I’ve received NanoPi NEO 2 boards, add-boards and sensor modules last week, where we could see how small the boards were, and how it could be suitable for IoT projects or “hardware hacking” education. Before testing the board with the add-ons, I have to select the image to run on the board, and currently we have two choices: Ubuntu 16.04.2 FriendlyELEC image with Linux 3.10 “legacy” kernel, or Armbian Ubuntu 16.04.2 Xenial nightly build with Linux 4.10 “mainline” kernel. So I decided to try both: dfssf
- nanopi-neo2-ubuntu-core-qte-sd4g-20170329.img.zip (296 MB) is the image from FriendlyELEC (previously FriendlyARM)
- Armbian_5.27.170401_Nanopineo2_Ubuntu_xenial_dev_4.10.0.7z (222 Mb) is the image from Armbian, which I downloaded on March 31st despite the filename including “170401” string
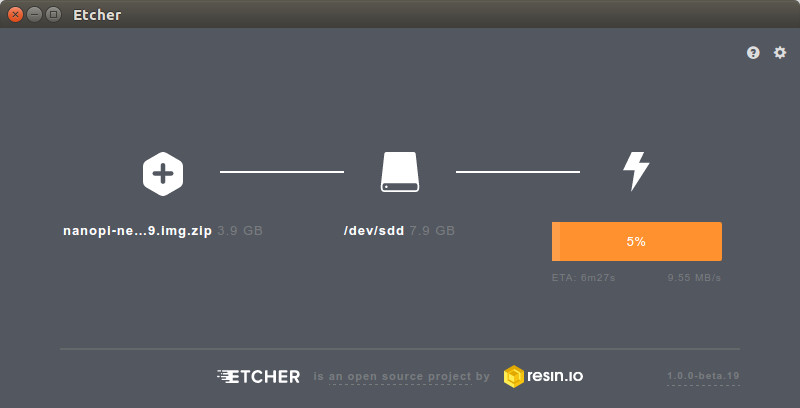
You can flash the image with Win32DiskImager (Windows) or dd (linux) to a micro SD card the usual way, and while I’ve never personally had troubles with dd, I’ve been told Etcher was better, as it verifies the SD card after flashing, and dd may miss errors. Etcher works in Windows, Linux, and Mac OS with a graphical user interface or from the command line. I used Etcher GUI in my Ubuntu 16.04 computer, and it’s indeed easy to use, shows the progress, and a big plus for me is that you can’t mess with your USB hard drive, as it will filter them. Another small advantage is that you don’t need to uncompress the firmware, as Etcher will do that for you, at least for zip files, but i had to manually uncompress Armbian .7z archive before loading to Etcher.
Note that I used the exact same micro SD card (the 8GB SanDisk Ultra sold by FriendlyELEC) and the same board for both images. I started with FriendlyELEC image, and then repeated the test with Armbian image.
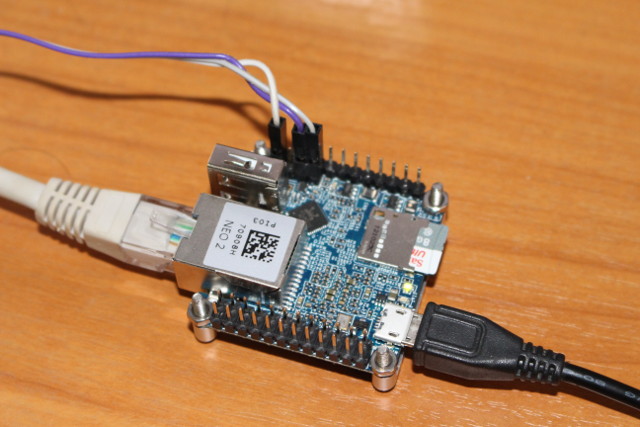
I connected the Gigabit Ethernet port to my GbE switch, as well as FriendlyELEC Matrix USB2UART board with the provide cabled including 5V, GND, Tx and RX. It will power the board too, but if you’re going to run benchmarks, there won’t always be enough, and I also used a USB power supply connected to the micro USB port. Having 5V on the serial cable makes it inconvenient, because when I need to power cycle the board I had to remove both the debug board and the extra USB power supply. So instead I used 3 jumper wires without 5V as shown in the picture below.
