AMD announced the G-Series SoC, AFAIK the first x86 SoC including CPU, GPU and chipset (ala ARM), at the end of April, and a few products are already available such as Win Enterprises MB-60830. One of those new SoCs, GX-416RA, is especially designed for headless applications, and does not features GPU. Deciso decided to use this processor in the standard version of their Netboard A10, a single board computer that can be used for network based appliances such as IP-PBX, Firewall & UTM or Load Balancer. The company also provides 2 other versions of the board that includes AMD G-Series SoCs with Radeon GPU. Netboard A10 Specifications: SoC: AMD Embedded GX-416RA G-Series SoC (4x 1.65GHz Jaguar cores, 2MB L2 cache, 15W TDP, no GPU) Option 1: AMD Embedded GX-415GA G-Series SoC (4 x 1.5GHz Jaguar cores, 2MB L2 cache, 15W TDP, Radeon HD 8330E GPU) Option 2: AMD Embedded GX-210HA […]
Compulab CM-T335 CoM with TI Sitara AM335x Sells for $27
Compulab, an Israeli company specialized in embedded computing, has just released CM-T335, a family of low cost computer-on-module powered by Texas Instruments Sitara AM335x SoC, and sells for as low as $27 per unit for the AM3352 version (no GPU) for 1k orders. The module is available in commercial, extended and industrial grades, and features up to 512 MB RAM, and 1 GB Flash. Specifications: SoC – Texas Instruments AM3352 CPU @ 275MHz, or AM3354 @ 600MHz + PowerVR SGX530 GPU System Memory – 128MB to 512MB DDR3-1066, 16-bit bus width Storage – 128MB to 1GB on-board NAND flash, 8bit, SLC Display – 24-bit Parallel display interface – up to 1366 x 768 Touchscreen – 4/5/8-wire resistive touch-screen support, capacitive touch-screen support through SPI interface Connectivity: Ethernet – 1000Base-T Ethernet interface implemented with AM335x integrated MAC and the Atheros AR8033 RGMII PHY WiFi – 802.11b/g/n implemented with TI WL1271 chipset […]
Wandboard Dual Benchmarks, Serial Console Fun, and Distributions List
Since last time I tried Android and Ubuntu on the Wandboard, a few things happened. I’m not talking about Wandboard Quad announcement, but instead I received a Class 10 SD card, which makes the system so much responsive, and a RS232 to USB adapter so that I can access the serial console. So today, I’ll publish some benchmark results on Wandboard Dual since none appear to be available, and play a little with the serial console. A few things also happened on the operating systems side with more distributions now available for the board. Prerequisites I ran benchmark in Android, so I installed the latest Android 4.1.2 image (11th of April 2012) to my new SD card (ADATA 16 GB Class 10), and contrary to my poor experience on a 4GB Class 4 micro SD, everything was very fluid. I’ve also installed Google Play in order to install the applications. […]
Geniatech Releases ATV510B Source Code, Teases Dual and Quad Core ATV130 and ATV180 mini PCs
