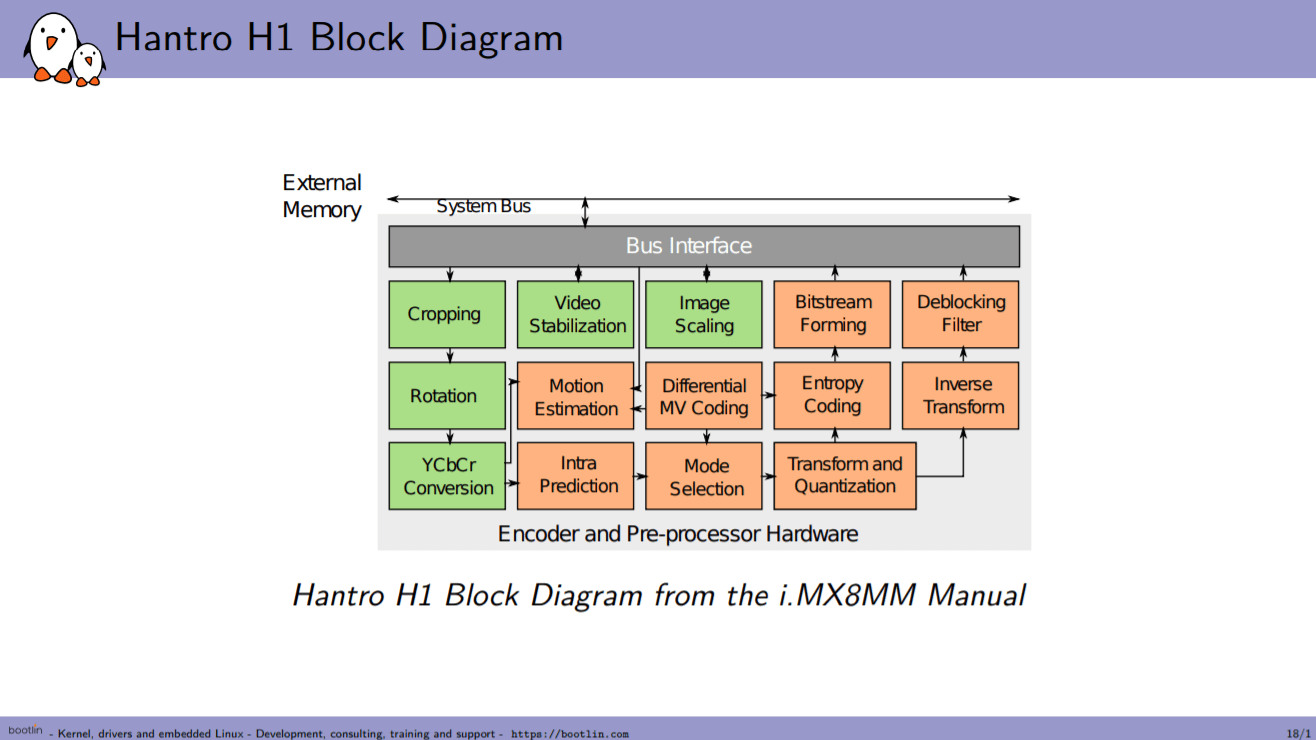
With the increasing need for video encoding, there are some breakthrough developments in hardware-accelerated video encoding for Linux. Bootlin has been working on the implementation of Hantro H1 hardware accelerated video encoding to support H.264 encoding on Linux which follows the company’s work on the previously-released open-source VPU driver for Allwinner processors. Hantro H1 Hardware Hantro H1 is a common hardware H.264 encoder, it can also do VP8 and JPEG. It is found in a few ARM SoCs including a lot of Rockchip (RK3288, RK3328, RK3399, PX30, RK1808) and NXP (i.MX 8M Mini). Depending on the version, it can support up to 1080p at 30 or 60 fps. Here we can see different blocks used for encoding. Hantro H1 is a stateless hardware implementation which means it has no microcontroller or firmware running. As can be seen in the diagram, it has a pre-processor that can do things like cropping, […]
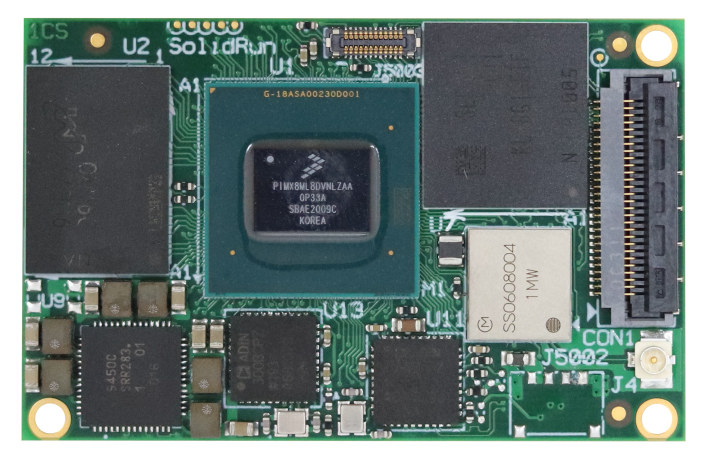
SolidRun launches i.MX 8M Plus SOM and devkit for AI/ML applications
SolidRun already offers NXP based solutions with AI accelerators through products such as SolidRun i.MX 8M Mini SoM with Gyrfalcon Lightspeeur 2803S AI accelerator, or Janux GS31 Edge AI server with NXP LX2160A networking SoC, various i.MX 8M SoCs and up to 128 Gyrfalcon accelerators. All those solutions are based on one or more external Gyrfalcon AI chips, but earlier this year, NXP introduced i.MX 8M Plus SoC with a built-in 2.3 TOPS neural processing unit (NPU), and now SolidRun has just unveiled the SolidRun i.MX 8M Plus SoM with the processor together with