FriendlyELEC Ubuntu 16.04.2 Boot Log and Info
I used minicom connected to /dev/ttyUSB0 with 115200 8N1 configuration to boot the board, and this is the boot log for Ubuntu 16.04.2 image with Linux 3.10 once I got the debug board issue mentioned above out of the way (so it’s not the very first boot):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 |
NOTICE: BL3-1: v1.0(debug):3ffd944 NOTICE: BL3-1: Built : 11:09:10, Aug 30 2016 NOTICE: BL3-1 commit: 3ffd9442d4769d7fc0002770e3b69b55150a288e INFO: BL3-1: Initializing runtime services ERROR: Error initializing runtime service tspd_fast INFO: BL3-1: Preparing for EL3 exit to normal world INFO: BL3-1: Next image address = 0x4a000000 INFO: BL3-1: Next image spsr = 0x1d3 U-Boot 2014.07 (Mar 29 2017 - 09:47:44) Allwinner Technology uboot commit : 7c8cc7f37ec0391e13186d04c698d6e48ff3f861 secure enable bit: 0 i2c: secure monitor exist [ 0.752]pmbus: ready u0:48105000 [ 0.755][ARISC] :arisc initialize [ 0.898][ARISC] :arisc_dvfs_cfg_vf_table: support only one vf_table [ 0.961][ARISC] :arisc para ok [SCP] :sunxi-arisc driver begin startup 2 [SCP] :arisc version: [sun8iw5_v0.03.00-244-gb750b8e] [SCP] :sunxi-arisc driver v1.20 is starting [ 0.976][ARISC] :sunxi-arisc driver startup succeeded axp: get node[charger0] error [SCP ERROR] :message process error [SCP ERROR] :message addr : 48105080 [SCP ERROR] :message state : 5 [SCP ERROR] :message attr : 2 [SCP ERROR] :message type : 80 [SCP ERROR] :message result : f3 [SCP WARING] :callback not install [SCP ERROR] :arisc twi read pmu reg 0x3 err probe axp806 failed axp_probe error [ 1.011]PMU: cpux 1008 Mhz,AXI=336 Mhz PLL6=600 Mhz,AHB1=200 Mhz, APB1=100Mhz MBus=400Mhz run key detect no key found no uart input DRAM: 512 MiB fdt addr: 0x56e9d320 Relocation Offset is: 15ef0000 axp: get node[charger0] error In: serial Out: serial Err: serial gic: sec monitor mode [box standby] read rtc = 0x0 [box standby] start_type = 0x1 [box standby] to kernel boot_init_gpio used ir boot recovery not used workmode = 0,storage type = 1 [ 1.266]MMC: 0 [mmc]: mmc driver ver 2016-05-20 17:18:00-test0 [mmc]: get card2_boot_para:sdc_ex_dly_used 0 [mmc]: no mmc-hs400-1_8v! [mmc]: no mmc-hs200-1_8v! [mmc]: no mmc-ddr-1_8v! [mmc]: delete max-frequency from dtb SUNXI SD/MMC: 0 [mmc]: 50 MHz... [mmc]: sample: 63 - 158(ps) [mmc]: 100 MHz... [mmc]: sample: 32 - 156(ps) [mmc]: 200 MHz... [mmc]: sample: 15 - 166(ps) [mmc]: media type 0x0 [mmc]: Wrong media type 0x0 [mmc]: ************Try SD card 0************ [mmc]: host caps: 0x27 [mmc]: MID 03 PSN 49731d8a [mmc]: PNM SL08G -- 0x53-4c-30-38-47 [mmc]: PRV 8.0 [mmc]: MDT m-6 y-2016 [mmc]: speed mode : HSSDR52/SDR25 [mmc]: clock : 50000000 Hz [mmc]: bus_width : 4 bit [mmc]: user capacity : 7580 MB [mmc]: ************SD/MMC 0 init OK!!!