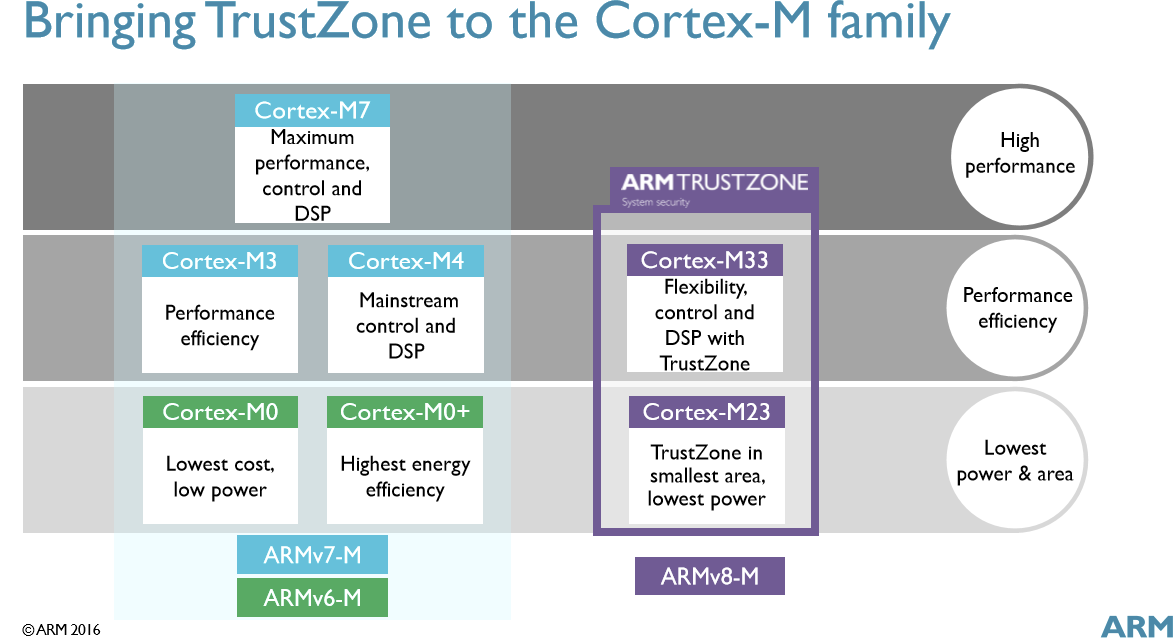
ARM TechCon 2016 is now taking place in Santa Clara, California, USA, as ARM has made three announcements for the Internet of Things, the focus of SoftBank going forward, with two ARM Cortex-M ARMv8-M cores integrating ARM TrustZone technology, namely Cortex-M23 low power small footprint core, and Cortex-M33 core with processing power similar to Cortex-M3/M4 cores, as well as Cordio Radio IP for Bluetooth 5 and 802.15.4 connectivity. ARM Cortex-M23 ARM Cortex-M23, based on the ARMv8-M baseline architecture, is the smallest and most energy efficient ARM processor with TrustZone security technology,and targets embedded applications requiring both a small footprint, low power, and security. Its power consumption is low enough to be used in batteryless, energy harvesting IoT nodes, and is roughly a third of Cortex-M33 processor size, and offers more than twice its energy efficiency. Cortex-M23 is a two-stage pipelined processor, software compatible with other processors in the Cortex-M family. […]
Webduino Smart ESP8266 Board is Designed to be Programmed via Websocket and Blockly Editor
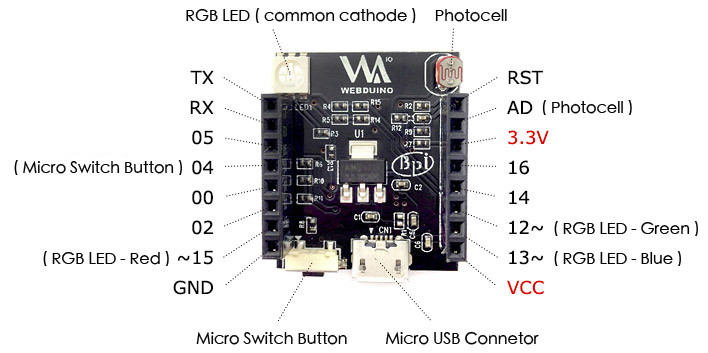
Webduino Smart board reminds me of Witty ESP8266 board with its RGB LED and photocell sensor, but the design is a little different, and does not come with an extra USB to TTL board, as it’s designed to be programmed over the air using Blockly Editor. Webduino Smart specifications: WiFi Module – AI Thinker ESP-12F module with Espressif ESP8266 WiSoC Connectivity – WiFi 802.11 b/g/n 2x 8-pin headers with GPIOs, ADC (Connected to Photocell), UART, VCC, 3.3V, GND, and Reset. USB – 1x micro USB port for power Misc – Photo resistor, RGB LED, micro switch button for firmware upgrade (connected to GPIO 4) Dimensions – 3 x 2.5 cm (See comparison to AA and AAA batteries below) While Witty board was mostly targeting mainland China market with all documentation in Chinese, Webduino Smart does have some documentation in English, and is made by Banana Pi team (SinoVoIP). The default […]
