It’s the last day of the year and the time to look at some of the highlights of 2022, some traffic statistics from CNX Software website, and speculate on what 2023 may bring us. The semiconductors shortage continued in 2022, but things are looking brighter in 2023 with the full reopening of the world mixed with forecasts of difficult economic times that should keep the demand/supply equation in check. On the Arm processor front the biggest news of the year, at least in this corner of the Internet, was the launch of the Rockchip RK3588 octa-core Cortex-A76/A55 processor together with interesting single board computers that we’ll discuss below. Announced last year, the Amlogic A311D2 octa-core Cortex-A73/A53 was finally made available in a few SBC’s, and we finally got some news about the Amlogic S928X Cortex-A76/A55 SoC showcased in 8K TV boxes, but we have yet to see it in action. […]
Linux 6.1 LTS release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V and MIPS architectures
Linus Torvalds announced the release of Linux 6.1, likely to be an LTS kernel, last Sunday: So here we are, a week late, but last week was nice and slow, and I’m much happier about the state of 6.1 than I was a couple of weeks ago when things didn’t seem to be slowing down. Of course, that means that now we have the merge window from hell, just before the holidays, with me having some pre-holiday travel coming up too. So while delaying things for a week was the right thing to do, it does make the timing for the 6.2 merge window awkward. That said, I’m happy to report that people seem to have taken that to heart, and I already have two dozen pull requests pending for tomorrow in my inbox. And hopefully I’ll get another batch overnight, so that I can try to really get as […]
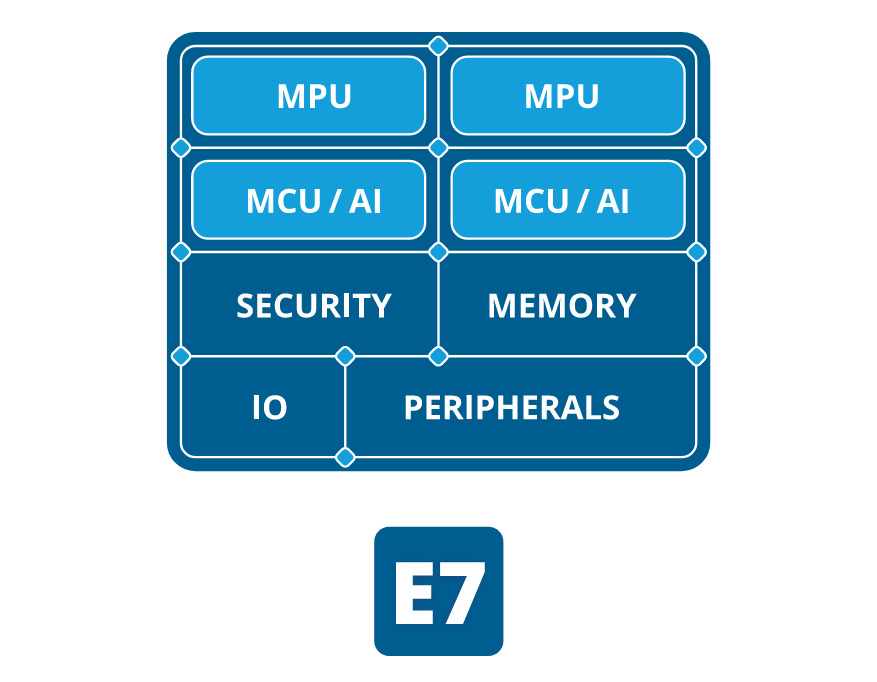
Alif Ensemble Cortex-A32 & Cortex-M55 chips feature Ethos-U55 AI accelerator