************ [mmc]: erase_grp_size : 0x1WrBlk*0x200=0x200 Byte [mmc]: secure_feature : 0x0 [mmc]: secure_removal_type : 0x0 [ 1.494]sunxi flash init ok mmc0 is current device [ 1.513]start drv_disp_init tv_init: tv_probe:000 no report hpd work,you need support the switch class! screen 0 don't support TV! tv_init: fetch tv1 err. drv_disp_init finish hdcp is closed by sys config. no the part:Reserve0 hpd_dev_num=2, id of def_output_dev is 0 hdmi hpd out, force open? fdt_setprop_u32 disp.init_disp(0x20b0404) code: fb_id=0, size=3686400, gd->ram_size=536870912, SUNXI_DISPLAY_FRAME_BUFFER_SIZE=6 [ 2.127]end PowerBus = 0( 2:vBus 3:acBus other: not exist) no battery, limit to dc no battery exist sunxi_bmp_logo_display [boot disp] can not find the partition Reserve0 bmp_name=bootlogo.bmp reading bootlogo.bmp 3686454 bytes read in 160 ms (22 MiB/s) fdt_setprop_string disp.boot_fb0(5f000000,500,2d0,20,1400,0,0,500,2d0). ret-cod> try to read logic blk 0 without env partition *** Warning - bad CRC, using default environment --------fastboot partitions-------- mbr not exist base bootcmd=run setargs_mmc boot_normal bootcmd set setargs_mmc no misc partition is found to be run cmd=run setargs_mmc boot_normal read item0 copy0 Item0 (Map) magic is bad the secure storage item0 copy0 is bad read item0 copy1 Item0 (Map) magic is bad the secure storage item0 copy0 == copy1, the data is good the secure storage map is empty no item name selinux in the map sunxi storage read fail no item name fsck.repair in the map sunxi storage read fail check user data form private the private part isn't exist update_fdt_para_for_kernel update dtb dram start update dtb dram end serial is: 34005035c2003c2a074c [ 2.533]inter uboot shell Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 reading boot.img 17256448 bytes read in 738 ms (22.3 MiB/s) Android's image name: sun50i_arm64 Kernel load addr 0x40080000 size 12302 KiB RAM disk load addr 0x41000000 size 4548 KiB [ 4.424]ready to boot prepare for kernel [mmc]: MMC Device 2 not found [mmc]: mmc 2 not find, so not exit Starting kernel ... INFO: BL3-1: Next image address = 0x40080000 INFO: BL3-1: Next image spsr = 0x3c5 [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpu [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuacct [ 0.000000] Linux version 3.10.65 (root@wwd) (gcc version 4.9.3 20150113 (pr7 [ 0.000000] CPU: AArch64 Processor [410fd034] revision 4 [ 0.000000] Machine: sun50iw2 [ 0.000000] cma: CMA: reserved 16 MiB at 5f000000 [ 0.000000] On node 0 totalpages: 131072 [ 0.000000] DMA zone: 1792 pages used for memmap [ 0.000000] DMA zone: 0 pages reserved [ 0.000000] DMA zone: 131072 pages, LIFO batch:31 [ 0.000000] psci: probing for conduit method from DT. [ 0.000000] psci: PSCIv0.2 detected in firmware. [ 0.000000] psci: Using standard PSCI v0.2 function IDs [ 0.000000] PERCPU: Embedded 12 pages/cpu @ffffffc01ef98000 s20224 r8192 d202 [ 0.000000] pcpu-alloc: s20224 r8192 d20736 u49152 alloc=12*4096 [ 0.000000] pcpu-alloc: [0] 0 [0] 1 [0] 2 [0] 3 [ 0.000000] Built 1 zonelists in Zone order, mobility grouping on. Total pa0 [ 0.000000] Kernel command line: console=ttyS0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 in1 [ 0.000000] PID hash table entries: 2048 (order: 2, 16384 bytes) [ 0.000000] Dentry cache hash table entries: 65536 (order: 7, 524288 bytes) [ 0.000000] Inode-cache hash table entries: 32768 (order: 6, 262144 bytes) [ 0.000000] Memory: 512MB = 512MB total [ 0.000000] Memory: 457840k/457840k available, 66448k reserved [ 0.000000] Virtual kernel memory layout: [ 0.000000] vmalloc : 0xffffff8000000000 - 0xffffffbbffff0000 (245759 ) [ 0.000000] vmemmap : 0xffffffbc00e00000 - 0xffffffbc01500000 ( 7 ) [ 