Vocore2 Lite is a $4 Linux MIPS WiFi Module based on Mediatek MT7688AN SoC (Crowdfunding)
I’ve already written about Vocore v2 Crowdfunding campaign, where the second generation Vocore WiFi module supports audio, PoE, and ultimate dock, and price starting at $12. But there has been some development since the launch of the campaign, as the developer received request for a cheaper board, and after looking into it, has now added Vocore2 Lite WiFi module reward for only $4, or $7 once shipping included. He obviously had to make some trade-offs to bring the cost down, but the Lite board impressively still keep many of the same features. VoCore (2014) VoCore2 Lite (2016) VoCore2 (2016) Price 19.99 USD 3.99 USD 11.99 USD CPU RT5350, 360MHz MT7688AN MIPS24KEc @ 580MHz MT7628AN, 580MHz Memory 32MB SDRAM 64MB DDR2 128MB DDR2 Storage 16MB NOR 8MB NOR 16MB NOR Antenna Slot x1 x1 x2 On-Board ANTENNA √ × √ Wireless Speed ~75Mbps ~150Mbps ~300Mbps Ethernet Port x5 x1 / x5 […]
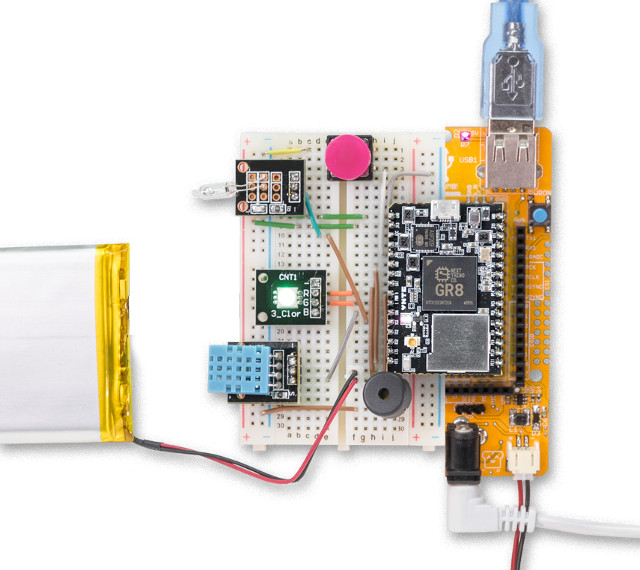
CHIP Pro is a $16 WiFi and Bluetooth 4.2 System-on-Module Powered by a $6 GR8 ARM Cortex A8 SIP
Next Thing CHIP board and corresponding PocketCHIP portable Linux computer have been relatively popular due to their inexpensive price for the feature set, as for $9, you’d get an Allwinner R8 ARM Cortex A8 processor, 512MB flash, 4GB NAND flash, WiFi & Bluetooth connectivity, and plenty of I/Os, which made it very attractive for IoT applications compared to other cheap boards such as Raspberry Pi Zero and Orange Pi One. The first board was mostly designed for hobbyists, but company has now designed a new lower profile system-on-module called CHIP Pro based on Next Thing GR8 SIP combining Allwinner R8 SoC with 256MB DDR3 RAM that can be used for easy integration into your own hardware project. While the original CHIP board exposed full USB ports and interface for video signal, the new CHIP Pro is specifically designed for IoT with the following specs: SIP – Allwinner R8 ARM Cortex […]
