Since I’ve just installed Ubuntu 17.10 on MeLE PCG35 Apo, I decided I should also run some benchmarks comparing with other ARM and x86 Linux platforms I’ve tested in the past.I was particularly interested to compare the performance of Intel Apollo Lake processors (Celeron J3455 in this case) against higher end ARM processors like Rockchip RK3399 (2x A72, 4x A53) since systems have a similar price (~$150+), as well as against the older Bay Trail processor to see the progress achieved over the last 2 to 3 years.
To do so, I used Phoronix Benchmark Suite against Videostrong VS-RK3399 results (RK3399 development board):
|
1 2 3 4 |
sudo apt install php-cli php-gd php-xml php-zip wget http://phoronix-test-suite.com/releases/repo/pts.debian/files/phoronix-test-suite_7.4.0_all.deb sudo dpkg -i phoronix-test-suite_7.4.0_all.deb phoronix-test-suite benchmark 1709271-TY-1704029RI26 |
The benchmark first issued a warning about “powersave” governor, but I still went ahead, and once completed I change it to “performance” governor:
|
1 2 |
sudo apt install cpufrequtils sudo cpufreq-set -r -g performance |
…and ran the tests again. All results are available on OpenBenchmarking.
Let’s address the governor results first. cpufreq-info reports that powersave governor can also switch between 800 MHz and 2.30 GHz (turbo freq).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
sudo cpufreq-info cpufrequtils 008: cpufreq-info (C) Dominik Brodowski 2004-2009 Report errors and bugs to cpufreq@vger.kernel.org, please. analyzing CPU 0: driver: intel_pstate CPUs which run at the same hardware frequency: 0 CPUs which need to have their frequency coordinated by software: 0 maximum transition latency: 0.97 ms. hardware limits: 800 MHz - 2.30 GHz available cpufreq governors: performance, powersave current policy: frequency should be within 800 MHz and 2.30 GHz. The governor "powersave" may decide which speed to use within this range. current CPU frequency is 629 MHz. |
As we’ll see from the results below pitting “MeLE PCG35 Apo – Ubuntu 17.10” (with powersave) and “MeLE PCG35 Apo- Ubuntu 17.10 Performance” that the governor settings did not matter one bit on the results, at least for the six benchmarks I ran.
Note that “MeUbuntu 14.04.3” represents MeLE PCG02U TV stick running Ubuntu 14.04.3. Every platform runs a different OS and kernel, so keep in mind the results may differ slightly (up or down) with different version. But as we’ll see the differences in performance are large enough that it likely does not matter that much.
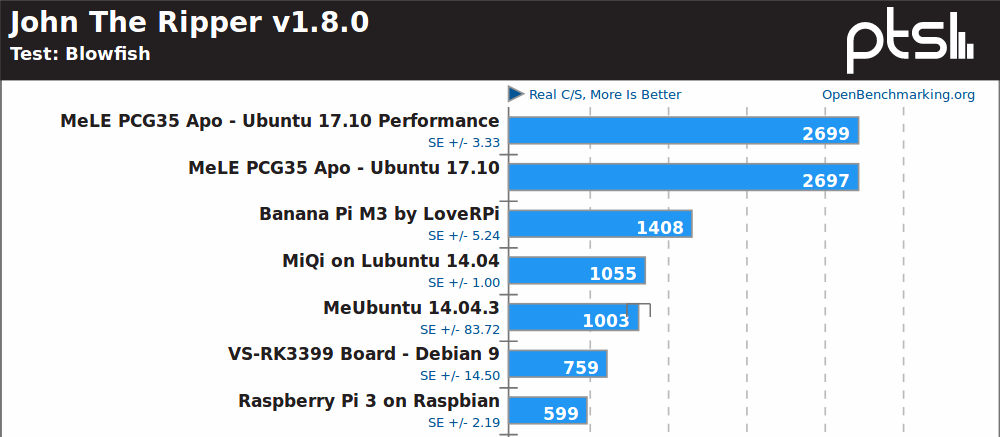 John the Ripper password cracker, a multi-threaded benchmark, shows the Apollo Lake processor is clearly ahead of Rockchip RK3399 hexa-core processor, and the fastest ARM platform, Banana Pi M3, is equipped with an Allwinner A83T octa-core Cortex A7 processor @ 2.0 GHz. The Bay Trail system is over twice as slow as the Apollo Lake one, also note the larg-ish standard deviation (+/- 83.72) due to some cooling problem in the small form factor.
John the Ripper password cracker, a multi-threaded benchmark, shows the Apollo Lake processor is clearly ahead of Rockchip RK3399 hexa-core processor, and the fastest ARM platform, Banana Pi M3, is equipped with an Allwinner A83T octa-core Cortex A7 processor @ 2.0 GHz. The Bay Trail system is over twice as slow as the Apollo Lake one, also note the larg-ish standard deviation (+/- 83.72) due to some cooling problem in the small form factor.
