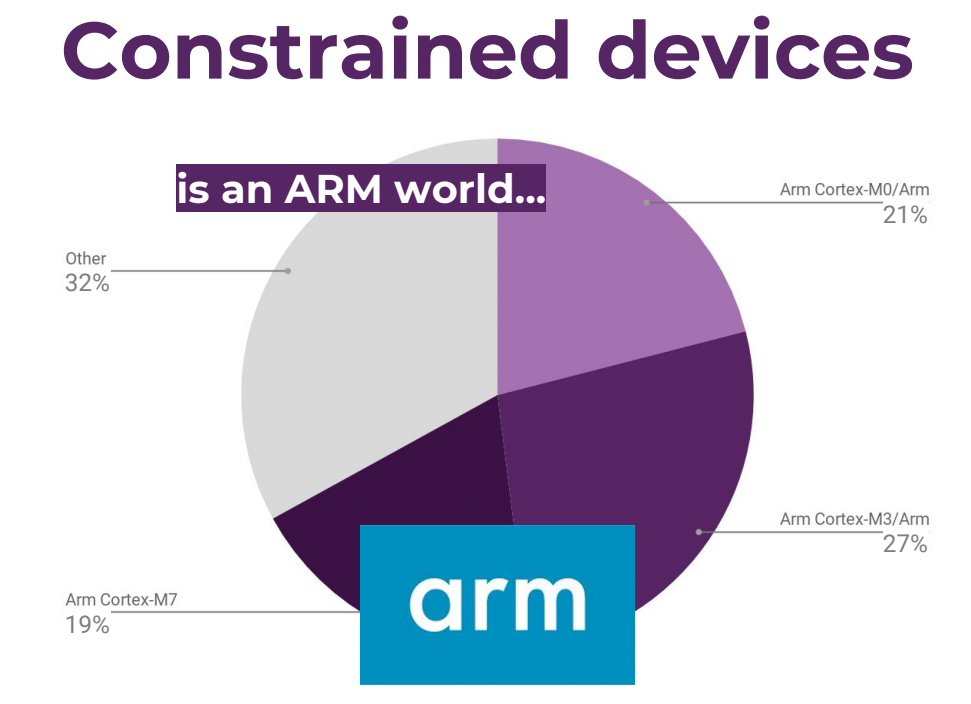
The Eclipse IoT Working Group has just released a report asking the global IoT developer community to share their perceptions, requirements, and priorities. And with over 1,700 individuals taking the survey between February and March 2019, the key findings are interesting: IoT drives real-world, commercial outcomes today. 65% of respondents are currently working on IoT projects professionally or will be in the next 18 months. IoT developers mostly use C, C++, Java, JavaScript, and Python AWS, Azure, and GCP are the leading IoT cloud platforms Top three industry focus areas remain the same as last year: IoT Platforms, Home Automation, and Industrial Automation / IIoT. MQTT remains the dominant IoT communication protocol leveraged by developers The Eclipse Desktop IDE is the leading IDE for building IoT applications The last point may be slightly biased because the survey was done by the Eclipse IoT Working Group, so most respondents were already […]
Panfrost is an Open Source Driver for Arm Mali Midgard GPUs
Getting GPU drivers to work on Linux with Arm SoCs was really a struggle a few years ago due to close-sources binary blobs that required all bugs to be fixed by a single team. But in recent years we’ve seen good progress with open source mobile GPU drivers including Freedreno for Adreno GPUs, and Etnaviv for Vivante GPUs. Arm Mali also got its own open source Lima driver worked on for many years but only for older Utgard GPUs (Mali 400, Mali 450). However, during the Opensource GPU Drivers BoF at Linaro Connect Bangkok 2019, Rob Herring, Technical Architect at Linaro and Tomeu Vizoso, Principal Software Engineer at Collabora, discuss the status of drivers, and I learned about an open source driver for Mali Midgard (Mali-T6xx, Mali-T7xx) GPU called Panfrost. As we’ll see below, the driver is already capable of running basic demos, has been upstreamed to Mesa, and tested […]
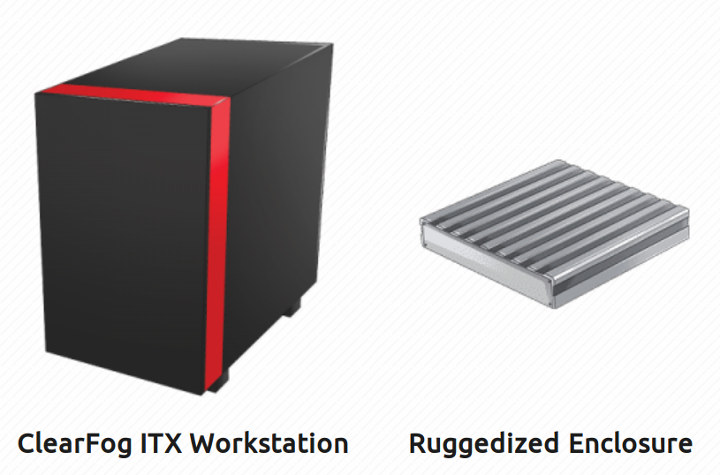
ClearFog ITX Workstation May be the Ultimate Arm Developer Platform
Most people are still doing Arm development work on x86 platforms, because there aren’t really any viable equivalent in the Arm world. Current options include Edge Server SynQuacer E-Series (aka Linaro Developer Box), a $1,250 Arm PC shipping with a 24-core Arm Cortex-A53 processor, 4GB RAM (by default), a 1TB hard drive, and Geforce GT710 graphics cards, as well as the much more powerful GIGABYTE ThunderXStation workstation with up to two Cavium ThunderX 32-core Armv8 processors, 32GB to 128GB RAM configuration, NVMe storage, and more. The former was a good place to get started, but the Arm Cortex-A53 cores clicked at 1GHz provided limited performance, and the GIGAGYTE workstation costs over $12,000, so it’s only suitable for projects with specific needs and/or a high expected return on investment. That’s why there will be a discussion about Designing a next generation ARM Developer Platform at Linaro Connect 2019 next week in […]
