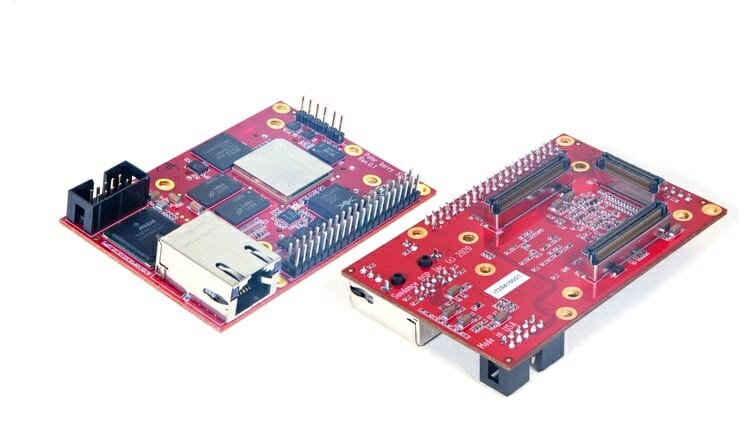
SiFive may just have announced a mini-ITX motherboard for RISC-V PCs, but if you’d like a RISC-V Linux platform in a more compact form factor, Sundance PolarBerry may better fit your requirements, albeit the board will target different use cases. Powered by Microchip PolarFire RISC-V SoC FPGA, PolarBerry is both a single board computer with Gigabit Ethernet and 40-pin GPIO header, as well as a system-on-module thanks to three Samtec board-to-board connectors. PolarBerry specifications: SoC – Microsemi PolarFire FPGA MPFS250T-FCVG484 penta-core processor with 1x RV64IMAC monitor core, 4x RV64GC application cores, FPGA fabric with 254K x logic elements (4LUT + DFF), 784 x math blocks (18 x 18 MACC), and 16 x SERDES lanes at 12.5 Gbps; 12 W maximum power consumption System Memory – 4 GB of 32-bit wide DDR4 memory Storage – 4GB eMMC flash, 128 Mbit SPI Serial NOR flash for boot image Networking – Gigabit Ethernet […]
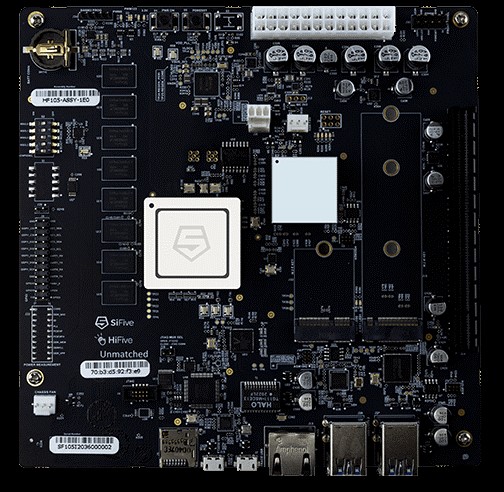
SiFive launches HiFive Unmatched mini-ITX motherboard for RISC-V PC’s
When it comes to RISC-V based SoC, SiFive has always set a benchmark in the RISC-V ecosystem. On 29th October 2020, SiFive confirmed the first-ever RISC-V PC. After an increased demand for AI-focused RISC-V microarchitecture, targeting all applications from artificial intelligence, the internet of things, high-performance computing, and now even desktop PCs. SiFive Freedom U740 powered HiFive Unmatched mini-ITX motherboard comes with a complete development environment which allows developers to create RISC-V based applications from bare-metal to Linux-based systems. “HiFive Unmatched ushers in a new era of RISC-V Linux development with a platform in a PC form factor. Powered by the SiFive Freedom U740, a high-performance multi-core, 64-bit dual-issue, superscalar RISC-V processor.”, SiFive says. It is the world’s fastest native RISC-V development platform. SiFive HiFive Unmatched Board At the heart of the SiFive board is a SiFive FU740 processor coupled with 8 GB DDR4 memory and 32 MB SPI Flash. It […]