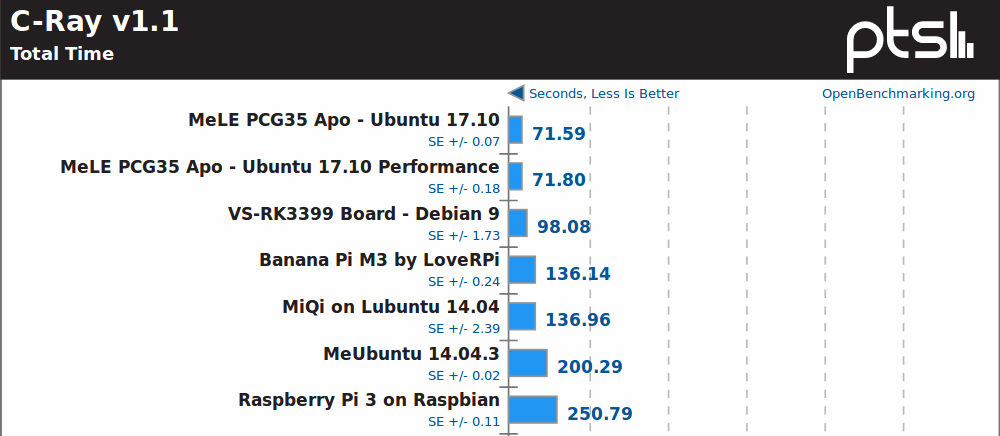
C-Ray is another multi-threaded benchmark, and here Rockchip RK3399 SoC does fairly well, but still but quite as well as the Celeron J3455.
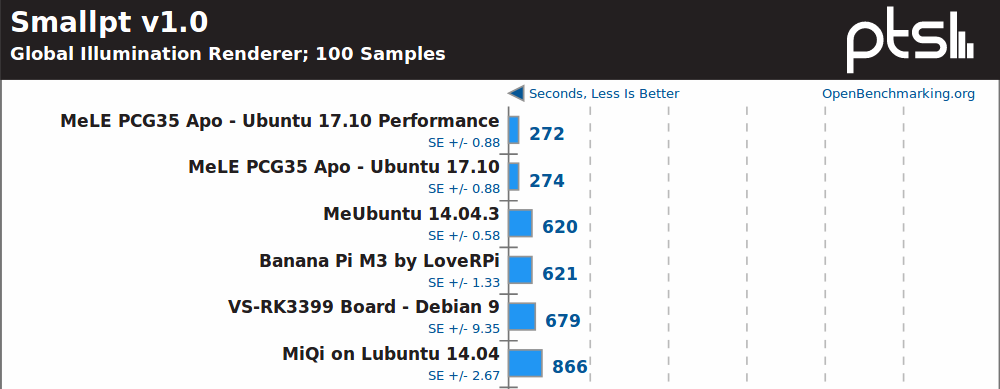
Smallpt, yet another multi-threaded benchmark, does not really change the order with MeLE PCG35 Apo well ahead.
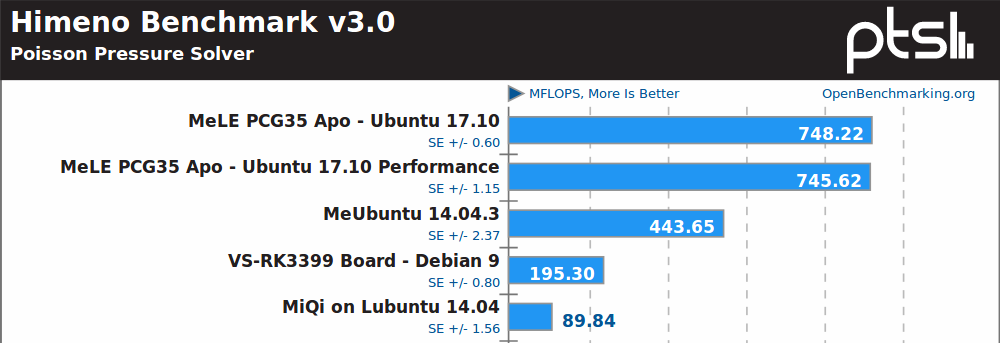
Himeno, a linear solver of pressure Poisson, must be using some x86 specific instructions or optimizations, as Intel platforms are well ahead, with Celeron J3455 about 2.5x faster than Rockchip RK3399 board.
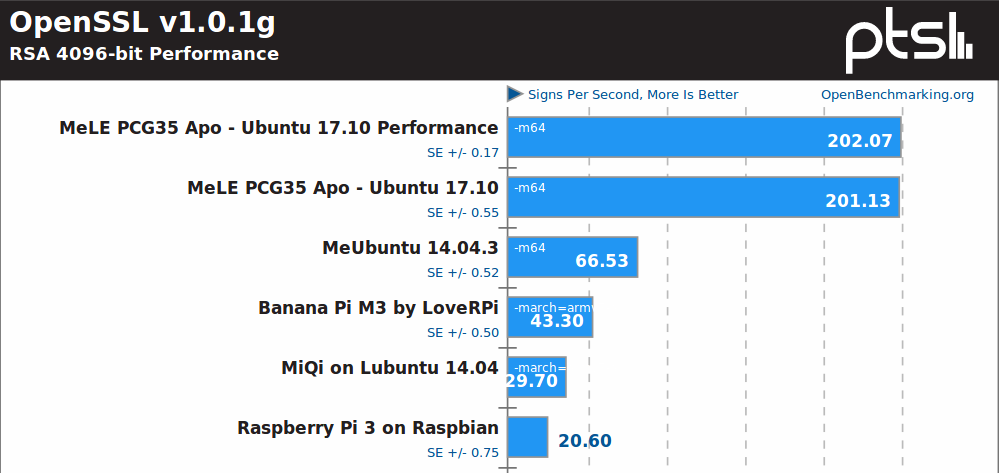
OpenSSL is the domain of Intel platforms likely benefiting from Advanced Encryption Standard instruction set (AES-NI). Performance improvement between Bay Trail and Apollo Lake is also impressive here. You’d need 10 Raspberry Pi 3 to match MeLE PCG35 Apo in this particular test.