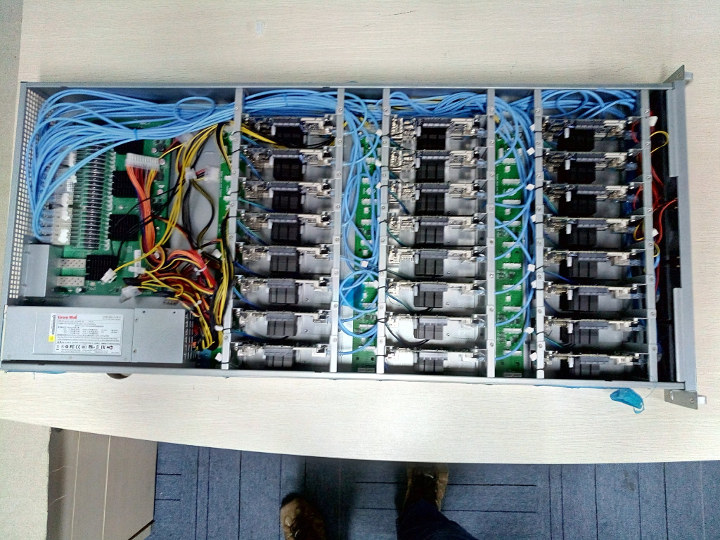
PINE64 Plans to Move their Website on a 24-node RockPro64 Cluster
Boards’ clusters are always fun to see, and PINE64 has shared pictures of two RockPro64 clusters with respectively 48 and 24 boards neatly packed into partially custom enclosures. The 48-node cluster will feature a total of 288 cores, including 96 Arm Cortex-A72 cores and 188 Cortex-A53 cores, as well as 192GB of LPDDR4 RAM. Low cost development boards may be seen as toys by some, so it’s interesting to learn that PINE64 plans to move their complete website infrastructure including the main website, a community website, forums, wiki, and possibly IRC on the 24-node cluster, while it seems the 48-node cluster may be used for their build environment. The company has just completed the assembly of the clusters, and did not disclose the full technical details just yet. However, a progress report may be written in due time. Once the migration is done, and everything works as it should, it […]
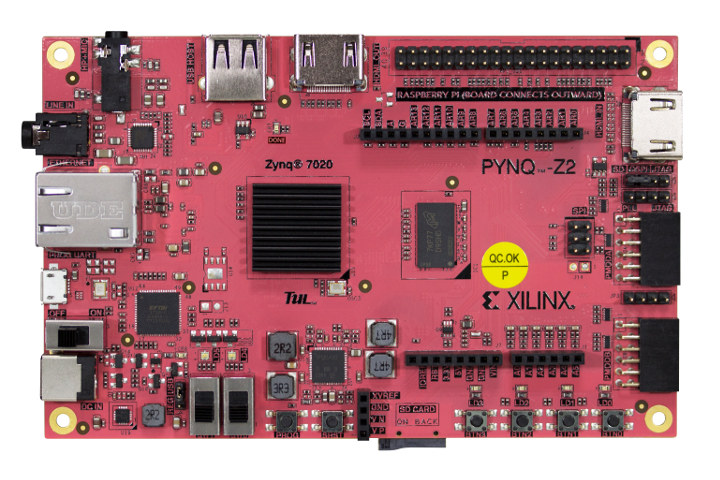
PYNQ-Z2 Python FPGA Board Adds Raspberry Pi Header, 24-Bit Audio Codec
PYNQ-Z1 is a board by Digilent powered by Xilinx Zynq-7020 Arm Cortex-A9 + FPGA SoC that’s designed specifically for PYNQ, an open-source project that aims to ease the design of embedded systems with Xilinx Zynq Systems on Chips (SoCs) by leveraging the Python language and libraries. PYNQ-Z2 is very similar to PYNQ-Z1, but it’s made by Taiwanese company TUL, and the board is slightly longer to allow for an extra 40-pin Raspberry Pi compatible header, and Analog Devices ADAU1761 24-bit audio codec. PYNQ-Z2 board specifications: SoC – Xilinx Zynq-7020 (XC7Z020-1CLG400C) dual core Arm Cortex-A9 processor @ 650 MHz with FPGA with 13,300 logic slices, each with four 6-input LUTs and 8 flip-flops System Memory – 512MB DDR3 Storage – Micro SD card slot, 16MB QSPI Flash with factory programmed globally unique identifier (48-bit EUI-48/64 compatible). Video – HDMI In and HDMI Out Audio – Mic in, Line Out ADAU1761 codec […]
Linux 5.0 Release – Main Changes, Arm, MIPS & RISC-V Architectures
