OK… I’m a bit late on that one. Linus Torvalds released Linux 5.7 last week: So we had a fairly calm last week, with nothing really screaming “let’s delay one more rc”. Knock wood – let’s hope we don’t have anything silly lurking this time, like the last-minute wifi regression we had in 5.6.. But embarrassing regressions last time notwithstanding, it all looks fine. And most of the discussion I’ve seen the last week or two has been about upcoming features, so the merge window is now open and I’ll start processing pull requests tomorrow as usual. But in the meantime, please give this a whirl. We’ve got a lot of changes in 5.7 as usual (all the stats look normal – but “normal” for us obviously pretty big and means “almost 14 thousand non-merge commits all over, from close to two thousand developers”), So the appended shortlog is only […]
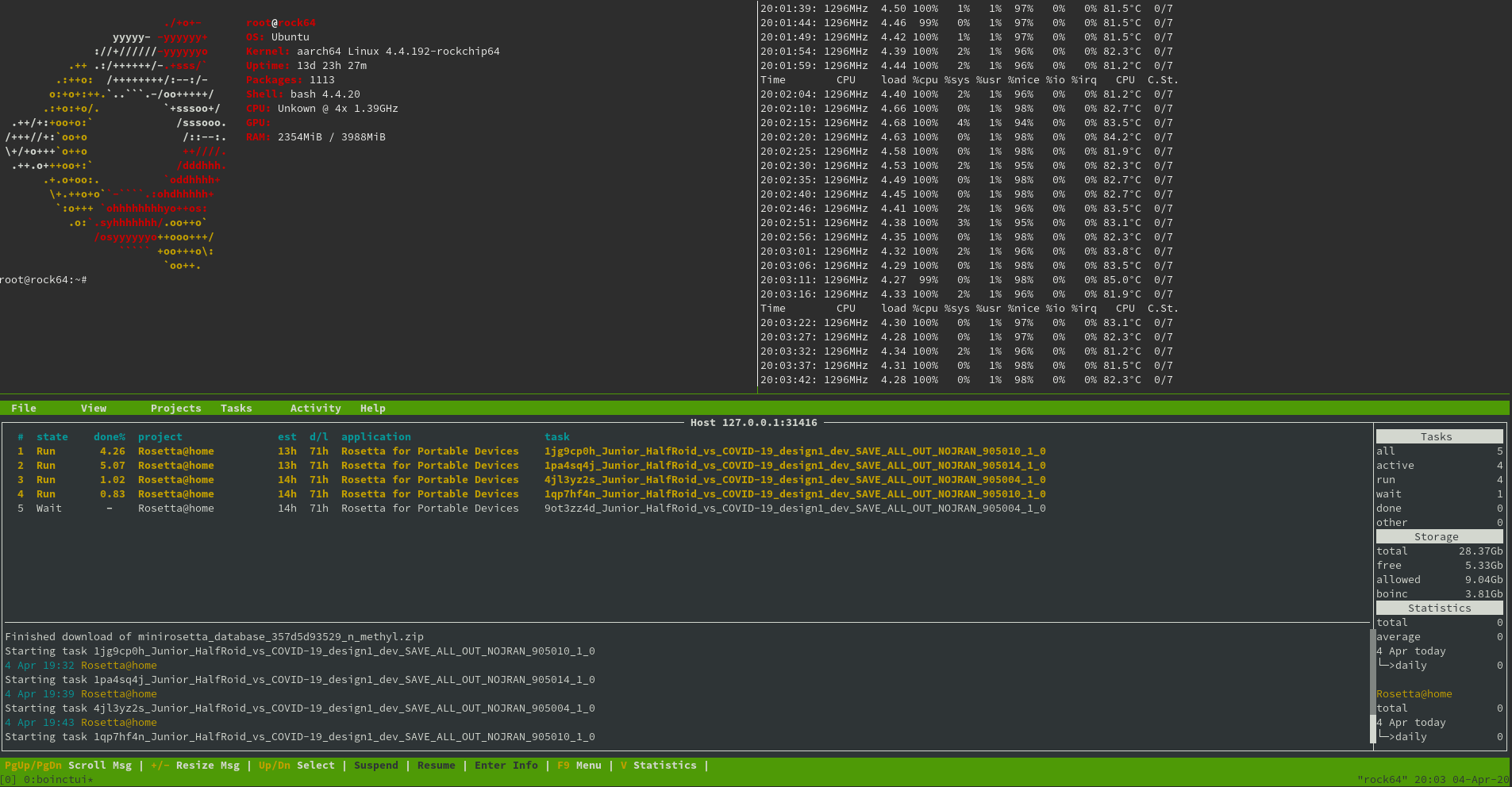
Rosetta@Home Now Supports 64-bit Arm SBC’s and Servers in the Fight against COVID-19
Folding@Home and Rosetta@Home projects aim to perform biomedical research using the computing power of volunteers. Basically, you just need to install a program on your computer, and it will use idle computing power to perform complex calculations without slowing down your computer as long as you are not short in RAM. The projects are now working on COVID-19 to understand how SARS-CoV-2 protein is structured which could help find a cure. The programs have been available for Windows, Linux and Mac OS on 32-bit and 64-bit x86 targets for years, but very recently Rosetta@Home has been made available for 64-bit ARM targets so people can also run BOINC program on Arm Linux SBCs such as Raspberry Pi 4, NVIDIA Jetson Nano, or Rock64, or even powerful Arm servers to help with Rosetta@Home project’s COVID-19 research. As explained in an article on miniNodes, you’ll need a board with at least 2GB […]
AWS EC2 6th Gen Instances are 7x Faster thanks to Graviton 2 Arm Neoverse N1 Custom Processor
Last year Amazon introduced their first 64-bit Arm-based ECS2 “A1” instances which were found to deliver up to 45% cost savings over x86 Instances for the right workloads. A few months ago, AWS (Amazon Web Services) provides a new offering with bare-metal A1 instances, and with re:invent 2019 now taking place the company has unveiled AWS ECS2 6th generation Arm instances (which they did not call A2 instances yet) powered by Graviton 2 processor comprised of custom Arm Neoverse N1 cores and promising up to 7x the performance of the original A1 instances. There will be three types of Graviton2-powered EC2 instances with the d suffix indicating NVMe local storage: M6g and M6gd for General Purpose workloads (application servers, mid-size data stores, microservices, and cluster computing) with 1 to 64 vCPUs and up to 256 GB of memory. C6g and C6gd for Compute-Optimized workloads (high-performance computing, video encoding, gaming, and […]