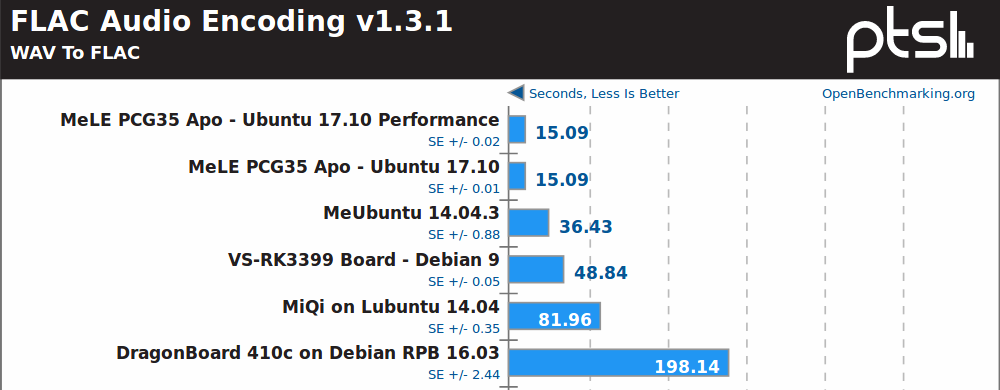
Intel is normally better with SIMD accelerated multimedia application, and FLAC audio encoding (single threaded) confirms that.
I was expecting a close fight between Rockchip RK3399 and Celeron J3455, but RK3399 only has two fast Cortex A72 cores against four x86 cores in the Intel Apollo Lake SoC.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress. We also use affiliate links in articles to earn commissions if you make a purchase after clicking on those links.




Two small remarks:
1) On Intel systems with intel_pstate driver running (Sandy Bridge or above and obviously a somewhat recent kernel) powersave and performance are expected to give similar results in synthetic benchmarks (since ramping up CPU clockspeeds fast enough). But on other platforms depending on kernel version powersave vs performance can result in huge performance differences (since powersave can lead to the CPU cores remaining on lowest allowed clockspeed all the time while performance chooses the maximum as on Intel)
2) OpenSSL performance and AES-NI:if we’re talking about AES here then ARMv8 SoCs with AES crypto extensions (like RK3399 that is missing above — why?) should be able to compete. At least when we (Armbian community) did some tests a while ago single threaded Banana Pi M3 ‘performance’ at 1.8 GHz (Cortex-A7) was ~30 times lower compared to a Cortex-A53 at 1.3 GHz with ARMv8 crypto extensions enabled.
For now I’ve been quite disappointed by RK3399’s performance. I managed to make my build farm run on the H96max at 1.8 GHz (A72) + 1.4 GHz (A53), and at 1.8 GHz, the A72 shows slightly lower performance than the RK3288 on the MiQi (ie 16.2 sec instead of 16.0 for a build). And that’s the best I can take out of it, it’s in 32-bit (armv7t or armv8l). In 64-bit (armv8), it’s about 10-15% slower for the same task. It was said that the A72’s architecture was very close to the A17, the former with 3-decode and 5-issue, the latter with 2-decode and 5-issue, but I suspect we’re caping out on the ALU after the instructions are decoded so the A72 isn’t faster in the end. By the way the test using JtR above shows the 4-core MiQi 35% faster than the 6-core RK3399, so that tends to confirm that there’s definitely a corner case where it doesn’t shine unfortunately.
@willy
Those settop boxes traditionally have notoriously bad thermal design, and a 28nm A72 can get really hot at near-2GHz — have you monitored the throttling?
Why not add a comparative about power consumption? It would be interesting…
Thanks.
Unless it is like for like hardware the results have no place in the real world.
Most TV boxes watch TV and comparing a £30 less board against a £130 + Intel J3455 Apollo Lake. Is like racing a child’s peddle bike against a F1 Racer. Funny but no value.
How about benchmarking a Xbox One against a Intel J3455 Apollo Lake? It would have just as much real world use.
@blu
Yes absolutely, and it’s really at 1.8 GHz while running such tests, and doesn’t throttle. BTW the advertised 1.5 and 2.0 GHz frequencies are not even part of the frequencies list at all, that’s the beauty of “up to”, it probably means that it can go “up to 2.0 GHz if you hack your DTB”.
Honestly the perf is not bad at all and it heats less than the 3288 at the same performance level, it just doesn’t have enough cores to compete with it. The RK3288 has 4 strong cores, but the 3399 has only two, and the 4 remaining A53 are just jokes compared to them. Basically you have less than an odroid C2 sharing the cache and RAM bandwidth with the two A72. It’s fine to run SSH or probably to run background music on a tablet but that’s almost all, as they’re less than half of the performance of the large ones.
The A75 is said to be a real performer. We’ll see when it’s available. For now I’m sticking to the A17.
ARM is not power efficient, it’s just cheap in some TV box :
50$ A53 x4 cpu burn = 5Watt
200$ intel I3 5005U cpu burn = 15-20W
Intel is 10x more powerfull in benchmark, so 3X more efficient benchmark pt / watt.
Conclusion expensive Arm is a no go
@willy
I don’t get it. Your workload scales horizontally? And 2 x A72 are as fast as 4 x A17?
@bob
The real fact is most Arm SoC spend most of the time not running at the claimed top speed, they can only run very sort bursts.
Even over designed cooler cannot help.
@bob
There are no quad-core A53 that a 5005U would be 10x as powerful — the average IPC difference between Broadwell and A53 is approx 2-2.5 in favor of the former. There might be isolated cases where AVX2-centric scenarios can produce 10x difference, but how common are they?
btw, 410c is a severely underclocked SBC — its normal ‘stock-cooling’ clock is ~600MHz IIRC.
