[Update: I’ve been told the project is actually launched by SkyTraq. But later, after Indiegogo perks are shipped, they expect to have our customer NAVIN handle later orders and manufacturing, the non-engineering development side of things. Updated post accordingly]
Navin, a Taiwanese start-up specialized in location products, SkyTraq, a fabless semiconductor company, which develops GPS chipset for consumer navigation and tracking applications, has recently launched an Indiegogo campaign for NavSpark, their low cost GPS / GNSS board with a 32-bit LEON3 SPARC V8 MCU that can be programmed with the Arduino IDE. Two other models are available: NavSpark-BD for GPS/Beidou, and NavSpark-GL for GPS/GLONASS.
NavSpark
NavSpark specifications:
- GSP Receiver – SkyTraq Venus 822 LEON3 Sparc-V8 MCU @ 100MHz with IEEE-754 Compliant FPU, 1024KB Flash Memory, 212KB RAM.
- GPS – quad-GNSS engine capable of handling 34 GPS / GLONASS/ Beidou / Galileo signals in parallel
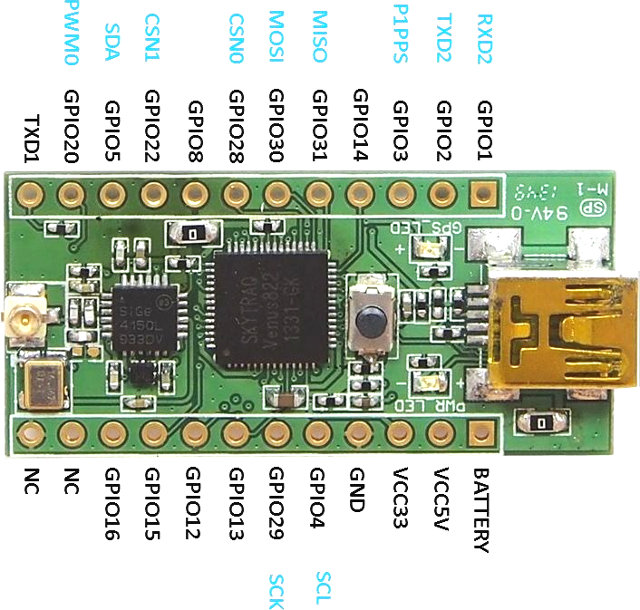
- I/Os – 1x full duplex asynchronous UART, 1x asynchronous UART transmit, 2x SPI with master/slave mode configurable, 1x I2C, 1x 24bit PWM, up to 17x digital I/O pins (shared)
- USB – mini USB port for power and programming
- Atomic clock – Synchronized P1PPS time reference with +/-10nsec accuracy
- Breadboard friendly
- Power consumption – ~80uA/MHz @ 3.3V
- Dimensions – 38mm x 18mm
NavSpark runs a version of Wiring, an open-source programming framework for microcontrollers, ported to SkyTraq receiver, and programming is done using sketches programmed with the Arduino IDE, in Windows only. Potential applications for the board include data loggers, outdoor GPS Clocks, time references, and more. The company claims NavSpark hardware design files (schematic, board design, and bill of materials) will be released and made available.
What are LEON CPU cores and SPARC-V8 architecture?
I’ve never heard about the LEON CPU core, nor SPARC-V8 architecture found in SkyTraq GPS receivers before. My friend Wikipedia told me that:
LEON is a 32-bit CPU microprocessor core, based on the SPARC-V8 RISC architecture and instruction set. It was originally designed by the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), part of the European Space Agency (ESA), and after that by Gaisler Research. It is described in synthesizable VHDL. LEON has a dual license model: An LGPL/GPL FLOSS license that can be used without licensing fee, or a proprietary license that can be purchased for integration in a proprietary product. The core is configurable through VHDL generics, and is used in system-on-a-chip (SOC) designs both in research and commercial settings.
and
SPARC (from “scalable processor architecture”) is a RISC instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems and introduced in mid-1987.
….
In SPARC Version 8, the floating point register file has 16 double precision registers. Each of them can be used as two single precision registers, providing a total of 32 single precision registers. An odd-even number pair of double precision registers can be used as a quad precision register, thus allowing 8 quad precision registers.
…
The endianness of the 32-bit SPARC V8 architecture is purely big-endian
You can find the 295-page SPARC Architecture Manual Version 8 for further details.
So if you want to make your own (open source) LEON3 based SoC / MCU, or cheaper, try it with a Xilinx FPGA, you can find the source and documentation on Gaisler LEON/GRLIB Download page.
Status of NavSpark, and Pledges
Back to NavSpark. The board is basically a shrunk down version of SkyTraq Venus 822 development board, and appears to be completed. On the software side, the company still has to customize the Arduino IDE to work with the Sparc-V8 compiler and Venus 822 hardware. It should be completed by the end of January 2014.
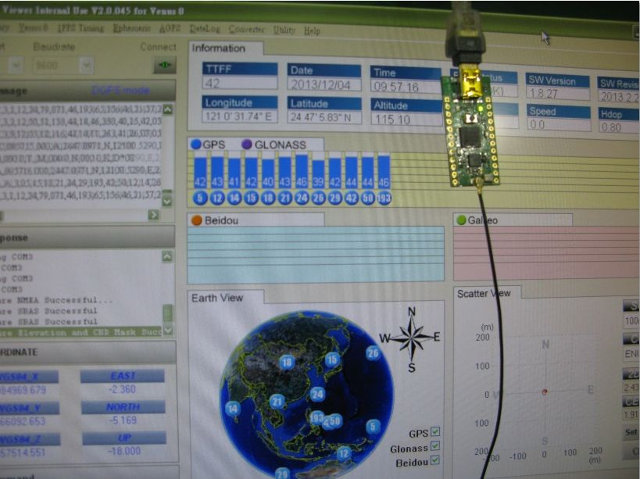
A pledge of $15 (early bird) will get you NavSpark with an antenna (10cm length, UFL connector) and free shipping, whereas you can pledge $17 (early bird) for the Biedou and GLONASS version. Once the early birds are all taken, there’s now way to back the project for only one board, so you’ll need to get two for $35 or $39 (Beidou or GLONASS). Delivery is expected in March 2014. Bear in mind that free shipping is done by standard mail without tracking, but you can add $20 to your pledge to get the board shipped by Fedex. This is not the first product from the company, and at least one of them, Navi miniHomer GPS position finder / data logger has been sold on sites like Amazon for a little while.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress





Looks nice, I ordered the GPS/Glonass version 🙂
> I’ve never heard about … SPARC-V8
Oh my, is everything that Sun did (except Java?) went past most of the people? 😉 SPARC was a major high-end architecture for a decade pre-2000. Good to hear it’s not completely dead…
And I never heard about Beidou. Turns out that the system is just being built and works only in Asia-Pacific region so far. Funnily, wikipedia says that Beidou prototype was a 2-way system, where Chinese could track everyone who used it. Of course, production system can’t be like that, well, not in that part of world definitely, or it would be under constant DDoS ;-).
All in all, the board is good enough even as a specimen in a personal computing museum due to SPARC CPU. A little worrying is a big gap in shipping between no tracking at all and FedEx. Where’s public post tracking at $5-8?
@Paul
The chip better have one hell of an amp to send a signal back to the SATs. Epic FAIL.