development kits based on HummingBoard carrier boards. Specifications: SoC – NXP i.MX 8M Plus Dual or Quad with dual or quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 processor @1.6 GHz (industrial) / 1.8 GHz (commercial), with Arm Cortex-M7 up to 800MHz, Vivante GC7000UL 3G GPU (Vulkan, OpenGL ES 3.1, OpenCL 1.2), 2.3 TOPS NPU, 1080p60 H.264/H.265 video encoder, 1080p60 video […]
Box86 is an x86 Emulator for Raspberry Pi and other 32-bit Arm platforms
Last week, we wrote about Raspberry Pi 4 Vulkan project status and future plans, and one person commented they are currently trying to get dxvk to work Box86, and that CNX Software should write about the latter. Cool, but what does that mean? dxvk is an open-source Vulkan-based implementation of D3D9, D3D10, and D3D11 for Linux, and Box86 is a Linux userspace x86 emulator that works on 32-bit Arm targets like the Raspberry Pi SBC. Nice, and I remember I ran x86 Linux and Windows on Raspberry Pi a few years ago using a closed-source commercial program called Exagear, but having an open-source solution is even better. That means 64-bit Arm is not supported at all, and Box86 can not even be built for Aarch64 targets. Since many x86 games require OpenGL, as opposed to OpenGL ES, Box86 works best in conjunction with gl4es. By installing Box86 on Raspberry Pi […]
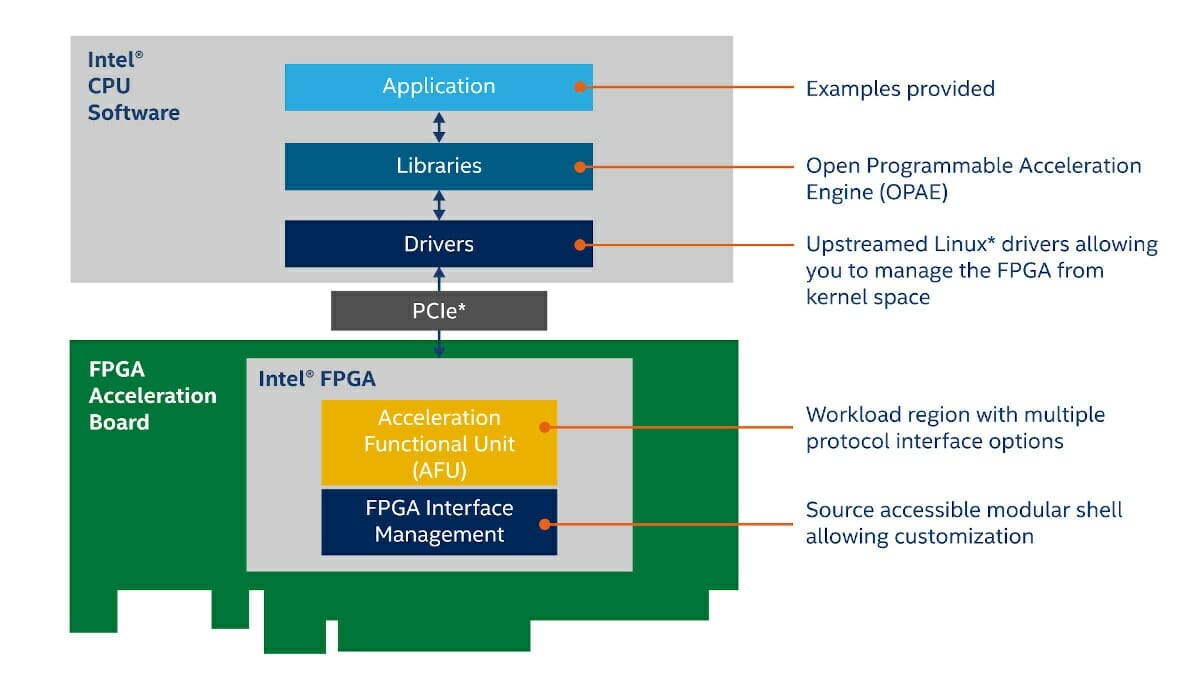
Intel unveils eASIC N5X Structured ASIC, and the Open FPGA Stack