@theguyuk
Right about idle/low use cpu need, for that i don’t understand strategy of arm don’t provide hw encoder/decoder driver for a good power efficiency…it’s a shame for their business
And maybe we miss a compilation souce code benchmarck, because i don’t think my little H3 compile 10X slower than my intel cpu…
What are the RAM speeds and configurations on these boxes? I suspect that may tell as much or more of the story, especially if the benchmark is blowing out the icache on the ARMs.
@theguyuk
As mentioned in the post RK3399 and Apollo Lake devices are in the same price range.
@tkaiser
OpenSSL benchmark is missing on RK3399 because the test failed. If I remember correctly, the download failed.
@Jonathan
The Phoronix test suite as well as the results on openbenchmarking.org should be considered useless garbage especially when trying to compare different platforms in the way it’s done here. Most of the ‘benchmarks’ use questionable or no optimization settings at build time so results vary a lot with the OS used and the platform it’s running on (compiler shipped and default settings).
I’ve seen some of these ‘benchmarks’ performing 3 times faster on the same hardware just by exchanging the OS and thereby default compiler and settings (switching from GCC 4.x to 6.x for example).
@theguyuk
when thinking about (relatively) low power server I actually do think whenever should I go with arm and x86 and such benchmark did made sense for me.
You can argue like other commenters the metric used was not the best, but the idea itself? no. Look at the scores, they are clearly comparable, especially if you think about the price involved for the performance.
Which kind of server task(s) could be represented by the collection of synthetic benchmarks above? Really curious 🙂
@bob
That may be true for these cheap implementations of A53 cores. Have a look at Nvidia Jetson TX2 benchmarks. Phoronix did some a good while back. Same is true for Apple’s cores.
My results for Hikey 960
https://pastebin.com/twarU4eC
@m][sko
Himeno Benchmark 3.0 -> 1033.08
That’s really a big gap compared to other ARM platforms (5x faster than RK3399), and even faster than the Apollo Lake processor.
I wonder what may have caused the jump beside just the faster cores.
@m][sko
Can you please provide output from
@cnxsoft
Those benchmarks are extremely sensitive to compiler version and flags. One wrong flag and/or compiler version can make all the difference. It’s essential when doing synthetic benchmarking to know very well what a given compiler produces from the sources (e.g. ‘Hey, it’s not generating AES instructions!’, ‘Hey, it produced this snafu in the inner-most loop!’, etc)
Arm boards for the general use case have lost their initial promise. Lack of support from Arm, lack of proper software support from vendors, and the throttling and performance has left the promise in tatters.
And the cost of higher performing boards, even the 3399, takes one into low power lower priced Intel platforms at which point its game over as the software support on Intel just cannot be compared.
But for boards like the Pi or Odroid with better software support, at least things like a low power HTPC makes sense. And if the SOC provider decides to provide support, sometimes even a NAS or router can become possible. But on the whole the ecosystem showed early promise but years later its not really gone anywhere,
@raul
I would say that there are vendors who don’t suffer the problems you mention. ODROUD from Hard Kernel for one provides boards without cooling problems. They support their boards with software.
And that’s the main reason no one with a brain in his head should use this terrible Phoronix crap. I used Jean-Luc’s last results to rely on and tested on a ROCK64: https://openbenchmarking.org/result/1710279-TY-1710254TY63
According to the Phoronix results ROCK64 shows just 41% OpenSSL performance compared to the octa core Banana Pi M3 and less than 9 percent compared to the Apollo Lake box (obviously the latter making use of AES-NI here). So obviously the Phoronix ‘benchmark’ uses weird compiler flags and makes no use of ARMv8 crypto extensions. Let’s have a closer look and compare the openssl binary Phoronix built from sources with the one the distro contains:
So Phoronix managed to build the binary that strangely that it performs 2.4 times lower than the distro package every real-world task will use. But that’s still not talking about ARMv8 crypto extensions, so let’s have a look too (full command output for both tests — check especially build options!):
Hey, the Ubuntu package that every real-world task on this device will use is just 4 times faster with really small chunks of data and up to 20 times with 8K data blocks. Srsly? Why do we use a ‘benchmark’ suite that is well known since years to only produce numbers without meaning especially when trying to compare different architectures?
@cnxsoft
In case you have the Apollo Lake box still running with Ubuntu… care to repeat just those 4 OpenSSL runs (one time using the distro’s openssl binary and one time the one Phoronix built. I’m especially interested in the build options reported since I’m wondering why AES-NI is used on Intel for the sign/verify benchmark)
@tkaiser
OpenSSL testes on MeLE PCG35 Apo:
Not sure how to do that with Phoronix Suite yet. Going to bed soon.
Found out how (.phoronix directory). Openssl Phoronix:
@cnxsoft
Thank you. So on x64 we’re talking about:
With both tests the PTS binary scores even better than Ubuntu’s (but on Intel totally different compiler flags are used and those make the real difference) while on ARM the PTS binaries score 2.4 to 20 times lower than the Ubuntu distro package. So when switching from stupid passive benchmarking mode to active benchmarking an interesting approach would be to analyze compiler flags above, then rebuild then openssl binary and only stop when results with active ARMv8 crypto extensions outperform the AES-NI numbers.
At least it should be obvious that this Phoronix crap is not an option to compare performance of different architectures since it ignores everything that’s important and is only able to provide a bunch of numbers without any meaning.
@tkaiser
Nice catch. Yes, that’s part of what I was talking about — in this particular case what phoronix has produced is literally apples to shotshells.
I know lots will think I am nuts for suggesting it, but if you want TV boxes and ARM SBC to improve, people need to be encouraged to play more 3D games on them.