Station P1 & M1 fanless mini PCs run media or desktop-optimized Android OS
T-Chip has recently introduced two fanless “Geek” mini PCs under their Firefly brand with Station P1 & M1 respectively powered by Rockchip RK3399 hexa-core processor, and RK3328 quad-core processor. Both mini PCs can run Firefly’s Station OS in either desktop or media mode, as well as Android or Ubuntu. There are also some community efforts to port Armbian and LibreELEC to the devices. Station P1 specifications Specifications: SoC – Rockchip RK3399 hexa-core processor with two Cortex A72 cores @ up to 1.8 GHz and four Cortex-A53 cores, Mali-T860 MP4 GPU with support for OpenGL ES1.1/2.0/3.0/3.1, OpenVG1.1, OpenCL, DX11, VPU with support for 4K H.265 10-bit 60fps video decoding, multi-channel 1080p video decoding and encoding System Memory – 4GB LPDDR4 dual-channel 64-bit RAM Storage – 32GB eMMC flash (16GB/64GB/128GB Optional), onboard 16MB SPI flash, MicroSD card slot Video Output HDMI 2.0a up to 4Kp60, HDCP 1.4/2.2 DisplayPort 1.2 up to 4Kp60 […]
STMicro unveils VL53L5 multi-zone ToF ranging sensor
We’ve previously covered or even tested STMicro Time-of-Flight (ToF) ranging sensors with devices like VL53L0X with up to 2-meter range or VL53L1X extending the range to a maximum of 4 meters to measure the distance to one object aka region of interest (ROI). Those are used in various applications including the autofocus function in smartphones for example. The company has now introduced a new model with VL53L5 ToF laser-ranging sensor boasting increased camera Field-of-View coverage and 64-zone spatial resolution to enable new features such as touch-to-focus, multiple-target identification, flash dimming, or video tracking assistance. VL53L5 highlights: 940 nm invisible Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) and integrated analog driver 61° diagonal square system field of view (FoV) using diffractive optical elements (DOE) on both transmitter and receiver Receiving array of single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) Parallel multi-zone output – Either 4×4 (16 zones @ 60 fps) or 8×8 (64 zones @ […]