0.000000] modules : 0xffffffbffc000000 - 0xffffffc000000000 ( 64 ) [ 0.000000] memory : 0xffffffc000000000 - 0xffffffc020000000 ( 512 ) [ 0.000000] .init : 0xffffffc000b28000 - 0xffffffc000bb7f00 ( 576 ) [ 0.000000] .text : 0xffffffc000080000 - 0xffffffc000b27754 ( 10910 ) [ 0.000000] .data : 0xffffffc000bb8000 - 0xffffffc000c83490 ( 814 ) [ 0.000000] Preemptible hierarchical RCU implementation. [ 0.000000] NR_IRQS:64 nr_irqs:64 0 [ 0.000000] Architected cp15 timer(s) running at 24.00MHz (virt). [ 0.000000] Console: colour dummy device 80x25 [ 4.535949] Calibrating delay loop (skipped), value calculated using timer f) [ 4.535959] pid_max: default: 32768 minimum: 301 [ 4.536435] Security Framework initialized [ 4.536452] SELinux: Disabled at boot. [ 4.536742] Mount-cache hash table entries: 256 [ 4.538709] Initializing cgroup subsys debug [ 4.538722] Initializing cgroup subsys freezer [ 4.538926] ftrace: allocating 29140 entries in 114 pages [ 4.576571] CPU0: update cpu_power 1024 [ 4.576591] hw perfevents: enabled with arm/armv8-pmuv3 PMU driver, 7 countee [ 4.578398] virtual base = 0xffffff800000a000. [ 4.578412] gicd_base = 0xffffff800000c000. [ 4.578417] gicc_base = 0xffffff800000e000. [ 4.580317] CPU1: Booted secondary processor [ 4.580344] CPU1: update cpu_power 1024 [ 4.582087] CPU2: Booted secondary processor [ 4.582101] CPU2: update cpu_power 1024 [ 4.583798] CPU3: Booted secondary processor [ 4.583810] CPU3: update cpu_power 1024 [ 4.583897] Brought up 4 CPUs [ 4.583922] SMP: Total of 4 processors activated (192.00 BogoMIPS). [ 4.585236] devtmpfs: initialized [ 4.616168] atomic64 test passed [ 4.616181] pinctrl core: initialized pinctrl subsystem [ 4.619093] NET: Registered protocol family 16 [ 4.621823] dump_class_init,839, success [ 4.623034] vdso: 2 pages (1 code, 1 data) at base ffffffc000bc1000 [ 4.623060] hw-breakpoint: found 6 breakpoint and 4 watchpoint registers. [ 4.625380] software IO TLB [mem 0x5d000000-0x5d400000] (4MB) mapped at [fff] [ 4.626678] DMA: preallocated 256 KiB pool for atomic allocations [ 4.627367] pll_audio-set_default_rate=24576000 success! [ 4.627398] pll_video-set_default_rate=297000000 success! [ 4.627436] pll_ve-set_default_rate=420000000 success! [ 4.627553] pll_de-set_default_rate=864000000 success! [ 4.627860] ahb1-set_default_rate=200000000 success! [ 4.628727] de-set_default_source=pll_de success! [ 4.628734] de-set_default_rate=432000000 success! [ 4.628793] tcon0-set_default_source=pll_video success! [ 4.628872] tve-set_default_source=pll_de success! [ 4.629174] hdmi-set_default_source=pll_video success! [ 4.633126] sun50iw2p1-r-pinctrl 1f02c00.pinctrl: initialized sunXi PIO drivr [ 4.636298] sun50iw2p1-pinctrl 1c20800.pinctrl: initialized sunXi PIO driver [ 4.638340] sunxi hwspinlock vbase:0xffffff800005c000 [ 4.720108] bio: create slab at 0 [ 4.721153] pwm module init! [ 4.727391] SCSI subsystem initialized [ 4.729661] usbcore: registered new interface driver usbfs [ 4.729964] usbcore: registered new interface driver hub [ 4.730245] usbcore: registered new device driver usb [ 4.732598] Linux video capture interface: v2.00 [ 4.739218] [ARISC] :sunxi-arisc driver v1.20 [ 4.740164] [ARISC] :sunxi-arisc driver v1.20 startup succeeded [ 4.740847] Advanced