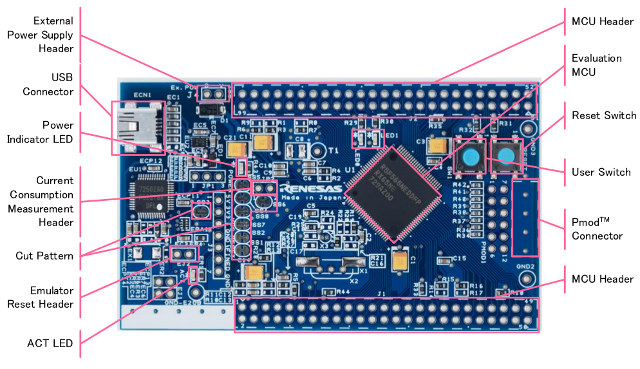
Renesas Electronics has announced three new Target Boards for the RX65N, RX130 and RX231 32-bit Microcontroller (MCU) groups designed for home appliance, building and industrial automation applications. Each board has minimal features with an on-chip debugger, a mini USB port, the micro-controller, and through-hole pin headers providing access to all MCU signals. This design allows to access all MCU features while keeping the price below $30. Renesas Target Board specifications: MCU Renesas RX65N (R5F565NEDDFP) 32-bit RXv2 MCU @ 120 MHz with 2MB+32KB ROM, 640KB RAM Renesas RX130 (R5F51308ADFP) 32-bit MCU @ 32 MHz with 512KB+8KB ROM, 48 KB RAM Renesas RX231 (R5F52318ADFP) 32-bit RXv2 MCU @ 54 MHz with 512KB+8KB ROM, 64 KB RAM Expansion Unpopulated 12-pin Pmod connector 2x unpopulated 50-pin MCU headers Misc 2-pin Current measurement header Reset and user push buttons Power LED (Green), ACT LED (Green), 2x user LEDs (Green) 2-pin emulator reset header Power Supply […]
$1 RDA5981 WiFi IoT Arm Cortex-M4 SoC is Designed for Smart Home Devices, Smart Speakers
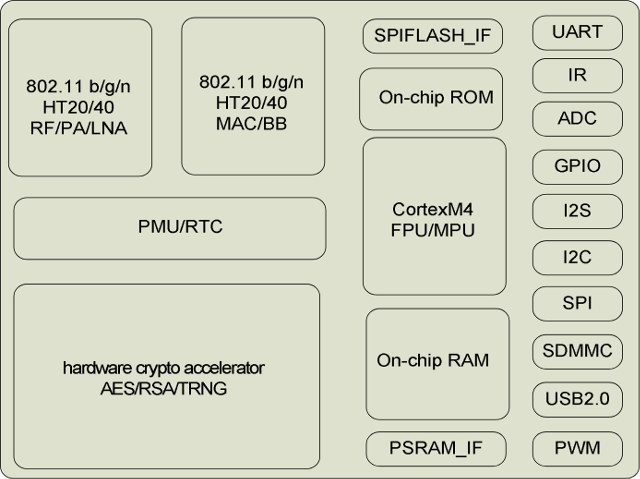
RDA Microelectronics processors are found in a few cheap smart and not-so-smart phones, as well as the even cheaper Orange Pi i96 board. But the company does not only design cellular chips, but their portfolio also includes solutions for the Internet of Things and TV & radio tuners. RDA5981 is a WiFi IoT chip specifically designed for smart home & audio application, such as smart speakers, and it’s found in devices running Baidu DuerOS, the Chinese equivalent of Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant. The company explains it can be widely used in televisions, set-top boxes, smart appliances, wireless monitors, and other products. RDA5981 A/B/C processor specifications: CPU – Arm Cortex-M4 @ up to 160 MHz with integrated MPU and mbed uvisor System Memory – Up to 448 KB SRAM for network stack and application, external PSRAM interface Storage – Up to 32Mbit SPI flash Connectivity WiFi 2.4 Ghz 802.11b/g/n WiFi […]
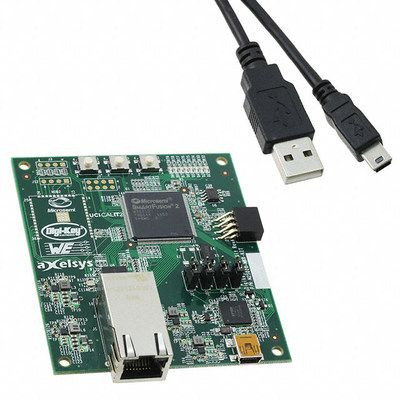
$34 SmartFusion2 Maker Board Arm Cortex-M3 + FPGA Board Supports ESP32 & ESP8266 Modules
Xilinx Zynq SoCs are probably the most well-known FPGAs with ARM cores, as their Cortex A9/A53 cores can run Linux, but they are not the only ones. Microsemi launched SmartFusion2 SoC comprised of FPGA fabric and an Arm Cortex-M3 core in 2013, as well as a $300 development kit. The company has now partnered with Digikey to launch SmartFusion2 Maker Board, a low-cost evaluation platform for the SoC that comes with Gigabit Ethernet, a USB port, a connector for ESP8266 module, PCB footprint for ESP32 module, among other features like a light sensor, LEDs, and buttons. SmartFusion2 maker board (M2S010-MKR-KIT) main features & specifications: SoC – Microsemi SmartFusion2 M2S010 SoC with: Arm Cortex-M3 @ 166 MHz, 6oKB+80KB eSRAM, 256KB eNVM FPGA with 12,084 logic element, 400 Kbits RAM Storage – 16 Mbit SPI Flash Connectivity Gigabit Ethernet via VSC8541 PHY, RJ45 connector Connector for ESP8266 (Sparkfun WRL-13678 – not included) […]