Just look how demanding 3D games have pushed Game Console and Gaming PC hardware. The same market can push ARM hardware.
Does the average office really need a i7, i5 to write letters etc, no.
Network gear is a different market same as financial data, Movie editing etc
@tkaiser
No Thomas, I meant 2*A72 are exactly as fast as 2*A17, or about half as fast as 4*A17. Yes the build workload scales reasonably well (provided the memory bandwidth is there and the number of files to build is high enough and these files are about the same size). So for this workload, the RK3288 is almost twice as fast as the RK3399 just because it has twice the number of really usable cores.
@bob
Power efficiency doesn’t compare like this because it decreases with peak performance. You need to compare the power drawn by a device capable of achieving a given peak performance. For example, my RK3288, while less power efficient than my Atom 8350, is significantly faster (15-20%). These two are the only ones in this thermal envelope capable of delivering more or less comparable performance. If I want higher performance on x86, I have to seek a significantly larger design (a much faster one) which will eat more power than the RK3288. It might be a bit more power efficient but the reality is that this efficiency isn’t interesting anymore due to extra cooling solutions.
Also the price per task is important in certain environments, just like the price per peak MIPS in other ones. In my case, for a build farm, I have to find a sweet spot between the power envelope, the price and the performance. With a very high price I can find a high frequency core i7 in a small thermal envelope being 3 times faster than my RK3288 but it will cost 20 times the price and will need more cooling.
I always understood that the main trick Intel use, is to do more things in memory, and have as much of the data as you can, as close to the CPU cores as possible.
Bigger faster cache and faster memory?
@theguyuk
That’s true for high end CPUs, when the cache algorithm are very advanced, allowing almost instant access to any memory location. But having compared memory performance between a few Atoms and the RK3288 in dual-channel configuration shows a significant difference in favor of the latter on in-cache and RAM patterns.
One feature helping x86 CPUs is the trace cache replacing the instruction cache. The principle is to store decoded and fused instructions, saving a few pipeline stages for hot code paths. This also allows some old CISC instructions (eg: “rep movs” for memcpy()) to be expanded to very efficient sequences that even possibly give hints to the cache about what lines to prefetch next, and when to flush the written ones, which is hardly possible using more RISC-like instruction sets.
The branch prediction on modern x86 is very efficient as well, inheriting from certain history mechanisms that once made the Alpha shine. These are typically the stuff that you observe on high performance calculations, crypto and such stuff.
RK3399 is more like Celeron N series, since Celeron J series usually have a higher power consumption.
@blu
Well, almost all of those Phoronix ‘benchmarks’ are totally broken since how they’re built and executed is not with providing useful numbers in mind but only focusing on ‘portability/compatibility’ so that PTS users being tricked into believing they would do serious benchmarking get all those tests compiled on their hosts regardless of platform, OS and environment.
Isn’t it really ‘funny’ when I’m interested in encryption performance of an inexpensive ARM thingie and compare with a way more expensive Intel box that Phoronix is telling me the ARM thing would be 11 times slower since the ‘test suite’ only produces BS numbers while using OpenSSL’s own benchmark mode avoiding ‘PTS crippled’ binaries ARMv8 crypto extensions seem to outperform AES-NI:
Whether/how these synthetic benchmarks relate with real-world encryption workloads like VPN endpoints/gateways or full disk encryption is another story — but if I’m told the ARM platform would be 11 times slower than the Intel box (while the official benchmark with normal openssl binaries shows quite the opposite)… who would start to even look into details?
While I fully understand that clueless people prefering data over information and like staring at nice looking graphs made of numbers without meaning truly love the Phoronix test suite I don’t understand why serious blogs like this here rely on the useless garbage numbers this tool creates, especially in situations where the PTS fails most: comparing different CPU architectures.
@tkaiser
Phoronix Suite shows the CFLAGS / CXXFLAGS used for compilation. For example for OpenSSL:
I’d assume all the rest is default. That would mean in the case of some of the results above that AES instructions are enabled by default for x86, but disabled for ARM (maybe
-march=armv8-ais required to enable those?).@willy
Re x86 i-cache — Atoms, at least up to Silvermont, don’t have either uop cache or trace cache (latter was something found in Netburst; former appeared in SNB). The only i-cache optimisation employed by Atoms (read: Silvermonts) is op boundary marks in the i-cache, and thus Atoms are often decode-bound (one of the reasons the Cortexes fair so well against them).
@cnxsoft
Yes, PTS is using $some defaults in ‘fire and forget’ mode. Sometimes build settings are hard encoded in the makefile, sometimes relying on what the environment defines (so if for example EXTRAOPTFLAGS=’-O3′ in /etc/profile some ‘benchmarks’ will show magnitudes better scores later, eg. the infamous Smallpt stuff) and sometimes just using what the operating system’s default compiler does for whatever reasons.
Please think about again: what PTS reports as ‘OpenSSL’ performance is RK3328 being 11 times slower than the J3455. While with another benchmark and when using a sanely built openssl binary the ARM SoC easily outperforms the Intel Celeron. Sorry, but this is not serious benchmarking. This is just what the PTS is well known for: a collection of numbers without meaning.
And this does not only apply to architecture comparisons (eg. ARM vs. Intel) but also to ‘benchmarks’ comparing membes of the same architecture. Your comparison above of Apollo Lake vs. Bay Trail is more importantly a comparison of Ubuntu 14.04 with 17.10 –> GCC 4.8.4 vs. GCC 7.2 — it is well known how different some of the Phoronix ‘benchmarks’ score depending on GCC version. Publishing such numbers as above definitely does not help getting an idea about ‘hardware performance’. Not with the way Phoronix creates numbers.