Alif Semiconductor’s Ensemble is a family of processors and microcontrollers based on Arm Cortex-A32 and/or Cortex-M55 cores, one or two Ethos-U55 AI accelerators, and plenty of I/Os and peripherals. Four versions are available as follows: Alif E1 single-core MCU with one Cortex-M55 core @ 160 MHz, one Ethos U55 microNPU with 128 MAC/c Alif E3 dual-core MCU with one Cortex-M55 core @ 400 MHz, one Cortex-M55 core @ 160 MHz, one Ethos U55 with 256 MAC/c, one Ethos U55 with 128MAC/c Alif E5 triple-core fusion processor with one Cortex-A32 cores @ 800 MHz, one Cortex-M55 core @ 400 MHz, one Cortex-M55 core @ 160 MHz, one Ethos U55 with 256 MAC/c, one Ethos U55 with 128MAC/c Alif E7 quad-core fusion processor with two Cortex-A32 cores @ 800 MHz, one Cortex-M55 core @ 400 MHz, one Cortex-M55 core @ 160 MHz, one Ethos U55 with 256 MAC/c, one Ethos U55 with […]
MediaTek unveils Dimensity 9200 Octa-core Cortex-X3/A710/A510 5G mobile processor
MediaTek has just launched the Dimensity 9200 octa-core flagship 5G mobile processor with one Cortex-X3 core, two Cortex-A710 cores, and four Cortex-A510 cores, as well as the latest Arm Immortalis-G715 GPU. Manufactured for a TSMC 4nm processor for efficiency, the new flagship processor supports mmWave 5G and sub-6GHz cellular connectivity, LPDDR5x 8,533 Mbps memory, UFS 4.0 storage, and embeds a faster MediaTek APU 690 AI processor MediaTek Dimensity 9200 specifications: Octa-core CPU subsystem 1x Arm Cortex-X3 core at up to 3.05 GHz 3x Arm Cortex-A710 cores at up to 2.85 GHz 4x Arm Cortex-A510 cores up to 1.80GHz 8MB L3 cache 6MB system cache GPU – Arm Immortalis-G715 with support for Vulkan 1.3, hardware-based ray tracing engine AI Accelerator – MediaTek APU 690 AI processor with MDLA (MediaTek Deep Learning Accelerator), MVPU (MediaTek Vision Processing Unit), SME (I don’t know what that is), and DMA Memory I/F – LPDRR5x 8,533 […]
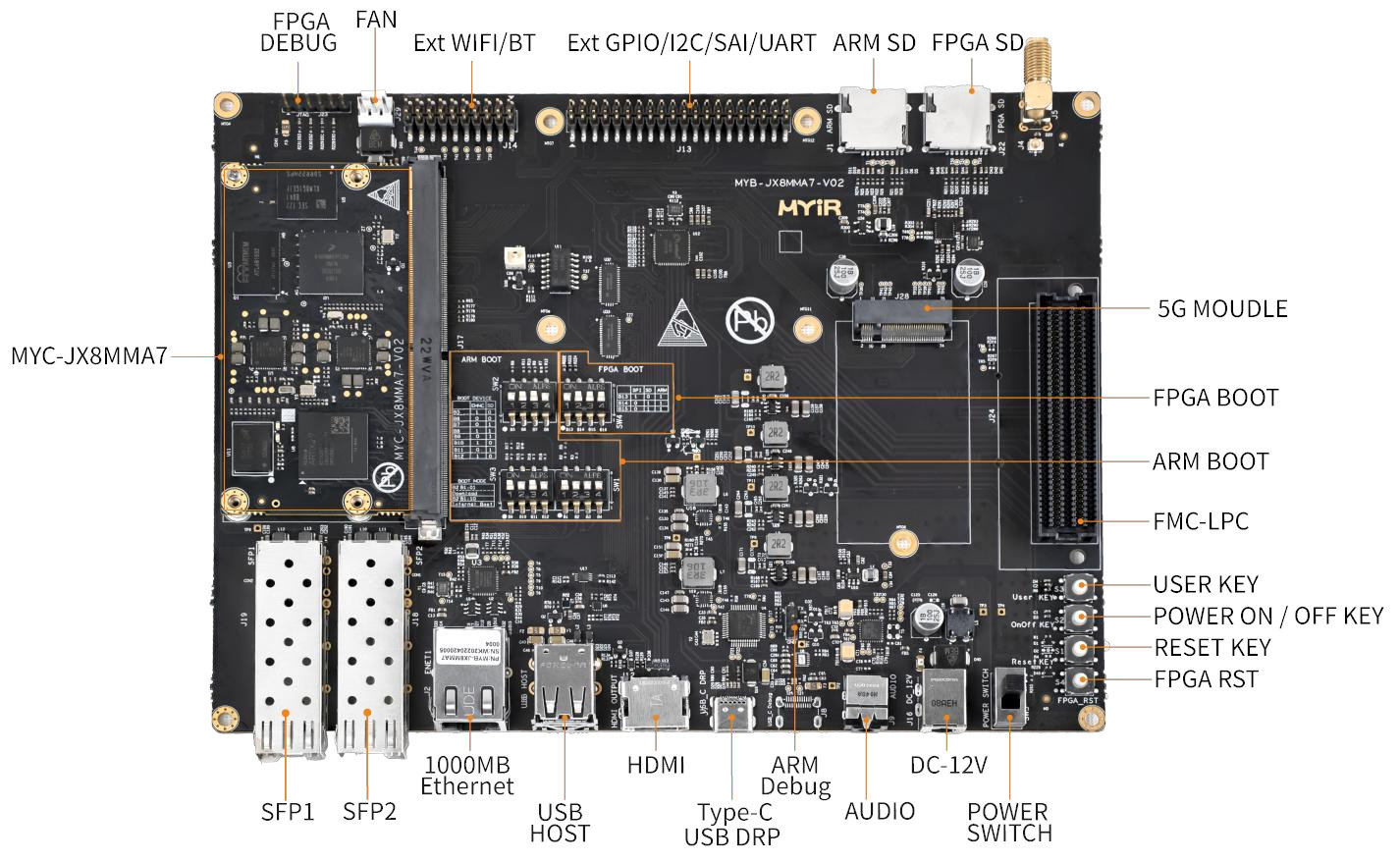
System-on-module combines NXP i.MX 8M Mini Arm CPU and Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA
