GPU compute promises to deliver much better performance compared to CPU compute for application such a computer vision and machine learning, but the problem is that many developers may not have the right skills or time to leverage APIs such as OpenCL. So ARM decided to write their own ARM Compute library and has now released it under an MIT license.
The functions found in the library include:
- Basic arithmetic, mathematical, and binary operator functions
- Color manipulation (conversion, channel extraction, and more)
- Convolution filters (Sobel, Gaussian, and more)
- Canny Edge, Harris corners, optical flow, and more
- Pyramids (such as Laplacians)
- HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients)
- SVM (Support Vector Machines)
- H/SGEMM (Half and Single precision General Matrix Multiply)
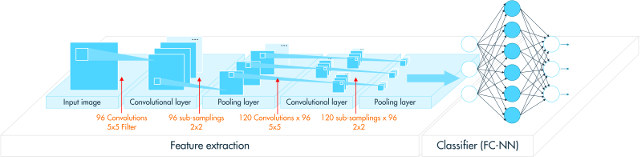
- Convolutional Neural Networks building blocks (Activation, Convolution, Fully connected, Locally connected, Normalization, Pooling, Soft-max)
The library works on Linux, Android or bare metal on armv7a (32bit) or arm64-v8a (64bit) architecture, and makes use of NEON, OpenCL, or NEON + OpenCL. You’ll need an OpenCL capable GPU, so all Mali-4xx GPUs won’t be fully supported, and you need an SoC with Mali-T6xx, T-7xx, T-8xx, or G71 GPU to make use of the library, except for NEON only functions.
In order to showcase their new library, ARM compared its performance to OpenCV library on Huawei Mate 9 smartphone with HiSilicon Kirin 960 processor with an ARM Mali G71MP8 GPU.
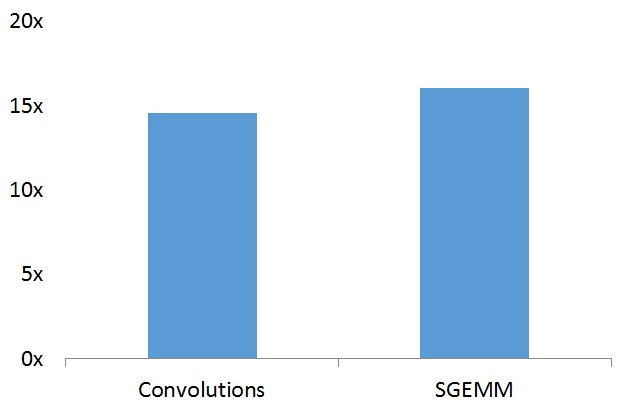
Even with some NEON acceleration in OpenCV, Convolutions and SGEMM functions are around 15 times faster with the ARM Compute library. Note that ARM selected a hardware platform with one of their best GPU, so while it should still be faster on other OpenCL capable ARM GPUs the difference will be lower, but should still be significantly, i.e. several times faster.
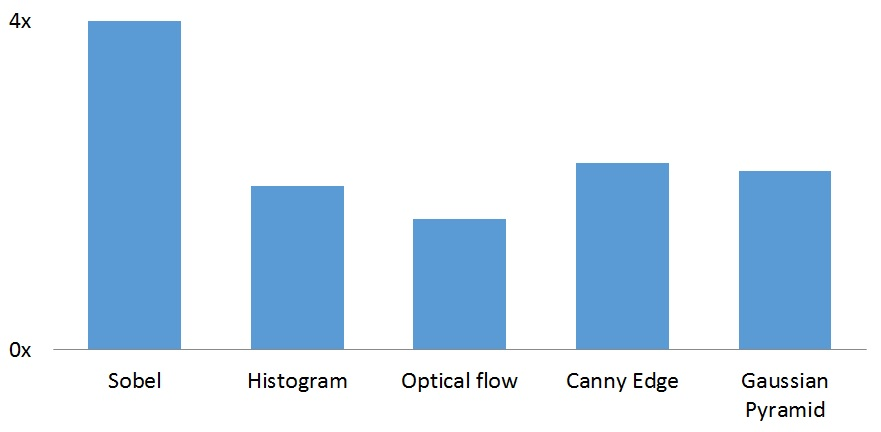
The performance boost in other function is not quite as impressive, but the compute library is still 2x to 4x faster than OpenCV.