Linux Sound Architecture Driver Initialized. [ 4.742280] Bluetooth: Core ver 2.16 [ 4.742482] NET: Registered protocol family 31 [ 4.742488] Bluetooth: HCI device and connection manager initialized [ 4.742520] Bluetooth: HCI socket layer initialized [ 4.742549] Bluetooth: L2CAP socket layer initialized [ 4.742605] Bluetooth: SCO socket layer initialized [ 4.743519] cfg80211: Calling CRDA to update world regulatory domain [ 4.744631] [pm]aw_pm_init! [ 4.744742] np name = /soc@01c00000/rtc@01f00000. [ 4.744749] base = ffffff800006c100, len = 4. [ 4.744755] pmu name: pmic0 . [ 4.744840] Warning: can not find np for pmic0. [ 4.744845] pmu name: pmic1 . [ 4.744868] Warning: can not find np for pmic1. [ 4.744951] add_sys_pwr_dm: get ldo name for id: vcc-lpddr failed [ 4.744959] add_sys_pwr_dm: get ldo name for id: vcc-pl failed [ 4.744966] add_sys_pwr_dm: axpdummy_ldo6 ldo already alwayson. [ 4.744988] add_sys_pwr_dm: vcc-pc not sys id. [ 4.744993] after inited: sys_mask config = 0x4855. [ 4.745016] Warning: can not find np for dynamic_standby_para. [ 4.745149] [pm]valid [ 4.745153] [pm]valid [ 4.745159] Notice: sun9i & sun8iw5 & sun50i not need support normal standby. [ 4.745184] [DISP]disp_module_init [ 4.746052] [DISP] init_disp:0x20b0404 [ 4.746062] [DISP] boot_disp:0x0 [ 4.746596] [DISP] fb_base:0x0 [ 4.762460] [DISP]disp_module_init finish [ 4.763663] sunxi budget cooling probe start ! [ 4.763689] CPU freq cooling register Success [ 4.763715] CPU hotplug cooling register Success [ 4.764059] CPU budget cooling register Success [ 4.765806] input: sunxi-ths as /devices/virtual/input/input0 [ 4.765861] thermal thermal_zone0: failed to read out thermal zone 0 [ 4.766411] Switching to clocksource arch_sys_counter [ 4.812086] FS-Cache: Loaded [ 4.812682] CacheFiles: Loaded [ 4.839252] NET: Registered protocol family 2 [ 4.840770] TCP established hash table entries: 4096 (order: 4, 65536 bytes) [ 4.840871] TCP bind hash table entries: 4096 (order: 4, 65536 bytes) [ 4.840957] TCP: Hash tables configured (established 4096 bind 4096) [ 4.841608] TCP: reno registered [ 4.841620] UDP hash table entries: 256 (order: 1, 8192 bytes) [ 4.841639] UDP-Lite hash table entries: 256 (order: 1, 8192 bytes) [ 4.842359] NET: Registered protocol family 1 [ 4.843376] RPC: Registered named UNIX socket transport module. [ 4.843382] RPC: Registered udp transport module. [ 4.843387] RPC: Registered tcp transport module. [ 4.843392] RPC: Registered tcp NFSv4.1 backchannel transport module. [ 4.844340] Unpacking initramfs... [ 5.107382] Freeing initrd memory: 4544K (ffffffc001000000 - ffffffc00147000) [ 5.108609] lock super standby defaultly! [ 5.108625] lookup_scene_lock_name: new scene lock super_standby [ 5.108631] scene_lock_init name=super_standby [ 5.108639] scene_lock: super_standby, type 5, count 1 [ 5.109896] audit: initializing netlink socket (disabled) [ 5.109973] type=2000 audit(0.560:1): initialized [ 5.114977] FS-Cache: Netfs 'nfs' registered for caching [ 5.116236] FS-Cache: Netfs 'cifs' registered for caching [ 5.117153] NTFS driver 2.1.30 [Flags: R/W]. [ 5.117880] fuse init (API version 7.22) [ 5.118886] msgmni has been set to 935 [ 5.120486] io scheduler noop registered [ 5.120494] io scheduler