If you are interested: This is how it looks on a ODROID XU4 ( Exynos5422 Cortex™-A15 2Ghz and Cortex™-A7 Octa core CPU ) on a Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS – Kernel 4.13.0
# openssl speed -elapsed -evp aes-128-cbc
You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time.
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 16 size blocks: 14966032 aes-128-cbc’s in 3.00s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 64 size blocks: 4189907 aes-128-cbc’s in 3.00s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 256 size blocks: 1104424 aes-128-cbc’s in 3.00s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 1024 size blocks: 279763 aes-128-cbc’s in 3.00s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 8192 size blocks: 35038 aes-128-cbc’s in 3.00s
OpenSSL 1.0.2g 1 Mar 2016
built on: reproducible build, date unspecified
options:bn(64,32) rc4(ptr,char) des(idx,cisc,16,long) aes(partial) blowfish(ptr)
compiler: cc -I. -I.. -I../include -fPIC -DOPENSSL_PIC -DOPENSSL_THREADS -D_REENTRANT -DDSO_DLFCN -DHAVE_DLFCN_H -DL_ENDIAN -g -O2 -fstack-protector-strong -Wformat -Werror=format-security -Wdate-time -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -Wl,-Bsymbolic-functions -Wl,-z,relro -Wa,–noexecstack -Wall -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_MONT -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_GF2m -DSHA1_ASM -DSHA256_ASM -DSHA512_ASM -DAES_ASM -DBSAES_ASM -DGHASH_ASM
The ‘numbers’ are in 1000s of bytes per second processed.
type 16 bytes 64 bytes 256 bytes 1024 bytes 8192 bytes
aes-128-cbc 79818.84k 89384.68k 94244.18k 95492.44k 95677.10k
# openssl speed rsa4096 -multi 4
OpenSSL 1.0.2g 1 Mar 2016
built on: reproducible build, date unspecified
options:bn(64,32) rc4(ptr,char) des(idx,cisc,16,long) aes(partial) blowfish(ptr)
compiler: cc -I. -I.. -I../include -fPIC -DOPENSSL_PIC -DOPENSSL_THREADS -D_REENTRANT -DDSO_DLFCN -DHAVE_DLFCN_H -DL_ENDIAN -g -O2 -fstack-protector-strong -Wformat -Werror=format-security -Wdate-time -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -Wl,-Bsymbolic-functions -Wl,-z,relro -Wa,–noexecstack -Wall -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_MONT -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_GF2m -DSHA1_ASM -DSHA256_ASM -DSHA512_ASM -DAES_ASM -DBSAES_ASM -DGHASH_ASM
sign verify sign/s verify/s
rsa 4096 bits 0.014487s 0.000225s 69.0 4438.8
Since it’s a 8 Core system, I also add the relevant 8 thread result:
# openssl speed rsa4096 -multi 8
sign verify sign/s verify/s
rsa 4096 bits 0.009657s 0.000149s 103.6 6698.3
I’m sorry but talking about efficiency comparing two different fabs is nonsense, each platform is designed for what they are, everything said.
Same numbers as in the referenced link in my first comment above (we tried to collect numbers from A7, A9, A15, A17, A53 — with and without ARMv8 crypto stuff — and A72. Currently A17 and A72 still missing).
With RSA signing the Exynos doesn’t look that bad but when it comes to AES encryption the SoC is far behind compared to those SoCs with ARMv8 crypto extensions, both considering ‘raw performance’ and especially ‘performance per Watt’. An ODROID XU4/HC1 doing AES stuff on the CPU cores compared to an ARMv8 SoC with crypto extensions enabled is ~40 times as inefficient if we keep consumption increase also in mind (details in the aforementioned link to Armbian forum):
@tkaiser
Let me know if and what A72 benchmarking you need – I have one macchiatobin idling here.
@blu
Would be great to get full output from
Compiler and version the binaries were built with are important of course. And if you can results from github.com/ssvb/tinymembench would also be great.
@tkaiser
On H96-Max, I get this on the 2 A72@1.8 GHz :
# openssl version -a
OpenSSL 1.0.2k 26 Jan 2017
built on: reproducible build, date unspecified
platform: linux-aarch64
options: bn(64,64) rc4(ptr,char) des(idx,cisc,16,int) idea(int) blowfish(ptr)
compiler: aarch64-gcc47l_glibc218-linux-gnueabi-gcc -I. -I.. -I../include -fPIC -DOPENSSL_PIC -DOPENSSL_THREADS -D_REENTRANT -DDSO_DLFCN -DHAVE_DLFCN_H -O3 -Wall -DSHA1_ASM -DSHA256_ASM -DSHA512_ASM
OPENSSLDIR: “/usr/share/openssl”
(built on linaro gcc-4.7.4, not rebuilt since).
# taskset -c 4,5 openssl speed rsa4096 -multi 2
sign verify sign/s verify/s
rsa 4096 bits 0.019186s 0.000257s 52.1 3887.3
And this on the 4 A53 cores at 1.4 GHz :
# taskset -c 0-3 openssl speed rsa4096 -multi 4
sign verify sign/s verify/s
rsa 4096 bits 0.022229s 0.000310s 45.0 3229.1
For AES, the numbers are pretty good :
A72:
type 16 bytes 64 bytes 256 bytes 1024 bytes 8192 bytes
aes-128-cbc 465434.04k 938648.81k 1221223.85k 1300021.93k 1349861.38k
A53:
type 16 bytes 64 bytes 256 bytes 1024 bytes 8192 bytes
aes-128-cbc 170812.96k 464463.87k 783981.14k 982121.81k 1059921.92k
On the MiQi (at 1.8 GHz as well) :
# openssl speed rsa4096 -multi 4
rsa 4096 bits 0.016024s 0.000230s 62.4 4342.0
# openssl speed rsa4096 -multi 2
rsa 4096 bits 0.031990s 0.000463s 31.3 2159.8
Here the 64-bit architecture definitely helps!
