Just a couple of days ago, Amazon introduced EC2 A1 Arm instances based on custom-designed AWS Graviton processors featuring up to 32 Arm Neoverse cores. Commenters started a discussion about price and the real usefulness of Arm cores compared to x86 cores since the latter are likely to be better optimized, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) pricing for EC2 A1 instances did not seem that attractive to some. The question whether it makes sense will obviously depend on the workload, and metrics like performance per dollar, and performance per watt. AWS re:Invent 2018 is taking place now, and we are starting to get some answers with Amazon claiming up to 45% reduction in costs. It sounds good, except there’s not much information about the type of workload here. So it would be good if there was an example of company leveraging this type of savings with their actual products or […]
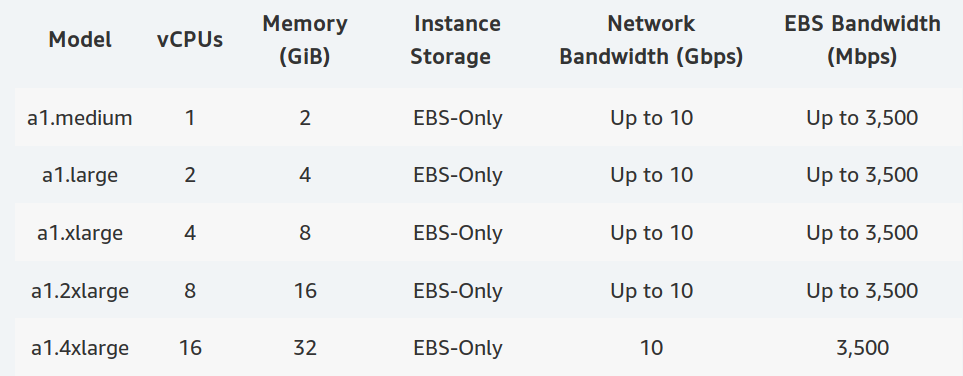
Amazon Launches 64-bit Arm Server “A1” Instances
Amazon has developed AWS Graviton processors optimized for cloud applications and delivering power, performance, and cost optimizations over their Intel counterpart. The processors feature 64-bit Arm Neoverse cores and custom silicon designed by AWS themselves, and can be found today in Amazon EC2 A1 instances. The screenshot above shows Amazon Linux 2, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6, Ubuntu 18.04 Server, and Ubuntu 16.04 Server machine images having options for either 64-bit x86 or 64-bit Arm servers. Amazon Arm server instance are particularly suitable for applications such as web servers, containerized microservices, caching fleets, distributed data stores, as well as development environments. Amazon further explains: A1 instances are built on the AWS Nitro System, a combination of dedicated hardware and lightweight hypervisor, which maximizes resource efficiency for customers while still supporting familiar AWS and Amazon EC2 instance capabilities such as EBS, Networking, and AMIs. Amazon Linux 2, Red Hat Enterpise Linux […]
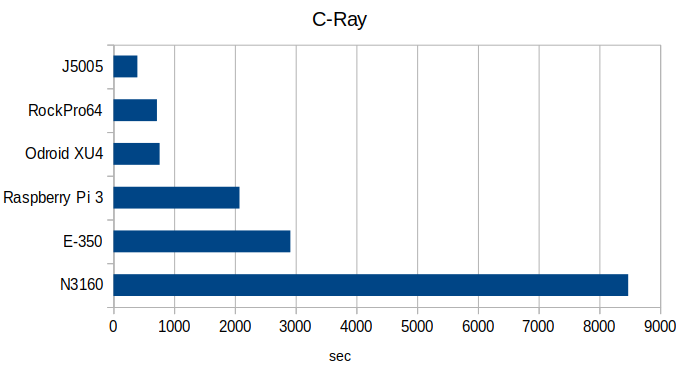
An Attempt to Benchmark Entry-level x86 Boards against RK3399 & Exynos Arm Boards
Some Arm boards have become quite powerful, while hardware based on low power Intel processor has generally become cheaper with both architectures somewhat converging in terms of performance and price. Piotr Maliński got interested and purchased some low cost (<$150) Intel hardware to compare to mid-range Arm boards, throwing a Raspberry Pi 3 B+ into the mix as well for comparison. Those are the Intel test boards / computers: Qotom motherboard with Intel Atom Z3735F Bay Trail processor, 2GB RAM, 32GB flash – $74 + shipping on Aliexpress Piesia nano ITX board with Intel Celeron N2806 Bay Trail processor, DDR3 SO-DIMM socket, SATA / mSATA interfaces – Piotr found it for around $85 on Aliexpress, but the price now jumped to over $150 plus shipping, which does not make it very attractive Generic thin mini ITX motherboard based on Celeron N3160 “Braswell” processor, DDR3 SO-DIMM socket, SATA / mSATA interfaces. $62.68 […]
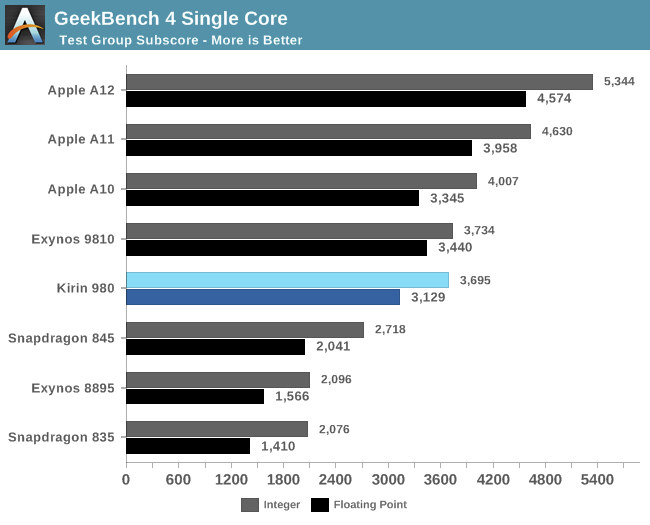
HiSilicon Kirin 980 Benchmarks Show Cortex A76’s Impressive Performance & Efficiency Improvements
HiSilicon Kirin 980 was the first processor announced with Cortex A76 cores, which were said to deliver laptop-class performance, with 35% performance improvement over Cortex A75, and around twice the performance of Cortex A73 cores thanks to improvements, and a higher CPU frequency up to 3.0 GHz. But now that Huawei Mate 20 / Mate 20 Pro smartphones are out, various reviews have been published, and Anandtech was mostly able to confirm the claims. In most case, actual results were inline with expectation despite Kirin 980 clock speed being “limited” to 2.6 GHz. Looking at GeekBench 4 single-thread integer and floating-point scores, the Cortex A76 core based Kirin 980 is significantly faster than Cortex A73 powered Snapdragon 835 clocked @ 2.45 GHz. Precisely: 1.77x faster in the integer score,and 2.21x faster in the floating point score. SPECS2006 confirmed the good performance with 1.89x higher integer score, and 2.04x faster for […]