MYIR Tech has launched the MYC-JX8MMA7 system-on-module combining an NXP i.MX 8M Mini quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 processor with an AMD Xilinx XC7A25T Artix-7 FPGA. The 82 x 45mm CPU module comes with 2GB LPDDR4, 8GB eMMC flash, and 32MB QSPI Flash for the Arm processor and 256MB DDR3 and 32MB QSPI Flash for FPGA. It exposes I/Os through an MXM 3.0 edge connector and can operate in the industrial temperature range (-40 to 85°C). MYC-JX8MMA7 CPU module specifications: SoC – NXP i.MX 8M Mini with quad-core Cortex-A53 processor @ up to 1.6 (industrial) or 1.8 GHz, Cortex-M4F real-time core @ 400 MHz, Vivante GC320 and Vivante GCNanoUltra 3D/2D GPUs, 1080p60 H.265, H.264, VP8, VP9 video decoder, 1080p60 H.264 & VP8 video encoder FPGA – AMD Xilinx Artix-7 XC7A25T-2CSG325 with 23,360 logic cells, 3x GTP System Memory and Storage SoC – 2GB LPDDR4, 8GB eMMC flash, and 32MB QSPI Flash FPGA […]
uConsole is a modular Arm or RISC-V handheld computer with optional 4G connectivity
Clockwork’s uConsole is a modular handheld computer with a 5-inch display, a built-in keyboard, and based on a carrier board supporting various Arm or RISC-V modules compatible with the Raspberry Pi CM3 or CM4 form factors. The device is offered with a system-on-module with up to 4GB RAM, a WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 5.0 wireless module, features micro HDMI video output, USB ports, and an audio jack, plus expansion connectors for more advanced users, and takes two 18650 batteries for power. The company also offers a 4G LTE module for cellular connectivity. The mainboard, called ClockworkPi v3.14 revision 5, offers the following: System-on-module socket – 200-pin DDR2 SODIMM socket compatible with Raspberry Pi CM3 and, through an adapter, Raspberry Pi CM4 and compatible modules Storage – MicroSD card socket Video Interfaces 40-pin MIPI DSI connector micro HDMI interface for external display Audio – 3.5mm audio jack with headphone and microphone […]