Linus Torvalds has just released Linux 5.0: Ok, so the last week of the 5.0 release wasn’t entirely quiet, but it’s a lot smaller than rc8 was, and on the whole I’m happy that I delayed a week and did an rc8. It turns out that the actual patch that I talked about in the rc8 release wasn’t the worrisome bug I had thought: yes, we had an uninitialized variable, but the reason we hadn’t immediately noticed it due to a warning was that the way gcc works, the compiler had basically initialized it for us to the right value. So the same thing that caused not the lack of warning, also effectively meant that the fix was a no-op in practice. But hey, we had other bug fixes come in that actually did matter, and the uninitialized variable _could_ have been a problem with another compiler. Regardless – all […]
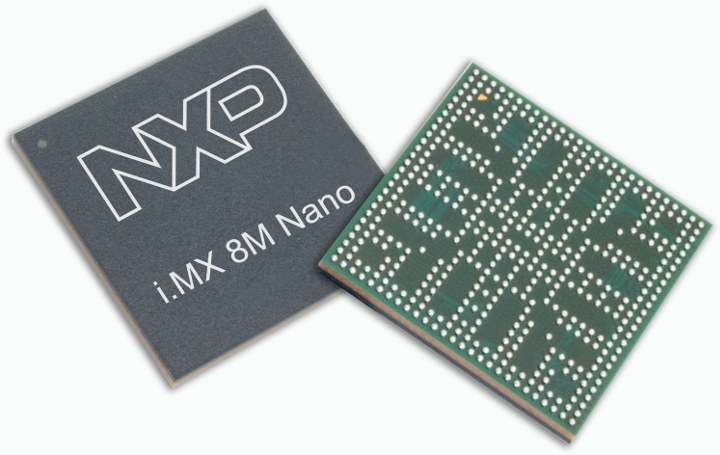
NXP i.MX 8M Nano is a Power-optimized Arm Cortex-A53/M7 Processor
NXP introduced their first 14nm i.MX processor at Embedded World 2018 last year with i.MX 8 Mini processor equipped with up to four Cortex A53 cores clocked at 2.0 GHz and one real-time Cortex-M4 cores clocked at 400+ MHz, and optional 1080p video output and decoding/encoding. The company has now added another 14nm member to their i.MX 8M family with NXP i.MX 8M Nano family also featuring four Cortex-A53 cores at up to 1.5 GHz, but replacing the Cortex-M4 by a more powerful Cortex-M7 core clocked at up to 600 MHz. The processor is also power-optimized for less than 2W total dynamic power (TDP) and sub-watt in many IoT edge applications. NXP i.MX 8M Nano key features and specifications: Application cores – One to four Arm Cortex-A53 cores up to 1.5 GHz per core; 32KB L1-I Cache/ 32 KB L1-D Cache; 512 KB L2 Cache Real-time core – Arm Cortex-M7 […]
Systems-on-Module Market Update – An Interview with Toradex CMO
I’ve been interviewing Daniel Lang, Toradex Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), over email just before Embedded World 2019, to learn a bit more about the system-on-module market, and what’s ahead. CNXSoft: We’ve already covered several Toradex systems-on-module and development kits on CNX Software, but for readers who may not know Toradex yet, could you provide a short description of what the company does in the embedded systems space? Daniel Lang: Thanks for having me. Toradex builds high reliable Arm-based System on Modules. Our focus is to make the life of developers easier and to reduce the complexity and time-to-market. We sell hardware, but most of our engineering resources focus on Software and Support. Our products are used in areas such as Industrial Automation, Medical, Transportation, Test and Measurement, Building Automation and many more. CNXSoft: Could you explain why / what type of customers go the SoM route instead of designing for […]