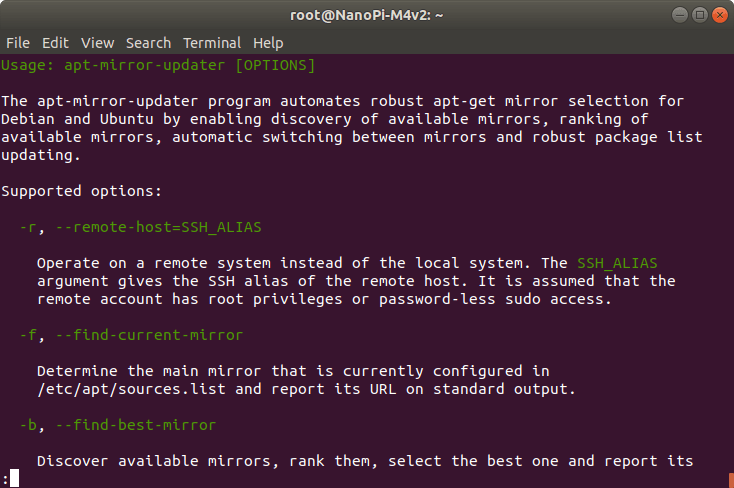
Changing Ubuntu Apt Mirror from the Command Line, and the Lack of Arm64 Mirrors
When you install Ubuntu on a computer, you’d normally go through the installation ISO which guides you through a wizard where you select your location among other things, and that means you get connected to the mirror closest to your location allowing timely updates. But for those of us who flash Ubuntu images on Arm SBC’s, the mirror is normally fixed to the one set by the developer be it in China or Slovakia, or defaults to the US mirror. It still works, but it can be slower than necessary. In a computer, an easy way to change that from Ubuntu desktop to launch Software & Update program and change the download from field to a mirror in your country or neighboring country as shown below. But I’ve found myself mostly connecting to boards over SSH since it’s easier that way for reviews. One way to change the mirror would […]
How to Sandbox an arm64 GCC on aarch64 Hardware with armv7 Userspace
CNXSoft: Guest post by Blu about setting up arm64 toolchain on 64-bit Arm hardware running a 32-bit Arm (Armv7) rootfs. Life is short and industry progress is never fast enough in areas we care about. That’s an observation most of us are familiar with. One would think that by now most aarch64 desktops would be running arm64 environments, with multi-arch support when needed. Alas, as of late 2019, chromeOS on aarch64 is still shipping an aarch64 kernel and an armhf userspace. And despite the fine job by the good folks at chromebrew, an aarch64 chromeOS machine in dev mode ‒ an otherwise excellent road-warrior ride, is stuck with 32-bit armhf. Is that a problem, some may ask? Yes, it is ‒ aarch64 is the objectively better arm ISA outside of MCUs, from gen-purpose code to all kinds of ISA extensions, SIMD in particular. That shows in contemporary compiler support and […]
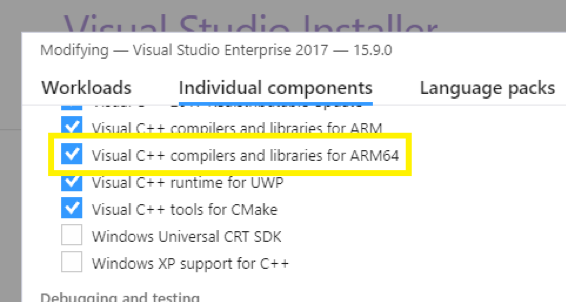
Microsoft now Supports ARM64 Apps in Visual Studio 15.9, Microsoft Store