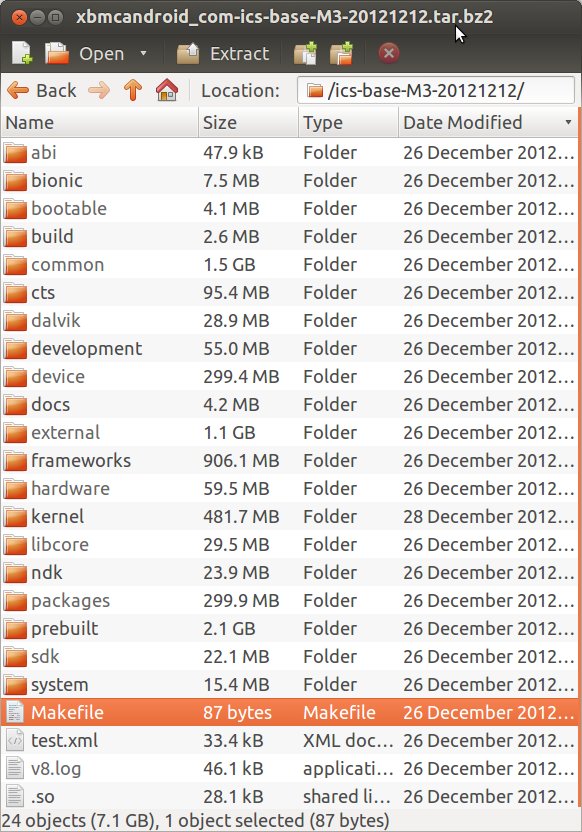
XBMCHUB (not affiliated with XBMC) reports that Geniatech has released the Android and Linux source code for ATV510B, one of Geniatech set-top boxes based on AML8726-M3 Cortex A9 processor. ATV510B is the design used by devices such as Pivos XIOS DS, Jynxbox Android HD, Sumvision Cyclone Nano M3, and MyGica ATV510B Enjoy TV Nano 3, among others. Pivos has made U-boot, Linux and XBMC source code available in github for a little while now, but this new release is a pretty large file (2.39 GB) called xbmcandroid_com-ics-base-M3-20121212.tar.bz2 that includes Android 4.0 source including the kernel and the bootloader. This source code should work with “stvmc” hardware, as found in build.prop’s ro.product.name or ro.product.device keys. I haven’t looked into details, but here’s the content of the root directory of the archive: On a separate note, Geniatech also showed the picture below on their Facebook page, with 2 new Android TV Sticks: […]
MiTAC Announces 7-Star 64-Bit ARM Server Powered by Applied Micro X-Gene Server-on-Chip
After unveiling their GFX servers based on Marvell ARM Cortex A9 SoC at Computex 2012, Mitac announced their new 7-Star server at Computex 2013. This new server is based on Applied Micro X-Gene SoC featuring ARMv8 architecture, and is one of the first, if not the first, 64-Bit ARM server ever. The key features of Mitac Server are as follows: 18x Front-loaded Computing Blades in 4U (176mm x 440mm x 650mm) Server Blade Spec SSI uModule v1.0 complaint (1) ARMv8 compliant 64-bit SoC /blade (2) DDR3 DIMM slots, and (2) 2.5” SATA 3.0 HDD support (1) 10G SFP+ and (1) GbE port IPMI V2.0 compliant Pass-through Ethernet Module Chassis Management Hot-swap FAN and (2+1) RPSU support It will be available by the end of the year. That’s about all I know for now, but more information should eventually come up on Mitac 7-Star page. Via PC Perspective. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc […]
Rockchip RK3188 Linux Source Code is Now Available
Good news! I’ve just read Rockchip RK3188 Linux source code has just been released via Rikomagic, and Alok Sinha, the main maintainer of RK3066 source code, has already imported into github, and we should soon see a PicUntu image for RK3188 mini PCs. Let’s have a look:
|
1 2 |
git clone git://github.com/aloksinha2001/Linux3188.git cd Linux3188 |
[Update: you may have to run “sudo apt-get install libc6-i386” before running make_kernel_ruikemei.sh below, as mkkrnlimg is a 32-bit binary] Usually, I immediately look into arch/arm/configs, but this time, there’s a “funny” script called make_kernel_ruikemei.sh, and .config already have some CONFIG_RK3188, so let’s run it:
|
1 2 3 |
export ARCH=arm export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- ./make_kernel_ruikemei.sh |
After just over a minute, success!:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