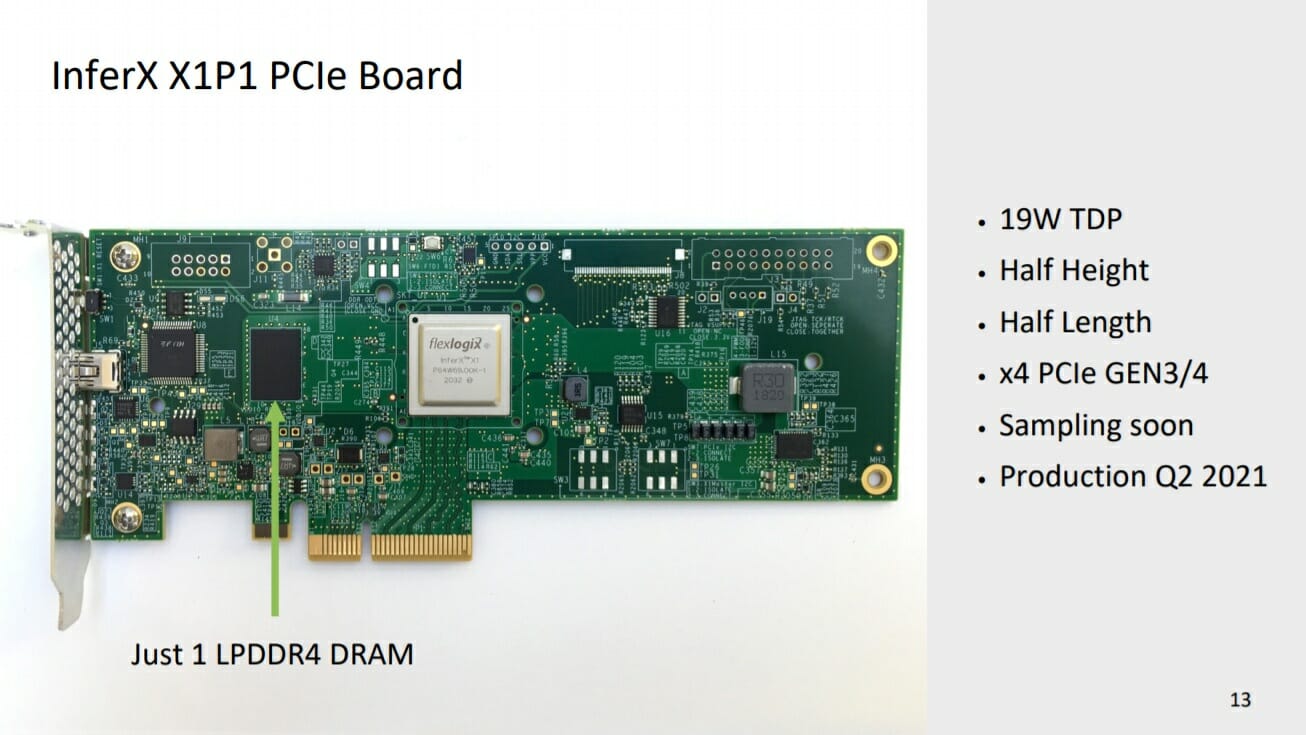
InferX X1 SDK, PCIe and M.2 Boards for edge inference acceleration
Last week, Flex Logix announced the InferX X1 AI Inference Accelerator at Linley Fall Conference 2020. Today, they announced the InferX X1 SDK, PCIe board, and M.2 board. InferX X1 Edge Inference SDK The InferX Edge Inference SDK is simple and easy. The input to the compiler can be an open-source high-level, hardware-agnostic implementation of the neural network model that can be TensorFlow Lite or ONNX model. The compiler takes this model and looks for the available X1 resources and generates a binary executable file. This goes to the runtime which then takes the input stream, for example, a live feed from a camera. The user has to specify which compiler model, then the InferX X1 driver takes it and sends it to hardware. The binary file generated is fed to InferX X1 through the runtime. Then it takes the input data stream with a user-specified model and gives the […]
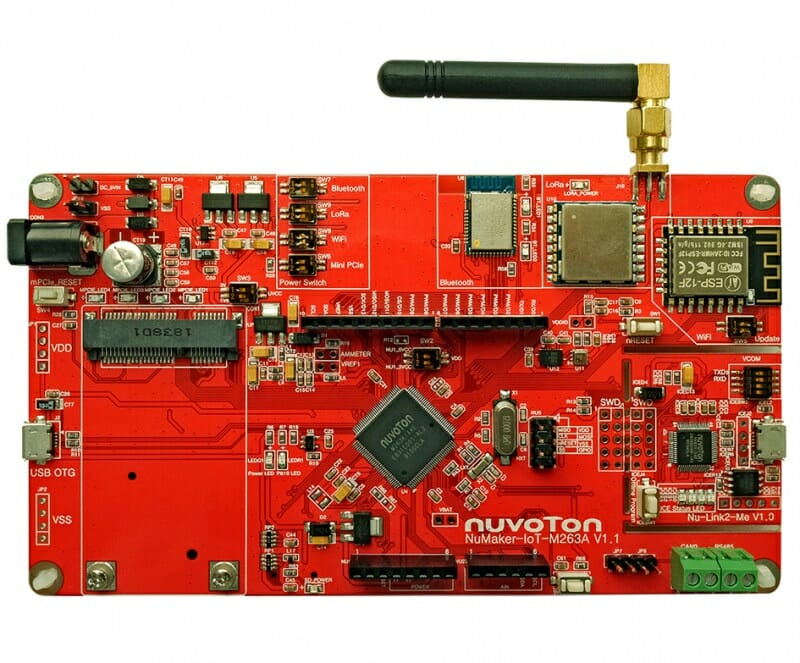
NuMaker-IoT-M263A board is the Swiss army knife of IoT development
If you’d like an MCU board to experiment with various wireless (and wired) protocols used for Internet of Things applications, the Nuvoton NuMaker-IoT-M263A development board may be worth a look. Powered by a NuMicro M263KIAAE Arm Cortex-M23 CPU microcontroller, the board offers WiFi, Bluetooth, and LoRa connectivity, plus an mPCIe socket for 3G, 4G, or NB-IoT cellular connectivity. It also comes with various sensors, as well as CAN and RS485 transceivers for industrial control applications. NuMaker-IoT-M263A key features and specifications: MCU – Novoton NuMicro M263KIAAE Arm Cortex-M23 microcontroller @ 64 MHz with 96KB SRAM, 512 KB dual-bank flash for OTA upgrade, 4 KB LDROM; LQFP128 package Storage – MicroSD card connector On-board wireless modules ESP12-F (ESP8266) 802.11b/g/n module MDBT42Q-PAT Bluetooth 4.2/5.0 LE module APC1278 (for 408 / 433 / 470 MHz) LoRa module plus antenna Serial – CAN and RS485 transceiver USB – 1x Micro USB OTG connector (to M263 […]