The first “proper” Windows Arm laptops became available earlier this year, but they disappointed most people due to their high price and relatively poor performance. They only really make sense for people who need LTE connectivity and very long battery life (over 20 hours). Price will likely stay elevated for the foreseeable future, but at least performance will increase thanks to faster processors such as Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 processor found in Lenovo Yoga C630 WOS Laptop ($849.99 and up once available), and the rumored sm8180 laptop processor that may be, or not, announced on December 4-6 during Snapdragon Tech Summit. Hardware is one thing, but software is also important. As far as I understand, while UWP (Universal Windows Platform) apps already supported native 32-ARM compilation , legacy Win32 apps relied on x86 “emulation” / binary translation, which may slowdown performance. But Windows users may also get some software optimization soon, […]
VMWare Showcases ESXi Bare Metal Hypervisor Support for ARM64 Edge Servers
As I checked my Twitter timeline in Thunderbird this morning, I started to see a lot of tweets about #VMworld2018 and “ESXi on 64-bit Arm”. What is that? VMWare has just announced and showcased several technology innovations at VMworld 2018, including Virtualization on 64-bit ARM for Edge, and the company demonstrated ESXi on 64-bit ARM running on a windmill farm at the Edge. It may be useful to readers (and this writer) to look up what ESXi is and does exactly. As explained on VMWare website: VMware ESXi is a purpose-built bare-metal hypervisor that installs directly onto a physical server. With direct access to and control of underlying resources, ESXi is more efficient than hosted architectures and can effectively partition hardware to increase consolidation ratios and cut costs for our customers. So basically it’s an hypervisor that stays a close as possible to the hardware to keep performance optimal, and […]
NetBSD ARM64 Images Now Available with SMP for Raspberry Pi 3, Some NanoPi Boards, and Pine64 Boards
NetBSD on Arm started in 2014 with the release of version 7.0, and last year device tree support was implemented and tested on some Allwinner H3 boards. But apparently, so far NetBSD only supported 32-bit Arm, with initial support for 64-bit Arm (ARM64) committed last April, but good progress has been made, and NetBSD ARM64 bootable firmware images are now available with SMP (multi-core) support. Eight different NetBSD ARM64 images can be downloaded: Generic NetBSD 64-bit image for Raspberry Pi 3 and NVIDIA Tegra X1 Two images for FriendlyELEC boards namely NanoPi NEO2 and NEO Plus2 boards Five images for the following Pine64 boards and hardware platforms Pine A64/A64+ Pine A64-LTS / Sopine with baseboard Pine H64 Pinebook laptop ROCK64 (ROCK64Pro not yet supported) The supported hardware matrix shows most features are supported, but there are still a few things missing such as GPU, crypto and MIPI CSI on all […]