HiSilicon Hi1620 Server SoC to Features up to 64 Arm “Ares” Cores
A few years ago we covered Hisilicon D02 server board powered by the company’s Hip05 SoC with 16 or 32 Arm Cortex A57 cores. I had not seen any updates since then myself, but HiSilicon has released new “TaiShan” Arm based server SoCs every year, and recently unveiled Hi1620, the world’s first 7nm datacenter Arm processor, featuring 24 to 64 Arm “Ares” cores clocked at up to 3.0 GHz. Ares cores are supposed to greatly improve single thread performance in order to compete with x86 server chips. HiSilicon Hi1620 processors specifications: CPU – 24 to 64 Ares ARMv8.2 cores clocked at 2.4 – 3.0 GHz Cache – L1: 64KB I-cache, 64KB D-cache; L2: 512KB private per core, L3: 24-64 shared among cores (1MB/core) Memory – 8x DDR4 channels up to 3200 MHz Interconnect – Coherent SMP interface for 2S & 4S, 3 ports up to 240 Gbit/s per port I/Os […]
Linux 4.19 Release – Main Changes, Arm and MIPS Architectures
With Linus Torvalds taking a leave from the Linux kernel project, Greg Kroah-Hartman was the one to release Linux 4.19 last Sunday: Hi everyone! It’s been a long strange journey for this kernel release… While it was not the largest kernel release every by number of commits, it was larger than the last 3 releases, which is a non-trivial thing to do. After the original -rc1 bumps, things settled down on the code side and it looks like stuff came nicely together to make a solid kernel for everyone to use for a while. And given that this is going to be one of the “Long Term” kernels I end up maintaining for a few years, that’s good news for everyone. A small trickle of good bugfixes came in this week, showing that waiting an extra week was a wise choice. However odds are that linux-next is just bursting so […]
Arm ServerReady is a Compliance Program for Arm-based Servers
The Server Base System Architecture (SBSA) specification was unveiled in 2014 in order to standardize all Arm based servers and let them all run the same operating system images. However so far, manufacturers would just test specification requirements by themselves without having their claims fully tested and certificated. That’s why Arm has just unveiled the Arm ServerReady certification program for Arm based servers which relies on the Architecture Compliance Suite (ACS) for SBSA and SBBR (Server Base Boot Requirements) verification. Basically the servers must be able to boot standard operating systems and run the ACS. The servers that pass the ACS are then granted the Arm ServerReady certificate. The current Arm ServerReady version 1.0 certification utilizes ACS version 1.6 for testing SBSA version 3.1 and SBBR version 1.0 compliance. Ampere, HXT, Marvell, Qualcomm, as well as ODMs such as Femrice, Gigabyte and UIT have already received Arm ServerReady version 1.0 […]
Arm Mbed Gets a Linux OS for Cortex-A Processors
Arm Mbed is known as a free, open source platform and operating system that makes it easier to design IoT products based on Cortex-M micro-controllers, but the company figured out it might be a good idea to make something similar for IoT devices based on Arm Cortex-A processor and that’s exactly what Mbed Linux OS is made for. Embedded & IoT devices normally need to be supported for many years, often optimized for cost and battery life, and make sure security patchsets are applying to your products. Companies often managed to do all those themselves but it’s not the most cost-effective solution, so instead Arm decided to leverage Linux and offer Mbed Linux OS optimized for IoT devices yo their customers. The solution comes with built-in security, device management (e.g. OTA firmware upgrades) via the Pelion IoT Platform, common development tools for faster time to market, and so on. Some […]