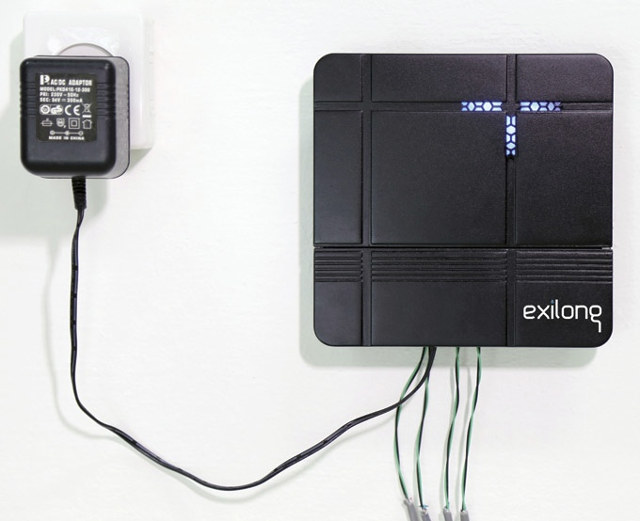
Exilong RF & WiFi Irrigation System Automatically Takes Care of Your Garden Watering (Crowdfunding)
I find it fun to spend time watering the flowers and grass in my garden, but if you’d rather do it automatically then Tevatronic Exilong might be for you as the irrigation system controls up to 4 valves, triggers watering based on RF water sensing sensors via a gateway connected to the cloud through your wireless router. The kit gateway takes care of RF communication with sensors, WiFi connectivity to the cloud server, and turn on and off up to four 24V DC water valve part of your existing installation. It can be configured by iOS or Android mobile app, or your web browser. The other part of the kit are the water pressure sensors that you need to insert into the soil of your garden in order to monitor trees, bushes, and/or flowers. The sensors are using RF (433/915 MHz) communication, send data back to the gateway every minute, […]
Sonoff Pow is a $10.50 ESP8266 WiFi Relay Box that also Measures Power Consumption
In a recent article about Sonoff TH10/TH16 WiFi relays with sensor probes support, we also saw that ITEAD Studio started to have a nice family of home automation products. The company has now added one more item to the Sonoff family with Sonoff Pow support up to 16A/3500W input, and the first to also include power consumption measurements. Sonoff Pow specifications: SoC – Espressif ESP8266 Tensila L106 32-bit MCU up to 80/160 MHz with WiFi Connectivity – 802.11 b/g/n WiFi with WPA/WPA2 support Relay – HF152F-T relay with 90 to 250 VAC input, up to 16A (3500 Watts) Terminals – 6 terminal for mains and load’s ground, live and neutral signals. Programming – Unpopulated 4-pin header for flashing external firmware Misc – LEDs for power and WiFi status, power consumption circuitry with 1% accuracy. Dimensions – 114 x 52 x 32mm Temperature range – -40 ℃ to 125 ℃ The […]