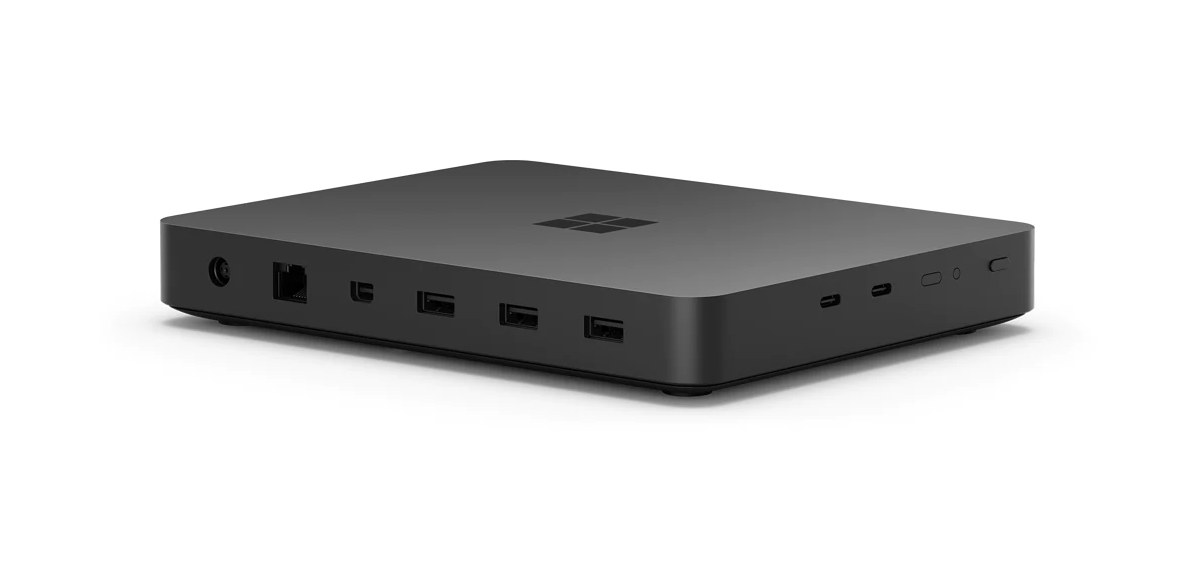
$600 Windows Dev Kit 2023 is powered by Qualcomm Snapdragon 8cx Gen 3 processor
Microsoft has just introduced the Windows Dev Kit 2023, that’s basically a Windows 11 Arm mini PC powered by a Qualcomm Snapdragon 8cx Gen 3 processor designed for developers of Windows programs. Previously known as “Project Volterra”, the system comes with 32GB RAM, 512GB NVMe storage, mini DP video output, Ethernet, WiFi 6, and Bluetooth 5.1 connectivity, as well as five USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports, and more. Windows Dev Kit 2023 specifications: SoC – Qualcomm Snapdragon 8cx Gen 3 compute platform with CPU – 4x 3.0 GHz Prime cores, 4x 2.4 GHz Efficiency Cores GPU – Unnamed Adreno GPU with DirectX 12 (DX12) API support DSP – Qualcomm Hexagon Processor, Qualcomm Sensing Hub AI – Qualcomm Neural Processing Engine SDK support for AI (up to 29+ TOPS) System Memory – 32GB LPDDR4x RAM Storage – 512GB NVMe SSD Video Output – Mini DisplayPort (mini DP) with support for HBR2 […]
Linux 6.0 release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V, and MIPS architectures
Linux 6.0 has just been released by Linus Torvalds: So, as is hopefully clear to everybody, the major version number change is more about me running out of fingers and toes than it is about any big fundamental changes. But of course there’s a lot of various changes in 6.0 – we’ve got over 15k non-merge commits in there in total, after all, and as such 6.0 is one of the bigger releases at least in numbers of commits in a while. The shortlog of changes below is only the last week since 6.0-rc7. A little bit of everything, although the diffstat is dominated by drm (mostly amd new chip support) and networking drivers. And this obviously means that tomorrow I’ll open the merge window for 6.1. Which – unlike 6.0 – has a number of fairly core new things lined up. But for now, please do give this most […]