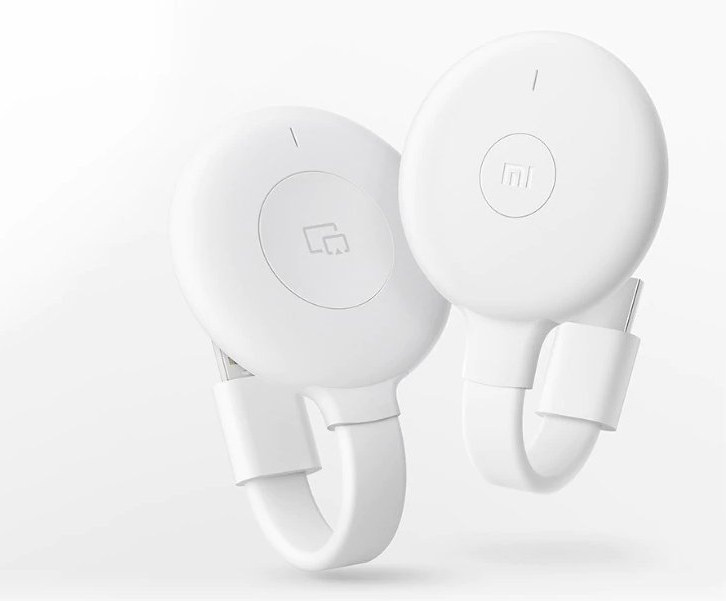
$54 Xiaomi Mijia Paipai wireless HDMI system connects your computer to your TV
A few years ago, we covered plenty of cheap Miracast adapters that plugged into your TV and used to mirror your Android or iOS smartphone display to a larger TV screen. It’s also possible to use Miracast on computers with WiFi, and since many TVs implement Miracast, extra hardware is often not needed. But in case your TV and computer are not compatible, Xiaomi Mijia Paipai wireless HDMI system [Update Nov 2020: actually called “Mi Wireless Casting Adapter” in English] solves this issue with a wireless HDMI receiver connected to your TV and a wireless HDMI transmitter connected to a USB port from your computer or laptop. Both the receiver and transmitter have similar dimensions (149.6 x 61 x 12.5 mm vs 152 x 60 x 11.9 mm) and weigh 38.5 grams in a form factor similar to Google Chromecast. The company says Windows 7 to 10 and Mac OS […]
The quest for a blob-free WiFi & Bluetooth stack for BL602 WiSoC
I thought I was done writing about Bouffalo Lab BL602 WiFI & Bluetooth RISC-V SoC for a while after first covering the chip itself, and then an inexpensive BL602 development board this weekend. But the BL602 SDK has shown up in various Github repositories, including Bouffalo Lab’s own bl_iot_sdk repository, and as more people are looking into it, there’s now an effort to develop a fully open-source blob-free WiFi & Bluetooth stack for BL602, and other Bouffalo Lab WiFi and/or Bluetooth wireless chips. Last day we communicate with Bouffalolab, finally they release the SDK of BL602 (RV32 chip of wifi+bt), all code is open, except libblecontroller.a, libatcmd.a, libbl602_wifi.a (while they have all symbol inside)https://t.co/giHsQ4ezXxwe have a fork too https://t.co/FiaAIxLBc8 — Sipeed (@SipeedIO) October 27, 2020 First, Sipeed says the code is mostly open-source except for three libraries: ibblecontroller.a, libatcmd.a, libbl602_wifi.a, all of which are un-obfuscated, and easy to disassemble. Then […]