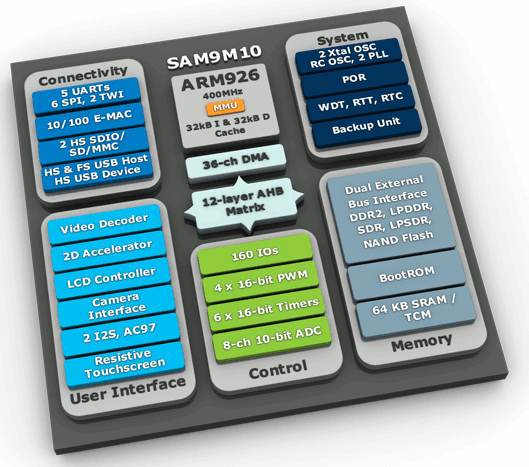
Atmel AT91SAM9 – or simply Atmel SAM9 – series are versatile microcontrollers and embedded microprocessors used in variety of products such as internet radios, embedded p2p downloaders, smart grid in-home displays, and much more. Atmel SAM9 series are divided into five subsets: The original SAM9 MCU based on ARM926EJ-S running at between 210 and 240 Mhz, namely AT91SAM9260, AT91SAM9261, AT91SAM9261S and AT91SAM9263 SAM9G eMPU (Embedded MPU) based on ARM926EJ-S, a new generation based on SAM9 MCU architecture but running at between 266 and 400Mhz: AT91SAM9G10, AT91SAM9G20, AT91SAM9G45 and AT91SAM9G46. SAM9M eMPU based on ARM926EJ-S clocked at 400Mhz and with a video decoder: AT91SAM9M10 and AT91SAM9M11 SAM9R MCU based on ARM926EJ-S running at 210 Mhz with similar characteristic as the original SAM9 MCU, except it does not support USB Host but can be used as a High Speed USB device: AT91SAM9R64 and AT91SAM9RL64 SAM9XE MCU are also based on ARM926EJ-S running […]
Third Generation OLPC XO Laptop powered by ARM Marvell Armada 610
OLPC (One Laptop Per Child) was also at CES 2011 in Marvell stand with their third generation OLPC XO laptop named OLPC XO-1.75, after the first generation using AMD and the second Via Technologies. Charbax interviewed Ed NcNierney, Chief Technology Office at OLPC. They only changed the PCB in this version, i.e. the casing, keyboard, monitor is the same as the previous generations.The processor used in OLPC XO-1.75 is the ARM based Marvell Armada 610 (single core) running at 1GHz with 1GB RAM and 4GB Flash. The laptop can be recharged with a hand crane for 1 minute, then the laptop can be used for 10 minutes (color) and about 12 minutes (black and white). With the third generation, the price is only marginally cheaper than the previous generation (<200 USD), but the power consumption is now 2 Watt (instead of 4 Watt) and it is the most important part, […]
Near Field Communication (NFC) Introduction and Software Development
Android 2.3 features near field communication (NFC) in order to allow payment through your phone as it is already implemented in Japan with FeliCa (Felicity Card), a contactless RFID smart card system from Sony, direct communication between NFC devices, RFID reader, etc… NFC is already supported in Samsung / Google Nexus S. In this blog post, we’ll see what near field communication is, which hardware is needed and what needs to be done at the software level (driver and NFC stack). What is Near Field Communication ? Extract from Wikipedia: Near Field Communication or NFC, is a short-range high frequency wireless communication technology which enables the exchange of data between devices over about a 10 centimeter (around 4 inches) distance. The technology is a simple extension of the ISO/IEC 14443 proximity-card standard (proximity card, RFID) that combines the interface of a smartcard and a reader into a single device. An NFC […]
Resources for NVidia Tegra 2
NVidia Tegra 2 is currently one of the most powerful processor used in smartphones and tablets such as the upcoming LG Optimus 2X smartphone or the new version of Samsung Galaxy Tab. NVidia describes the processor as follows: NVIDIA® Tegra™ 2 is the world’s most advanced mobile processor, featuring the world’s first mobile dual-core CPU for up to 2x faster Web browsing; the world’s only ultra-low power (ULP) NVIDIA® GeForce® GPU for up to 5x faster gaming; and the world’s first mobile 1080p HD video processor for flawless HD video conferencing and playback. Get never-before-seen experiences on a mobile device with NVIDIA Tegra. NVidia Tegra 2 is based on a dual core Cortex A9 running up to 1GHz, supports 32-bit DDR2 RAM and features NVidia Geforce GPU with OpenGL ES 2.0 support. Contrary to many other companies finding the development kit, documentations and tools is straightforward. Once you get to […]