Amazon FreeRTOS Released for NXP, Texas Instruments, STMicro, and (soon) Microchip Microcontrollers
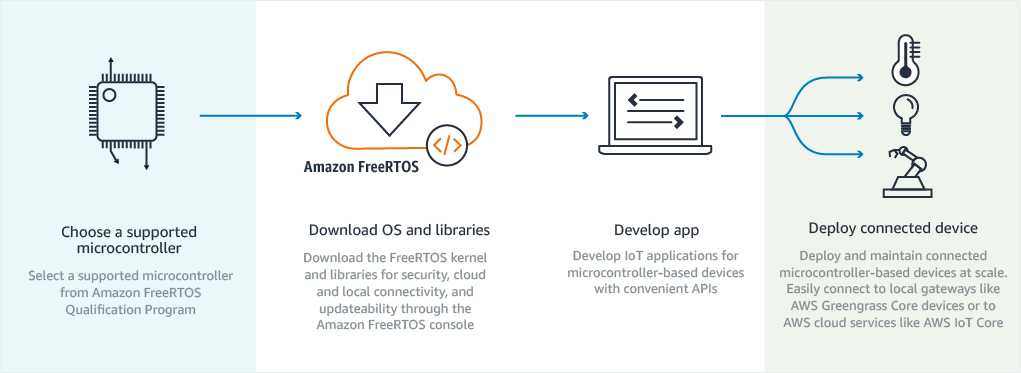
FreeRTOS is an open source real-time operating system for microcontrollers released under an MIT license, and when it comes to adoption in embedded systems it’s right there near the top with embedded Linux according to Aspencore 2017 embedded markets study. For example, some Espressif SDKs for ESP8266 or ESP32 are based on FreeRTOS, and so is Mediatek LinkIt Development Platform for RTOS. The recently announced Amazon FreeRTOS (a:FreeRTOS) leverages the open source operating systems, and extends it with with libraries that enable local and AWS cloud connectivity, security, and soon over-the-air updates. a:FreeRTOS is free of charge, open source, and available today. In order to get started, you’ll have a choice of 4 hardware platforms: STMicro STM32L4 Discovery Kit IoT Node (B-L475E-IOT01A) powered by STM32L475 ARM Cortex-M4 MCU with 802.11 b/g/n WiFi, Bluetooth 4.1 LE, RF (868 / 915 MHz), and NFC connectivity, plenty of sensors NXP LPC54018 IoT module (OM40007) […]
Geolocation on ESP8266 without GPS Module, only WiFi
When I think about geolocation in I normally think about global navigation satellite systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, or Beidou, as well as IP geolocation, but the latter is highly inaccurate, and often only good for find out about the country, region, or city. But if you’ve ever been into your phone location settings, you’d know GPS is only one option, as it can also leverage cellular base stations and WiFi SSIDs, where the former working where there’s coverage, and the later in area with a high enough density of access points. Somehow, I had never thought about using such technology to find location with WiFi modules until Espressif Systems released an application note entitled “Geolocating with ESP8266“. This document describes how the ESP8266 module may be used to scan for nearby Wi-Fi access points and, then, use their SSID, RSSI and MAC address to obtain a potential fix […]
HeartyPatch is an Open Source Wireless ECG Patch Powered by ESP32 WiSoC (Crowdfunding)