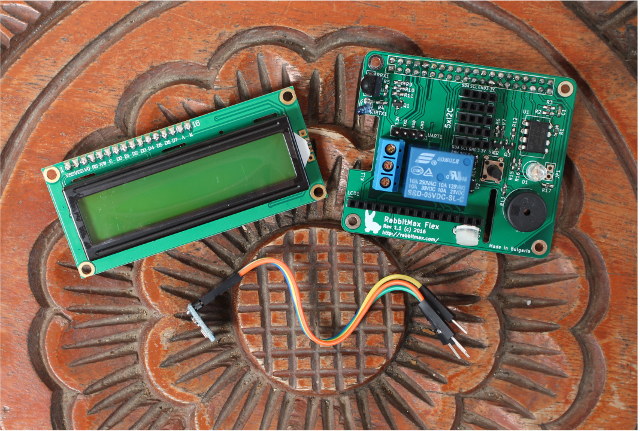
RabbitMax Flex IoT & Home Automation Board and Kit for Raspberry Pi
RabbitMax Flex is an add-on board for the Raspberry Pi boards with 40-pin headers, namely Raspberry Pi Model A+ and B+, Raspberry Pi 2, Raspberry Pi 3 and Raspberry Pi 0, destined to be used for Internet of Things (IoT) and home automation applications thanks to 5x I2C headers, a relay, an LCD interface and more. I’ve received a small kit with RabbitMax Flex boards, a BMP180 temperature & barometric pressure I2C sensor, and a 16×2 LCD display. RabbitMax Flex specifications: Relay – Songle SRD-05VDC-SL-C supporting 125V/250VAC up to 10A, 30VDC up to 10A Storage – EEPROM with some system information for identification IR – IR LED, IR receiver Misc – Buzzer, Button, RGB LED Expansion Header for LCD character display + potentiometer for backlight adjustment 5x 4-pin headers for I2C sensors Dimensions – Raspberry Pi HAT compliant The assembly of the kit is child’s play as you don’t even need […]
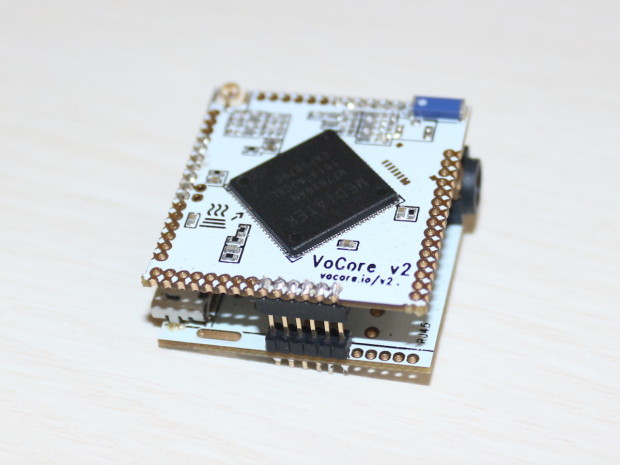
VoCore2 WiFi IoT Board Launched with Audio, PoE & “Ultimate” Docks (Crowdfunding)
Vocore WiFi IoT board was popular at its launch in 2014 because affordable WiFi boards with I/Os were not common at the time, and it came with an Ethernet dock making it a complete router within a tiny and cute cube. The developers have been working on VoCore2 (aka Vocore V2) with a faster processor, more memory, a lower power consumption, a better WiFi signal, and more I/Os for several months, and have now launched the board on Indiegogo aiming to raise at least $6,000 for mass production. Vocore2 board specifications: SoC – Mediatek MT7628AN MIPS processor @ 580 MHz System Memory – 128 MB DDR2 Storage – 16MB NOR FLASH, 1x SDXC via I/O pins Connectivity WiFi 802.11n 2T2R up to 300 Mbps with either 2 u.FL connector or 1 u.FL connector + on-board chip antenna (Max signal output >19.5dbm peak) 2x 10/100M Ethernet interfaces via I/O pins I/Os […]