Building Archos Gen8 Source on Ubuntu 10.10
[ad#Google Adsense-Leaderboard] In a follow-up post of GPL Source code and SDE for Archos Gen8 Devices earlier today, here are the steps I followed to build the toolchain, kernel and root file system with buildroot on Ubuntu 10.10 Desktop version: Extract the source code: tar xzvf ../Downloads/gen8-gpl-froyo.tgz Install extra packages for the build: sudo apt-get install flex bison build-essential zip curl libmpfr-dev libmpfr1ldbl automake autoconf libtool gettext texinfo Run the build to generate the toolchain, kernel and root file system: cd gen8-gpl-froyo/buildroot sudo make Then wait for a while (It took 1h15 on my machine) to get the binary images: zImage (kernel) in buildroot/linux/arch/arm/boot rootfs.arm.squashfs (rootFS) in buildroot/binaries/uclibc Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
GPL Source code and SDE for Archos Gen8 Devices
Right at the end of November, Archos released the first version of their Android 2.2 firmware (2.0.54). They now have also released the GPL code for this firmware. http://www.archos.com/support/download/software/sources/gen8-gpl-froyo.tgz In this package, you’ll find the following: Linux Kernel 2.6.29 buildroot – Set of tools to generate the cross-compilation toolchain, the kernel and the root file system A directory called “external” with the following libraries, tools and drivers: alsa-lib – Audio library blktrace – Driver debugging tool elfcopy – Tool to generate executable binaries grub – Bootloader iptables – Firewall Tool liblzo – LZO Compression Library webkit – Web Browser Engine alsa-utils – Audio Tools BlueZ – Bluetooth Protocol Stack elfutils – Tool to manipulate executable binaries hostapd – For Wifi Authentication jdiff – Java Code Analyzer openvpn – VPN Client/Server wpa_supplicant – Wifi tools for WPA/WPA2 bison – Parser Generator dbus – Libray and daemon for IPC (InterProcess Communication) genext2fs […]
Unusual USB Devices in Linux Kernel
Some USB devices (especially cheap ones) are not fully compatible with the USB Stack and when you connect such devices to your target board, the kernel may output errors similar to the one below even though most other devices work perfectly. sd 3:0:0:0: SCSI error: return code = 0x10070000 end_request: I/O error, dev sda, sector 0 Buffer I/O error on device sda, logical block 0 sd 3:0:0:0: SCSI error: return code = 0x10070000 end_request: I/O error, dev sda, sector 8 Buffer I/O error on device sda, logical block 1 sd 3:0:0:0: SCSI error: return code = 0x10070000 end_request: I/O error, dev sda, sector 16 sd 3:0:0:0: SCSI error: return code = 0x10070000 end_request: I/O error, dev sda, sector 24 sd 3:0:0:0: SCSI error: return code = 0x10070000 It previously happened to us with a IDE to USB adapter based on Super Top Bridge ( VID: 0x14CD / PID: 0x6600). The […]
Installing Chrome OS with CD or USB
Chrome OS is a lightweight Linux distribution build around the Google Chrome Browser, it is not related to Google Chrome OS. I suppose they may have to change the name sometimes in the future. To install it, simply download Chrome OS Live CD to try it out on your hardware. Bear in mind this is a Release Candidate version (Chrome OS 0.9.576 RC released on 7th of December 2010) at this time so it should be relatively stable, but expect a few bugs. Here are the main software packages installed in Chrome OS: GNOME 2.30 desktop environment Google Chrome 9.0.576 web browser Google Picasa 2.7 photo manager OpenOffice.org 3.2 office suite GIMP 2.6 image editor Flash Player 10.1 plugin Wine Windows emulator 1.2 Pidgin 2.6 instant messenger Dashboard in browser (See screenshot below) Here are the system requirements of Chrome OS: Processor: Intel Pentium, Xeon or newer; AMD Duron, Athlon, […]