Model: MACCHIATOBin-8040
Clock: CPU 1300 [MHz]
DDR 800 [MHz]
FABRIC 800 [MHz]
MSS 200 [MHz]
macchiato:~$ ./gov.sh # columns: core governor clock
0 performance 1300000
1 performance 1300000
2 performance 1300000
3 performance 1300000
tinymembench: https://pastebin.com/bg1Wha41
openssl: https://pastebin.com/WRnVa07L
7z: https://pastebin.com/Z6RFZLkh
bench mark we want to see is huawei fastest versus apple latest
@blu
Thank you! This is DDR4, right? As a quick reference Jean-Luc’s tinymembench numbers for RK3399 from few weeks ago. And the 7-zip numbers are the only ‘generic CPU’ benchmark resuilts I need for my use cases (server stuff).
A72 with ARMv8 crypto extensions performs really impressive, this time also with very small chunks of data (the A53 implementation suffers here somewhat).
@willy
I put your AES encryption numbers and the Celeron results together:
When running on the A72 cores RK3399 outperforms J3455 always and is already 2 times faster with 128 byte chunks. Really nice to see these crypto extensions working so well with AES. Now curious how PCIe performance with this SoC looks like.
@tkaiser
Yep, DDR4 at the lowest rate (1600) — board and DIMM are capable of 2400, but I keep mine at the lowest setting for minimal active cooling (side-mounted 80mm silent fan).
On an unrelated note, Teres-A64 acquired! ; ]
@tkaiser
Maybe file a bug against PTS instead of just complaining on a random article on another site?
PTS is mostly used/developed on x86_64 so they probably aren’t even aware it doesn’t work properly (much slower than distro defaults) on arm.
@Anonymous
He’s commented over there on a number of articles when this topic has come up. Nothing has come from it. Michael shows no interest in fixing PTS.
So, instead @tkaiser is addressing it where it’s used so that people there can be aware of what junk it is.
And it really helps to think about Phoronix Media’s business model to understand why this will never change. 🙂
PTS is great in a lot of areas (especially presenting/visualizing and comparing numbers) but unfortunately the first step to collect useful data and not just garbage is totally flawed. Which is understandable having PTS target audience in mind (people preferring data over information and happy looking at nice graphs representing numbers without meaning).
IMO most important lesson to learn: Switch from passive to active benchmarking!
run the benchmarks on rock960, some improvements over the other rk3399.
https://www.96rocks.com/blog/2017/11/02/rock960-linux-benchmarks/
https://openbenchmarking.org/result/1711019-TY-1709271TY72
@vamrs
For whatever reason, John the ripper seems to be very sensitive to CPU frequency.
Were the Cortex A72 cores clocked at 1.8 GHz or higher in your boards?
With regards to AES on OpenSSL, the important flags appear to be -DAES_ASM -DVPAES_ASM -DBSAES_ASM for hardware crypto, or SIMD accelerations
The implementations are shown @ https://github.com/openssl/openssl/tree/master/crypto/aes/asm
Even 32-bit ARM (ARMv7) would be accelerated, as while there’s no AES instructions, it would still be accelerated with NEON if the SoC supports it.
ARMv8 does not mean AES crypto instructions are enabled, as at least one Cortex A53 based SoC does not have those.
Nope, the problem is that for whatever reasons people try to use a tool that graphs numbers without meaning (PTS) as performance ‘benchmark’.
These are the settings your binaries have been built with
And these are @vamrs settings:
The PTS is known to produce only numbers without meaning in the most stupid ‘fire and forget’ mode possible. Why do people care about those wrong numbers produced?
If you compare the settings above it’s easy to spot why ‘performance’ differed (you ‘optimized’ for armv7-a while on ROCK960 aarch64 was set as target architecture — the PTS is all about (missing) compiler optimizations and if used correctly could be used to demonstrate how important it is to use ARMv8 64-bit settings on ARMv8 64-bit platforms. But instead the PTS is mis-used to draw conclusions about hardware performance)
It seems Amlogic are the greatest ‘offender’ here, as even Allwinner’s A53 have the crypto extensions.
Do we know exactly which SoCs by Amlogic lack the crypto extensions, besides the S905?
@blu
Don’t know, I just saw that in the code. They did not name names, just:
Maybe S905 (and variants?) SoC is the only one.
@cnxsoft
Now I can see S905 has it own crypto module according to: https://forum.odroid.com/viewtopic.php?t=22236#p151854
Yes, the crypto stuff is optional with A53 (BTW: it’s not only AES). Samsung/Nexell S5P6818 (A53) comes without, same with BCM2837 on RPi 3 and Amlogic S905 (while S905X is said to have crypto extensions enabled/licensed).
The problem with those vendor proprietary crypto modules is how to get them working and how do they perform (especially with small chunk sizes that might be typical for encryption/decryption of VPN traffic). If you check Banana Pi R2 AES performance in the referenced link in my first comment above you see that MediaTek’s own crypto module performs very poorly with small chunk sizes. Also it’s PITA to get this stuff working since you would need to rebuild the kernel to make use of cryptodev, then build OpenSSL from sources, then start to realize that you also have to take care about IRQ affinity since mtk-aes interrupts ending up all on cpu0 will bottleneck crypto stuff running in parallel and so on.