While the open source release was just about three weeks ago, the ARM Compute library has already been utilized by several embedded, consumer and mobile silicon vendors and OEMs better it was open sourced, for applications such as 360-degree camera panoramic stitching, computational camera, virtual and augmented reality, segmentation of images, feature detection and extraction, image processing, tracking, stereo and depth calculation, and several machine learning based algorithms.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress. We also use affiliate links in articles to earn commissions if you make a purchase after clicking on those links.





It’s not only about ‘boosting’ performance in synthetical benchmarks. But when a specific function can be done on OpenCL kernels running inside the GPU the CPU is free for other stuff. So even if benchmarks show only a 1.5x improvement… in case it’s done using OpenCL the overall performance might increase a lot if other stuff can be done in parallel on CPU cores.
The OS I’m using on my workhorse moved already years ago the whole window manager stuff to the GPU cores (or Execution Units in Intel speak) and does the same with some special stuff like compression/decompression. It’s always fun to decompress a large ZIP file with CPU utilization below 20% and when trying the same with tools basing on libzip performance drops horribly and even fans start to make some noise due to 100% CPU utilization on all cores 🙂
Open Source ARM Compute Library with binary blob drivers with terrible support. Tell them to come back when they have proper drivers with mainline kernel driver support.
What exactly has been opensourced?
Some open source GPU drivers would be much appreciated.
I could have really used this last year on a contract… It was really frustrating that I couldn’t easily leverage ARM GPUs and SIMD for an Android app I was contracted to port
What OpenCV calls are they benchmarking against? OpenCV has OpenCL kernels as well. Are they comparing them to those? And why didn’t they just add these features to OpenCV? (Maybe that’s political b/c OpenCV is an Intel project… but it already has limited support for NEON even now)
It’s a real shame ARM’s support for actually using their GPU/SIMD is lightyears behind Intel
And what about this seemingly aborted project?
http://projectne10.github.io/Ne10/
couldn’t they have at least merged the work so that this library had some limited FFT? (It’s 1D-FFT not 2D-FFT which kinda sucks)
They compared it to OpenCV with NEON + single thread. I don’t know which exact OpenCV calls were used.
ARM talked about Ne10 in their blog post about the Compute Library, and while there’s not that much activity, it’s still being updated.
Looks like a high-quality HPC codebase at first glance. And such code is always welcome.
OpenCV is pretty pants so this isn’t surprising.
I love using OpenCL but it’s pretty pointless for free software projects still due to lack of ubiquitous system support. NEON is also rather fun but developing for phones sux.
@notzed
I’m currently in the process of porting a small raytracing OCL project of mine to a Midgard. No phones involved whatsoever – it’s all self-hosted ; )
Upcoming ARM webinar about the Compute Library entitled “Compute Library: optimizing computer vision and machine learning on ARM” on May 16 at 9:00 and 17:00 BST.
http://pages.arm.com/index.php/email/emailWebview?mkt_tok=eyJpIjoiT0RSbFpUWXlOVEJoWWpFMSIsInQiOiJPRmg2T2hxSkVJWSt2U3luYi9MY0RtV1BrUEpTdGZmaVBnM1c4eVhkQXZZTGN5TFI3dldNVG9Vd3F6YTUyYkRxemNtcDJuYi9Rbm5vQjFFWklhblhsT1lxaHBkaTNNeUsrMy9nVkptY2F4ekYrcW42N0UxbEpRL3RpZ1lvQ0h3byJ9
Topics:
Intel releases Compute Library for Deep Neural Networks (clDNN) @ https://github.com/01org/cldnn
Compute Library 17.9 -> https://community.arm.com/graphics/b/blog/posts/announcing-the-compute-library-17-9
(Link not working for me right now).
@cnxsoft
Just wondering if someone could confirm – They still don’t have OpenCL running on CPU, right?
I saw this: https://www.arm.com/about/newsroom/media-alert-arm-extends-opencl-to-the-arm-cortex-a-processor-family.php
But actually trying to find “OpenCL for NEON” leads to nothing
Would have been nice to have write-once OpenCL kernels that you can run everywhere
@geokon
They seem to have given up it.
OpenCL on Arm is still possible via pocl. Blu tested it on Arm Cortex A72 @ https://www.cnx-software.com/2017/11/14/first-opencl-encounters-on-cortex-a72-some-benchmarking/
@cnxsoft
wow, thank you so much for pointing me in the right direction. I’m really glad I asked. I hadn’t seen that or heard of pocl. Really appreciate your work CNX-soft 🙂