deadline registered [ 5.120612] io scheduler cfq registered (default) [ 5.122155] sunxi_bootup_extend_probe: bootup extend state 1 [ 5.122163] bootup extend probe ok [ 5.123647] uart0: ttyS0 at MMIO 0x1c28000 (irq = 32) is a SUNXI [ 5.123671] sw_console_setup()1268 - console setup baud 115200 parity n bitsn [ 6.022122] console [ttyS0] enabled [ 6.026908] uart1: ttyS1 at MMIO 0x1c28400 (irq = 33) is a SUNXI [ 6.034086] uart2: ttyS2 at MMIO 0x1c28800 (irq = 34) is a SUNXI [ 6.041326] uart3: ttyS3 at MMIO 0x1c28c00 (irq = 35) is a SUNXI [ 6.049888] misc dump reg init [ 6.061293] loop: module loaded [ 6.064781] Boot type 1 [ 6.072098] tun: Universal TUN/TAP device driver, 1.6 [ 6.077644] tun: (C) 1999-2004 Max Krasnyansky <[email protected]> [ 6.087208] PPP generic driver version 2.4.2 [ 6.092423] PPP BSD Compression module registered [ 6.097575] PPP Deflate Compression module registered [ 6.103100] PPP MPPE Compression module registered [ 6.108344] NET: Registered protocol family 24 [ 6.113248] PPTP driver version 0.8.5 [ 6.117605] hso: drivers/net/usb/hso.c: Option Wireless [ 6.123946] usbcore: registered new interface driver hso [ 6.129969] usbcore: registered new interface driver asix [ 6.136084] usbcore: registered new interface driver ax88179_178a [ 6.142942] usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_ether [ 6.149511] usbcore: registered new interface driver net1080 [ 6.155893] usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_subset [ 6.162548] usbcore: registered new interface driver zaurus [ 6.168881] usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_ncm [ 6.175073] ehci_hcd: USB 2.0 'Enhanced' Host Controller (EHCI) Driver [ 6.182528] get ehci0-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.188721] [sunxi-ehci0]: probe, pdev->name: 1c1a000.ehci0-controller, sunx8 [ 6.202019] sunxi-ehci 1c1a000.ehci0-controller: SW USB2.0 'Enhanced' Host Cr [ 6.211944] sunxi-ehci 1c1a000.ehci0-controller: new USB bus registered, ass1 [ 6.221988] sunxi-ehci 1c1a000.ehci0-controller: irq 104, io mem 0xffffffc008 [ 6.242474] sunxi-ehci 1c1a000.ehci0-controller: USB 0.0 started, EHCI 1.00 [ 6.250221] usb usb1: New USB device found, idVendor=1d6b, idProduct=0002 [ 6.257651] usb usb1: New USB device strings: Mfr=3, Product=2, SerialNumber1 [ 6.265552] usb usb1: Product: SW USB2.0 'Enhanced' Host Controller (EHCI) Dr [ 6.273738] usb usb1: Manufacturer: Linux 3.10.65 ehci_hcd [ 6.279730] usb usb1: SerialNumber: sunxi-ehci [ 6.285591] hub 1-0:1.0: USB hub found [ 6.289710] hub 1-0:1.0: 1 port detected [ 6.294437] get drv_vbus is fail, 84 [ 6.298339] get ehci1-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.304501] [sunxi-ehci1]: probe, pdev->name: 1c1b000.ehci1-controller, sunxa [ 6.317788] sunxi-ehci 1c1b000.ehci1-controller: SW USB2.0 'Enhanced' Host Cr [ 6.327710] sunxi-ehci 1c1b000.ehci1-controller: new USB bus registered, ass2 [ 6.337597] sunxi-ehci 1c1b000.ehci1-controller: irq 106, io mem 0xffffffc008 [ 6.360552] sunxi-ehci 1c1b000.ehci1-controller: USB 0.0 started, EHCI 1.00 [ 6.368275] usb usb2: New USB device found, idVendor=1d6b, idProduct=0002 [ 6.375705] usb usb2: New USB device strings: Mfr=3, Product=2, SerialNumber1 [ 6.383606] usb usb2: Product: SW USB2.0 