While with the ARMv8 crypto extensions it just works as long as you use a somewhat decent ARMv8/aarch64 userland and the kernel has been built correctly… and avoid the Phoronix way to build unoptimised binaries of course 😉
AES performance and A53 without crypto extensions (Raspberry Pi 3 / BCM 2837):
Two times tested, first time with RPi foundation software (32-bit kernel ‘4.9.59-v7+ #1047 SMP Sun Oct 29’) and Raspbian Stretch userland (build ‘optimization’ for ARMv6!), then with a true 64-bit OS (64-bit kernel ‘4.11.12-pi64+ #1 SMP PREEMPT Sun Jul 30’ and original Debian Stretch arm64 userland). OpenSSL distro package (OpenSSL 1.1.0f 25 May 2017) used with ‘openssl speed -elapsed -evp aes-128-cbc’
When using the useless Phoronix test suite we would see same high differences like with RK3399 above (Videostrong VS-RK3399 vs. ROCK960, one time tested with Debian armhf distro, the other time with Debian arm64 userland) and also as expected other benchmark numbers differ, the best example for ‘benchmarking gone wrong’ as usual the stupid sysbench pseudo benchmark (sysbench –test=cpu –cpu-max-prime=20000 run –num-threads=4):
Same hardware and the ‘renowned’ sysbench ‘benchmark’ running 11 times faster with an arm64 userland compared to Raspbian’s armhf/ARMv6 (BTW: when using sysbench from Jessie then Raspbian ARMv6 number is 120 sec — that’s just the difference between GCC 4.9 vs. GCC 6.3) while 7-zip performs slower with the Debian arm64 variant (due to Raspberry Pi folks using pretty good compiler settings for their ARMv6 Raspbian).
@cnxsoft
The S905 in the ODROID C2 is one such AARCH64 processor without AES. If you need numbers from one, I would be glad to provide them if you don’t have one.
@willmore
I use your C2 OpenSSL numbers below you posted to Armbian forum a while back. All results done with ‘openssl speed -elapsed -evp aes-128-cbc’ using arm64 Binaries on 64-bit platforms (since otherwise numbers are lower, see RPi 3 example above):
BPi R2 and M3 are Cortex-A7, Clearfog A9, ODROID XU4 is A15, MiQi A17. Raspberry Pi 3, ODROID-C2 and NanoPi M3 use A53 without ARMv8 crypto extensions. Orange Pi PC2, EspressoBin, Pinebook and ROCK64 is A53 with crypto extensions and both MacchiatoBin and H96-Max use Cortex-A72.
Obviously ARMv8 crypto extensions simply outperform everything else. Especially the A72 implementation rocks even with very small data chunks. If we compare Cortex-A72 with A7 (Banana Pi M3 running at the same clockspeed) then we get 13 times better performance with small chunks and up to 30 times better results with large chunks (use cases: VPN vs. full disk encryption). A53 with crypto extensions performs not that great with small chunks but still outperforms easily all ARMv7 cores.
A53 without crypto extensions performs at Cortex-A9 level but will be outperformed by both A15 and A17 (comparing identical clockspeeds).
S905 lacks them while S905X and S912 have them enabled.
It’s easy to check using the results searchable at browser.geekbench.com of another flawed benchmark collecting also mostly numbers without meaning: Geekbench. Forget about the ‘total scores’ since total BS but check detailed results and there AES numbers. AML-S905X-CC AKA ‘Le Potato’ gets a multi-core AES score of 1648 points (1.24 GB/sec), a Beelink GT1 2739 points (2.06 GB/sec) while a Raspberry Pi 3 for example scores just 79 points (61.0 MB/sec). The difference in results between S905X/S912 and BCM2837 is of course questionable but at least it’s easy so spot where ARMv8 crypto extensions are available and where not.
Le Potato single-core AES score is 392 points (302.5 MB/sec) so obviously this number is too low compared to quad-core result of 1648 (it can’t be more than 4 times more)
For Beelink GT1 single-core result is 448 points (345.5 MB/sec) which looks somewhat realistic given that the SoC has 8 cores and multi-core number is 6 times higher.
I still can’t figure out what thought process goes in the head of vendors who decide that:
1. Their SoC will target crypto applications, yet
2. They won’t license the proven and easilly accessible aarch64 crypto extensions, instead they’ll provide some proprietary engine.
@blu
Well, at least Amlogic corrected this later and both S905X and S912 can be considered being the fastest AES/SHA crypto performers with A53 cores (since 1.5GHz clockspeed). Some new results (I partially fail to understand): https://forum.armbian.com/topic/5570-some-basic-benchmarks-for-le-potato/?tab=comments#comment-42725
Wrt proprietary crypto modules it depends. Marvell’s CESA for example is able to increase the above AES performance numbers for Clearfog (Cortex-A9) by 3 to 4 times. It’s also said that more recent ARMv8 Marvell SoCs like Armada 37xx (EspressoBin) contain a new ‘Marvell 5Gbps Security Engine’ (do a web search for) outperforming both CESA and the already licensed ARMv8 crypto extensions with mainline kernel support landing next year.
On the other hand the preliminary results we collected eg. for Banana Pi R2 show clearly that proprietary crypto modules might have massive downsides since currently performance pretty much sucks with MTK’s AES implementation as long as the data chunks aren’t rather large:
@blu
They probably added that crypto module back in ARMv5 or so and there’s that *one* customer who uses it, so they just carry it along and that customer is happy.
Crypto customers are either silly middle managers who see ‘crypto’ in the list of features and check a box saying “yep, has crypto” or the legacy people mentioned above.