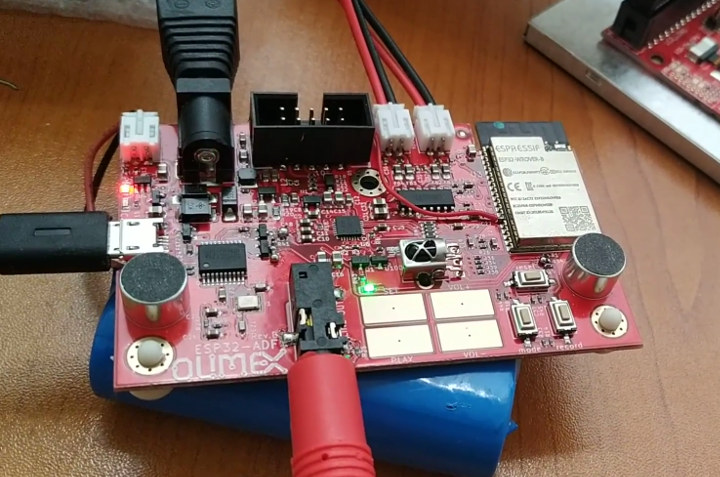
Olimex ESP32-ADF Board is Made for Smart Speakers, Internet Radios, VoIP Phones, and More
We’ve already covered several (smart) audio boards based on ESP32 WiSoC, including the Espressif’s own ESP32-LyraTD-MSC Audio Mic HDK, as well as third party boards such as TTGO TAudio or Seeed Studio ESP32-A1S all compatible with the company’s ESP-ADF (Audio Development Framework) compatible with Baidu DuerOS, Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa. Olimex ESP32-ADF adds another ESP32 audio option, and AFAIK the first one that is open source hardware, with two speakers, and a dual-microphone that enable projects such as Alexa smart speaker, internet radio receiver, or SiP VoIP phone. Olimex ESP32-ADF specifications: Wireless Module – ESP32-WROVER-B with 8MB PSRAM, 4MB Flash, WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 4.2 LE Audio Stereo microphones Stereo 2x3W speakers with amplifier Audio output jack Display – UEXT connector for optional 2.8″ LCD display USB – 1x micro USB port for power supply and programming Misc – IR receiver, 4x touch buttons, 3x tactile buttons Build-in programmer […]
Linux 5.2 Release – Main Changes, Arm, MIPS & RISC-V Architectures
Linus Torvalds announced the release of Linux 5.2 last Sunday: So I was somewhat pre-disposed towards making an rc8, simply because of my travels and being entirely off the internet for a few days last week, and with spotty internet for a few days before that [*]. But there really doesn’t seem to be any reason for another rc, since it’s been very quiet. Yes, I had a few pull requests since rc7, but they were all small, and I had many more that are for the upcoming merge window. Part of it may be due to the July 4th week, of course, but whatever – I’ll take the quiet week as a good sign. So despite a fairly late core revert, I don’t see any real reason for another week of rc, and so we have a v5.2 with the normal release timing. There’s no particular area that stands […]
Google Fuchsia Operating System Gets its own Developer Website
Google has been developing Fuchsia open source operating system based on Zircon kernel for several years. It’s still unclear what’s the end goal. Will it replace Android or/and Chrome OS, ditching the Linux kernel for Zircon in the process? We don’t know, and Google claims its an experimental endeavor. Only the future will tell. We’ve had access to the source code since 2016, but Google has now launched a dedicated developer website for Fuchsia: fuchsia.dev This is year 2019, and Google being a Western company it should not be surprising the first part of the documentation is a Code of Conduct, but there’s also plenty of technical documentation with a glossary, getting started guide, building instructions, an overview of the OS, code samples, and instructions to contribute either by testing or submitting changes to Gerrit. Fuchsia is strictly a 64-bit operating system at this stage with support for Arm64 and […]