Intel’s virtual FPGA Technology Day 2020 is taking place today, and the company made two announcements before the event. First, the company introduced the new Intel eASIC N5X structured eASIC family with an Intel FPGA compatible hard processor system to design to quickly create applications across 5G, artificial intelligence, cloud, and edge workloads. In addition, Intel also announced the Intel Open FPGA Stack (aka Intel OFS), a scalable, open-source (intel calls it “source-accessible”) hardware and software infrastructure available through git repositories design to ease the work of hardware, software, and application developers. Intel eASIC N5X eASIC N5X is the first structure ASIC from the company to integrate an Intel FPGA compatible Quad-core Armv8 hard processor system. The new chips will help customers bring custom solutions faster to market compared to traditional ASICs thanks to the FPGA fabric, and at a cheaper cost and with up to 50% lower core power […]
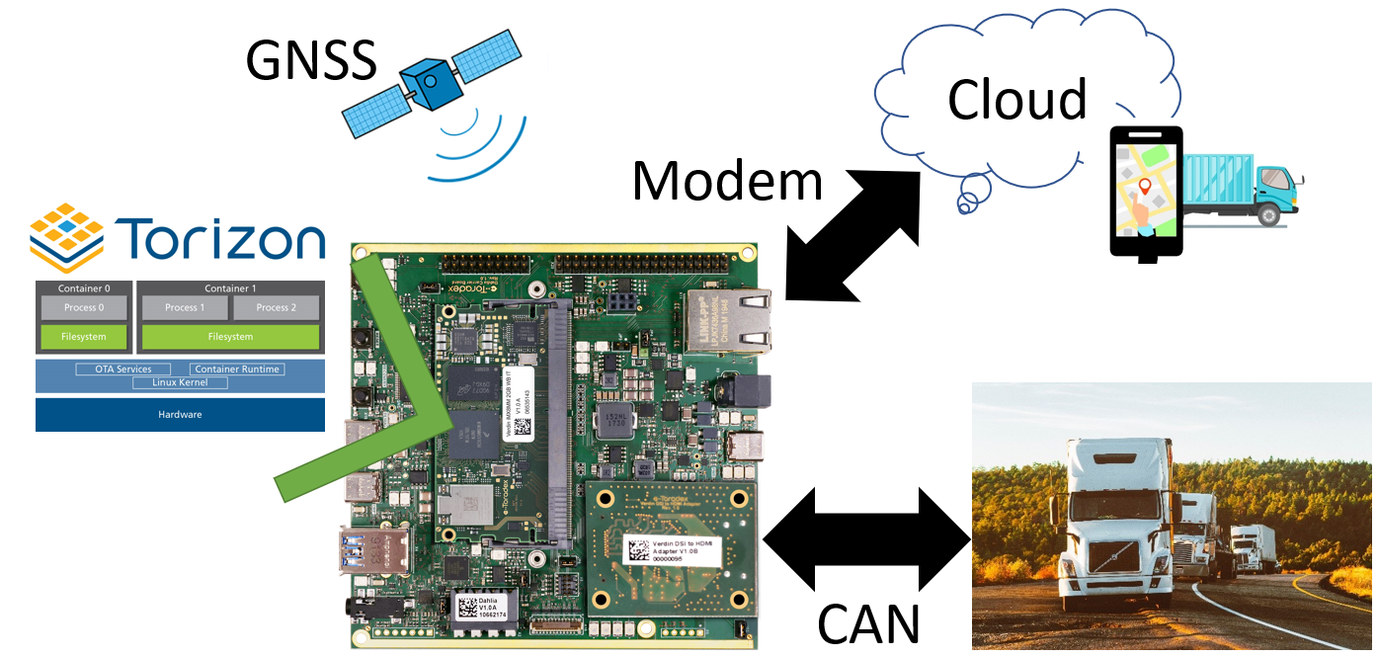
Reading Vehicle OBD-II data through CAN within a containerized application in Embedded Linux
CNXSoft: This is a guest about OBD-II and CAN support in embedded Linux by Andre Márcio de Lima Curvello, Sr. FAE and Technical Evangelist, Toradex A connected world makes it possible to track your online orders being shipped to your home through your smartphone in real-time, and getting information about your vehicle such as tire pressure, outside temperature, and even details like if a lamp is broken – has begun to be possible via smartphones in modern vehicle models. But behind the magic of knowing where the truck carrying your package is at all times and other details of the vehicle, there is a very complex world made of embedded devices ‘talking’ to each other so the information makes its way from the device to you. In this article, you will learn how to create an application to communicate with a vehicle through CAN via the OBD-II standard. We use […]