LD vmlinux SYSMAP System.map SYSMAP .tmp_System.map OBJCOPY arch/arm/boot/Image Kernel: arch/arm/boot/Image is ready mkkrnlimg V20120220 cmd:/home/jaufranc/edev/sandbox/rk3188/Linux3188/arch/arm/boot/Image /home/jaufranc/edev/sandbox/rk3188/Linux3188/kernel.img [(null)] kernel Image:/home/jaufranc/edev/sandbox/rk3188/Linux3188/kernel.img for mid is ready. Image: kernel.img is ready |
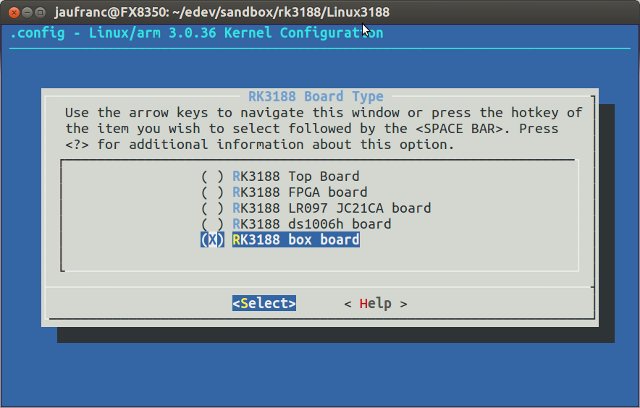
This kernel image is for Android only, and there’s a little work to modify it as a “pure” Linux kernel, so that it can be used to boot PicUnutu for RK3188. Let’s go back to arch/arm/configs, and we’ll find several RK3188 configs: rk3168_86v_defconfig rk3188_dongle_defconfig rk3188_ds1006h_defconfig rk3188_ds1006h_v1_0_defconfig rk3188_hotdog_defconfig rk3188_LR097_defconfig rk3188_magicwand_defconfig […]
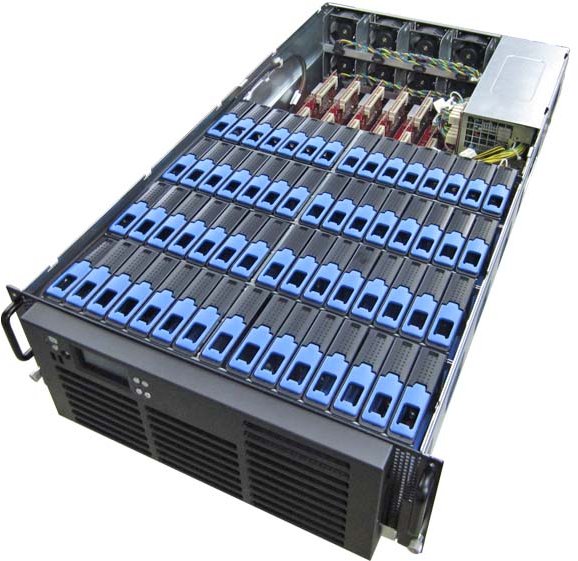
Calxeda Showcases Aaeon and Foxconn ARM Servers at Computex 2013
ARM started to get involved in servers in 2011 with the announcements of Calxeda Energy Core, Marvell, and Applied Micro X-Gene Servers-on-a-Chip, and in 2012, products made by companies such as HP and Mitac started to appears. We’ve got to see some more ARM based servers this year thanks to Charbax, who filmed some Aaeon and Foxconn servers powered by Calxeda EnergyCore quad core ARM Cortex A9 SoC at Computex 2013. The first server is Aaeon Indus 1U cloud storage appliance: 1U Chassis 2x Calxeda Energycore nodes 10x 3.5″ HDD 2x 10 GbE uplinks and 4x 10GbE chassis-to-chassis interconnects Foxconn server shown at Computex has slightly higher specs: 4U chassis 12 Calxeda Energycore nodes 60x 3.5″ HDD for up to 240TB storage 4x 10 GbE uplinks and 6x 10 GbE chassis-to-chassis interconnects for 100 GbE total bandwidth There’s also a Gigabyte server, but I could get details. Server based on […]
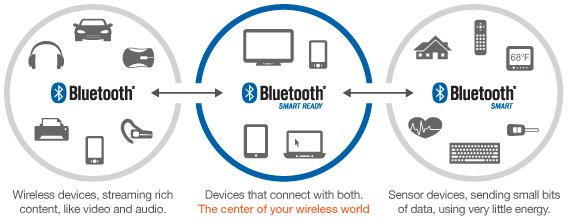
Bluetooth Versions Walkthrough, and Bluetooth 4.0 Low Energy Development Resources
I’ve seen more and more Bluetooth 4.0 LE devices in the last few months including RFDuino, Wimoto Motes, TI SensorTag, and Scadanu Scout, so I thought it would be good to write a bit about Bluetooth. First, I’ll write about the different version of Bluetooth, since I was still confused with the practical implications between the versions, and then I’ll show some development kits and software resources to play around and/or develop Bluetooth 4.0 LE applications both on devices and hosts. Bluetooth Versions Bluetooth v1.0 and v1.0B The Bluetooth 1.0 Specification was released in 1999, and according to an entry in Wikipedia, 1.0 and 1.0B devices had many issues, mainly interoperability issues. You won’t find any Bluetooth 1.0 device today. Bluetooth v1.1 Bluetooth v1.1 was ratified as IEEE Standard 802.15.1-2002 in 2002. It fixed many issues found in the previous specifications, added the option to use non-encrypted channels, as well […]