'Enhanced' Host Controller (EHCI) Dr [ 6.391825] usb usb2: Manufacturer: Linux 3.10.65 ehci_hcd [ 6.397818] usb usb2: SerialNumber: sunxi-ehci [ 6.403611] hub 2-0:1.0: USB hub found [ 6.407734] hub 2-0:1.0: 1 port detected [ 6.412448] get drv_vbus is fail, 84 [ 6.416350] get ehci2-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.422445] sunxi ehci2-controller is no enable [ 6.427394] sunxi-ehci 1c1c000.ehci2-controller: init_sunxi_hci is fail [ 6.434685] get drv_vbus is fail, 84 [ 6.438586] get ehci3-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.444744] [sunxi-ehci3]: probe, pdev->name: 1c1d000.ehci3-controller, sunxe [ 6.458028] sunxi-ehci 1c1d000.ehci3-controller: SW USB2.0 'Enhanced' Host Cr [ 6.467949] sunxi-ehci 1c1d000.ehci3-controller: new USB bus registered, ass3 [ 6.477828] sunxi-ehci 1c1d000.ehci3-controller: irq 110, io mem 0xffffffc008 [ 6.498313] sunxi-ehci 1c1d000.ehci3-controller: USB 0.0 started, EHCI 1.00 [ 6.506058] usb usb3: New USB device found, idVendor=1d6b, idProduct=0002 [ 6.513519] usb usb3: New USB device strings: Mfr=3, Product=2, SerialNumber1 [ 6.521426] usb usb3: Product: SW USB2.0 'Enhanced' Host Controller (EHCI) Dr [ 6.529613] usb usb3: Manufacturer: Linux 3.10.65 ehci_hcd [ 6.535605] usb usb3: SerialNumber: sunxi-ehci [ 6.541562] hub 3-0:1.0: USB hub found [ 6.545678] hub 3-0:1.0: 1 port detected [ 6.550892] ohci_hcd: USB 1.1 'Open' Host Controller (OHCI) Driver [ 6.557922] get ohci0-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.564071] hci: request ohci0-controller gpio:354 [ 6.569316] ohci0-controller get usb clk_usbohci12m clk failed. [ 6.575782] ohci0-controller get usb clk_hoscx2 clk failed. [ 6.581881] ohci0-controller get usb clk_hosc failed. [ 6.587407] ohci0-controller get usb clk_losc clk failed. [ 6.593305] [sunxi-ohci0]: probe, pdev->name: 1c1a000.ohci0-controller, sunx0 [ 6.603550] sunxi-ohci 1c1a000.ohci0-controller: SW USB2.0 'Open' Host Contrr [ 6.613088] sunxi-ohci 1c1a000.ohci0-controller: new USB bus registered, ass4 [ 6.622578] sunxi-ohci 1c1a000.ohci0-controller: irq 105, io mem 0x6b6c632060 [ 6.689319] usb usb4: New USB device found, idVendor=1d6b, idProduct=0001 [ 6.696749] usb usb4: New USB device strings: Mfr=3, Product=2, SerialNumber1 [ 6.704641] usb usb4: Product: SW USB2.0 'Open' Host Controller (OHCI) Driver [ 6.712448] usb usb4: Manufacturer: Linux 3.10.65 ohci_hcd [ 6.718450] usb usb4: SerialNumber: sunxi-ohci [ 6.724167] hub 4-0:1.0: USB hub found [ 6.728300] hub 4-0:1.0: 1 port detected [ 6.732955] get drv_vbus is fail, 84 [ 6.736869] get ohci1-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.743010] ohci1-controller get usb clk_usbohci12m clk failed. [ 6.749487] ohci1-controller get usb clk_hoscx2 clk failed. [ 6.755582] ohci1-controller get usb clk_hosc failed. [ 6.761098] ohci1-controller get usb clk_losc clk failed. [ 6.767005] [sunxi-ohci1]: probe, pdev->name: 1c1b000.ohci1-controller, sunx0 [ 6.777241] sunxi-ohci 1c1b000.ohci1-controller: SW USB2.0 'Open' Host Contrr [ 6.786774] sunxi-ohci 1c1b000.ohci1-controller: new USB bus registered, ass5 [ 6.796262] sunxi-ohci 1c1b000.ohci1-controller: irq 107, io mem 0x736f6c5f60 [ 6.866441] usb usb5: New USB device found, idVendor=1d6b, idProduct=0001 [ 