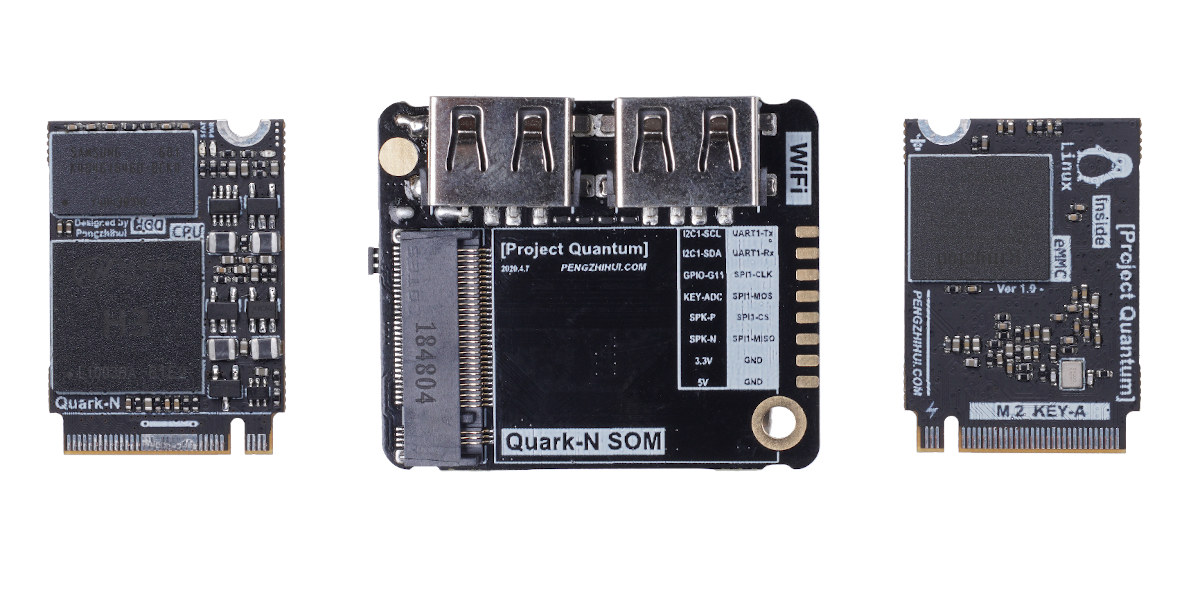
Quantum Mini devkit combines Allwinner H3 M.2 SoM with baseboard
Quantum Mini may be yet another Allwinner H3 Arm Linux development board, but what makes it special is the company used the standard M.2 Key-A 22mm form factor to create Quark-N Allwinner H3 system-on-module with storage and memory. The kit is completed by Atom-N baseboard that takes the M.2 module and offers two USB 2.0 ports, one USB Type-C port, as well as 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 4.0 connectivity, and a MicroSD port for additional storage. Quantum Mini development kit specifications: Quark-N SoM SoC – Allwinner H3 quad-core Cortex-A7 @ 1GHz with Mali-400MP2 GPU System Memory – 512MB LPDDR3 Storage – 16GB eMMC flash Interfaces exposed via M.2 connector – Ethernet, SPI, I2C, UART, GPIO, MIC, LINEOUT Dimensions – 31 x 22mm (6-layer PCB) Temperature Range – 0-80°C Atom-N baseboard M.2 socket for Quark-N system-on-module Storage – MicroSD card slot Display – TFT display Connectivity – 2.4 GHz […]
LibIIO – Library for interfacing Linux industrial I/O devices
For more than 6 years, the LibIIO library has existed to ease the development of software interfacing Linux Industrial I/O (IIO) devices. It is part of the Linux Kernel and a subsystem that provides support for devices like analog to digital or digital to analog converters (ADCs, DACs). This subsystem includes ADCs, accelerometers, pressure