Smart health gadgets will soon have a bigger part to play in our lives, especially for health monitoring. It mainly started with fitness trackers, but now we are starting to see connected devices such as blood pressure monitors, including the upcoming watch like Omron HeartVue, thermometer, scales, vital sign monitoring systems, certified medical SBC‘s to allow engineers to developer their own medical applications, and even open source surgical robots. HeartPatch is one of those medical board that specifically aims at measuring ECG data, and sent it over Bluetooth or WiFi thanks to Espressif ESP32 WiSoC. HeartPatch specifications: SoC – Espressif Systems ESP32 dual core Tensilica LX6 processor with Wi-Fi/Bluetooth ECG Chip – Maxim MAX30003 analog front-end USB – 1x micro USB connector for programming, data, power, and battery charging Debugging – USB-UART bridge based on CP2104 Misc – Onboard Snap-on Buttons for disposable electrode pads, RGB LED, Battery – 450 […]
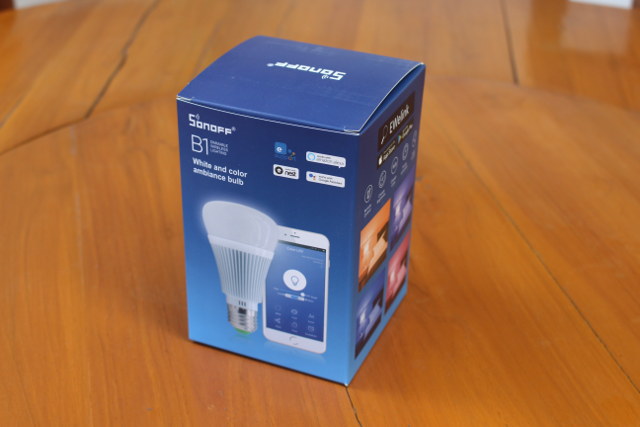
Sonoff B1 Smart Light Bulb Review – Part 1 : eWeLink Android App and Teardown
ITEAD Studio has a popular family of home automation devices call Sonoff with WiFi switches, smart sockets, RF to WiFi bridges and so on. All WiFi devices are based on Espressif ESP8266 or ESP8285, and while the company provide a stock firmware working with eWelink app, at least two communities have formed around Sonoff and other similar devices providing two open source firmware alternatives: ESPurna and Sonoff-Tasmota. The company has sent me Sonoff B1 smart RGB light bulb for review. Today, I’ll check out the light with eWelink app for Android, and do a teardown, before trying one of the open source firmware in the second part of the review. Sonoff B1 Unboxing Some Chinese products come in a blank cardboard boxes, but Sonoff’s light bulb comes with in a nice looking retail package that would look good on store’s shelves. One of the side lists the specifications with an […]
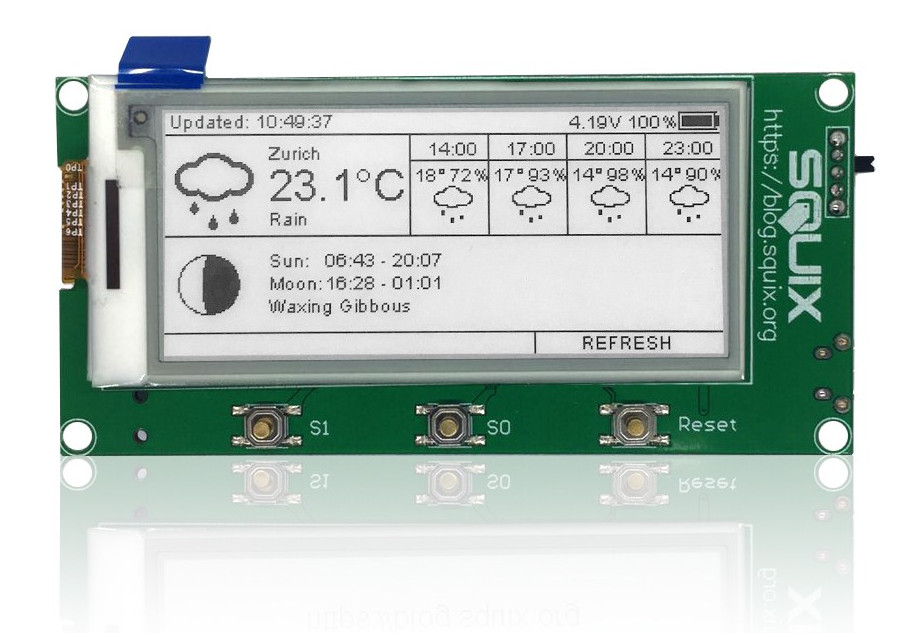
2.9″ ESPaper Lite Kit is a $40 ePaper Display Kit with an ESP8266 WiFi Module
Squix (Daniel Eichhorn) has designed a 2.9″ ESPaper Lite Kite is a battery powered kit based on a black and white ePaper module, and ESP-WROOM-02 module based on Espressif Systems ESP8266 WiSoC. 2.9″ ESPaper Lite Kit specifications: Wireless Module – ESP-WROOM-02 WiFi module with Espressif ESP8266 Display – 2.9″ B&W ePaper module with 296×128 pixels resolution connect over SPI to ESP8266 Debugging / Programming – 6-pin serial port header USB – 1x micro USB port for programming Misc – 3 buttons: Reset (wake up from deep sleep); S0 (flash/GPIO0); S1: user button connected to GPIO12; power switch; charging and (firmware) flashing LEDs Power – JST connector for LiPo battery; charging circuit You’ll need a 3.3V USB to TTL debug board for flashing the firmware to the board, and a LiPo battery to power it up. The solution is particularly useful if you want a battery powered display that is infrequently […]