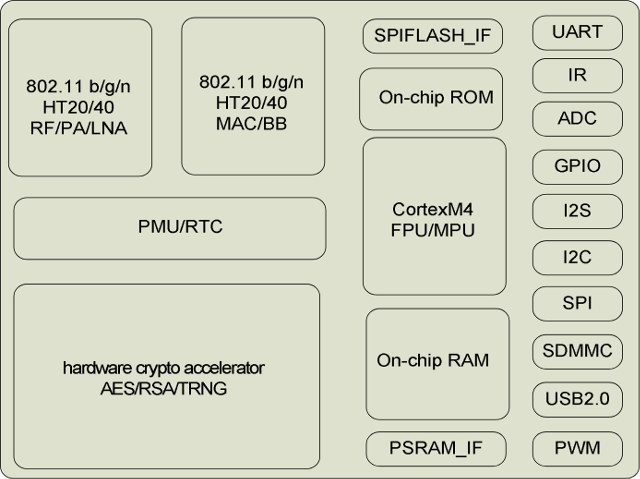
RDA Microelectronics processors are found in a few cheap smart and not-so-smart phones, as well as the even cheaper Orange Pi i96 board. But the company does not only design cellular chips, but their portfolio also includes solutions for the Internet of Things and TV & radio tuners. RDA5981 is a WiFi IoT chip specifically designed for smart home & audio application, such as smart speakers, and it’s found in devices running Baidu DuerOS, the Chinese equivalent of Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant. The company explains it can be widely used in televisions, set-top boxes, smart appliances, wireless monitors, and other products. RDA5981 A/B/C processor specifications: CPU – Arm Cortex-M4 @ up to 160 MHz with integrated MPU and mbed uvisor System Memory – Up to 448 KB SRAM for network stack and application, external PSRAM interface Storage – Up to 32Mbit SPI flash Connectivity WiFi 2.4 Ghz 802.11b/g/n WiFi […]
LittleFS is an Open Source, Low Footprint, Resilient File System Designed for Tiny Devices
Most devices need to store data either configuration files, sensor data firmware updates, and while it’s in theory possible to write directly to the storage device, it’s normally not a good idea to do so due to issues such as wear, which could lead to a premature death of your storage… LittleFS is an open source file system specifically designed for small devices such as IoT nodes for SPI NOR flash and SD card storage, and introduced in Mbed OS 5.7. The “high-integrity embedded file system” is resilient to power-cuts, supports wear-leveling, and comes in a small memory and storage footprint. Mbed support both FAT and LittleFS, so the latter was compared to the former with the following key highlights: Footprint – Code for LittleFS takes 13KB less storage than FAT, and 4KB less RAM Power loss resilience – The file system has strong copy-on-write guarantees, and storage on disk […]
Top Programming Languages & Operating Systems for the Internet of Things
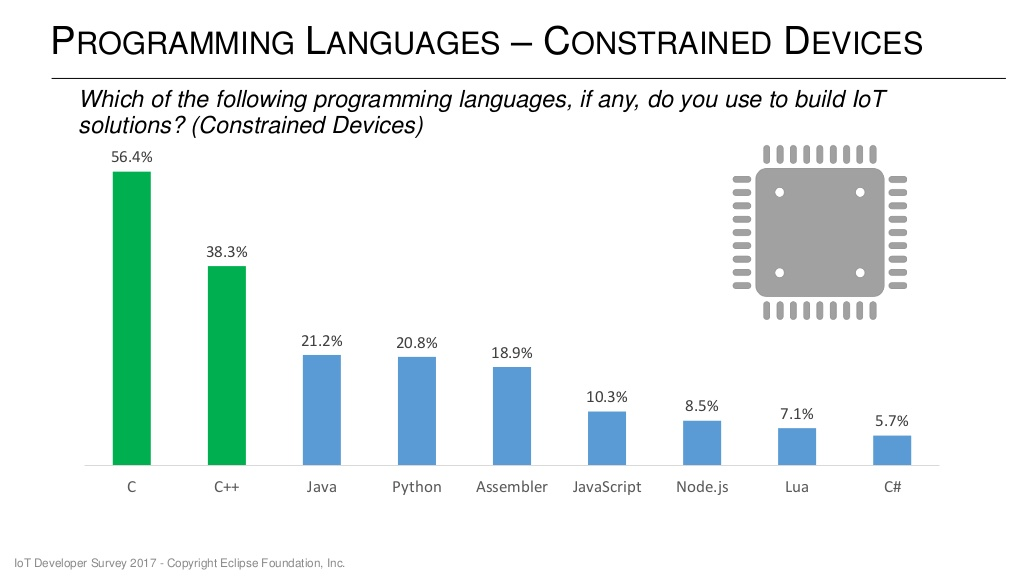
The Eclipse foundation has recently done its IoT Developer Survey answered by 713 developers, where they asked IoT programming languages, cloud platforms, IoT operating systems, messaging protocols (MQTT, HTTP), IoT hardware architectures and more. The results have now been published. So let’s have a look at some of the slides, especially with regards to programming languages and operating systems bearing in mind that IoT is a general terms that may apply to sensors, gateways and the cloud, so the survey correctly separated languages for different segments of the IoT ecosystem. C and C++ are still the preferred languages for constrained devices, and developers are normally using more than one language as the total is well over 100%. IoT gateways are more powerful and resourceful (memory/storage) hardware, so it’s no surprise higher level languages like Java and Python join C and C++, with Java being the most used language with 40.8% […]
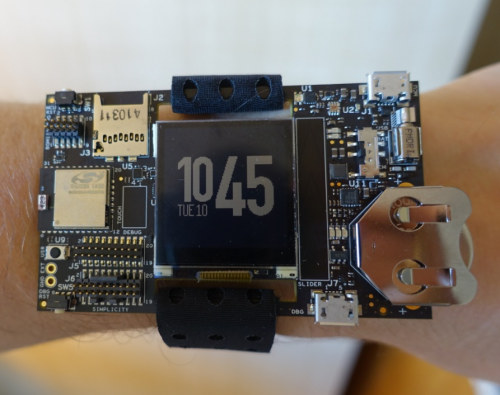
Thunderboard Wear is a $75 Smartwatch Development Board by Silicon Labs
A few days ago I watched an ARMDevices.net’s video about an ARM’s smartwatch reference design running mbed OS 3.0, powered by a Silicon Labs EFM32 Giant Gecko Cortex M3 MCU, and promising up to 2 months battery life on a 160 mAh battery. While I could not find the full details about the reference design, I noticed Silicon Labs also launched a development board called Thunderboard Wear, based on the same platform, just quite bigger, and still wearable… (Sort of) Thunderboard Wear specifications: MCU – Silicon Labs EFM32GG995F1024 ARM Cortex-M3 MCU up to 48 MHz with 128 kB RAM,1 MB Flash External Memory – 256 kB external SRAM External Storage – micro SD card slot Display – 128×128 pixel Memory LCD from Sharp Connectivity – Bluetooth 4.1 smart module (Silicon Labs BGM111), upgradeable to Bluetooth 4.2 Sensors Ambient Light Sensing (ALS) and Proximity/Gesture via Silicon Labs Si1141. Optical hear-rate monitoring […]