sensors, color, light and proximity sensors, temperature sensors, RF transceivers, and many more. You can use LibIIO natively on an embedded Linux target. It is cross-platform, supporting Linux, Windows, and Mac OS. Analog Devices Inc. was the main company behind LibIIO development, which is currently an active open-source library, which many people have contributed to. What does LibIIO do? LibIIO will identify the channels that belong to each device. It will assign specific attributes, one for the channels and one for the devices. Then, it will also create a context that is a place where all […]
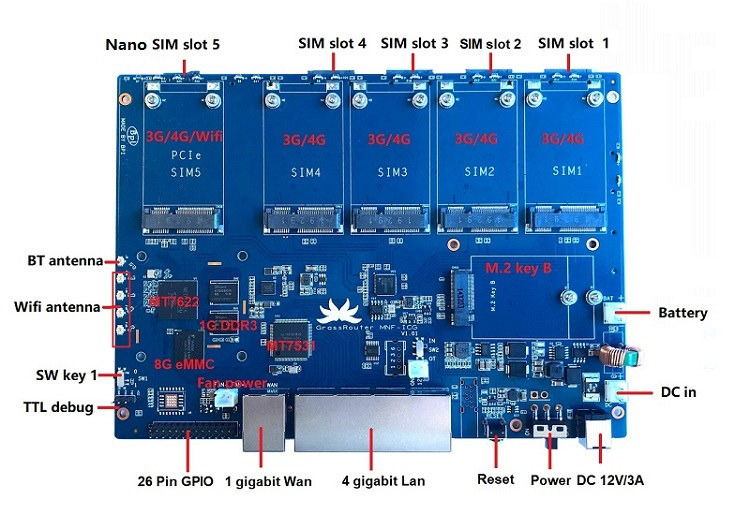
Cellular gateway board takes up to five 4G mini PCIe cards, one 5G M.2 module, seven SIM cards
One Banana Pi customer asked them to customize Banana Pi BPI-R64 Linux router board based on MediaTek MT7622 WiFi processor as part of their “BPI 4.0 server” OEM/ODM customization service. Specifically, they were asked to design a cellular gateway board with the same five Gigabit Ethernet ports as on the original board, but adding five mini PCIe sockets and SIM card slots for 3G/4G cards, and one M.2 socket plus two SIM cards for a 5G module. Here’s the result! Banana Pi “GrassRouter” cellular gateway board specifications: SoC – MediaTek MT7622E dual-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor @ 1.35GHz System Memory – 1 or 2GB RAM Storage – 8GB eMMC flash, MicroSD card slot Connectivity Cellular 1x 5G via M.2 Key-B module (USB 3.0 or PCIe bus), 2x SIM card slots. Up to 5x 3G/4G LTE via mPCIe expansion socket, 5x SIM card slots Ethernet – 5x Gigabit Ethernet ports (4x LAN […]