6.873872] usb usb5: New USB device strings: Mfr=3, Product=2, SerialNumber1 [ 6.881764] usb usb5: Product: SW USB2.0 'Open' Host Controller (OHCI) Driver [ 6.889570] usb usb5: Manufacturer: Linux 3.10.65 ohci_hcd [ 6.895572] usb usb5: SerialNumber: sunxi-ohci [ 6.901282] hub 5-0:1.0: USB hub found [ 6.905409] hub 5-0:1.0: 1 port detected [ 6.910074] get drv_vbus is fail, 84 [ 6.913987] get ohci2-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.920072] sunxi ohci2-controller is no enable [ 6.925032] ohci2-controller get usb clk_usbohci12m clk failed. [ 6.931507] ohci2-controller get usb clk_hoscx2 clk failed. [ 6.937593] ohci2-controller get usb clk_hosc failed. [ 6.943119] ohci2-controller get usb clk_losc clk failed. [ 6.949014] hci: ERR: sunxi_ohci is null [ 6.953302] hci: ERR: sunxi_ohci_hcd_probe, sunxi_ohci is null [ 6.959682] sunxi-ohci: probe of 1c1c000.ohci2-controller failed with error 1 [ 6.967636] get drv_vbus is fail, 84 [ 6.971548] get ohci3-controller, regulator_io is no nocare [ 6.977684] ohci3-controller get usb clk_usbohci12m clk failed. [ 6.984161] ohci3-controller get usb clk_hoscx2 clk failed. [ 6.990248] ohci3-controller get usb clk_hosc failed. [ 6.995772] ohci3-controller get usb clk_losc clk failed. [ 7.001710] [sunxi-ohci3]: probe, pdev->name: 1c1d000.ohci3-controller, sunx0 [ 7.011950] sunxi-ohci 1c1d000.ohci3-controller: SW USB2.0 'Open' Host Contrr [ 7.021485] sunxi-ohci 1c1d000.ohci3-controller: new USB bus registered, ass6 [ 7.030972] sunxi-ohci 1c1d000.ohci3-controller: irq 111, io mem 0x6c6320637f [ 7.092752] usb usb6: New USB device found, idVendor=1d6b, idProduct=0001 [ 7.100182] usb usb6: New USB device strings: Mfr=3, Product=2, SerialNumber1 [ 7.108075] usb usb6: Product: SW USB2.0 'Open' Host Controller (OHCI) Driver [ 7.115881] usb usb6: Manufacturer: Linux 3.10.65 ohci_hcd [ 7.121887] usb usb6: SerialNumber: sunxi-ohci [ 7.127595] hub 6-0:1.0: USB hub found [ 7.131729] hub 6-0:1.0: 1 port detected [ 7.137047] usbcore: registered new interface driver usb-storage [ 7.143835] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-alauda [ 7.150518] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-cypress [ 7.157274] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-datafab [ 7.164035] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums_eneub6250 [ 7.170994] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-freecom [ 7.177757] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-isd200 [ 7.184410] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-jumpshot [ 7.191265] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-karma [ 7.197848] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-onetouch [ 7.204714] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-realtek [ 7.211478] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-sddr09 [ 7.218144] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-sddr55 [ 7.224801] usbcore: registered new interface driver ums-usbat [ 7.232028] usbcore: registered new interface driver usbserial [ 7.238613] usbcore: registered new interface driver option [ 7.244881] usbserial: USB Serial support registered for GSM modem (1-port) [ 7.253968] mousedev: PS/2 mouse device common for all mice [ 7.260883] usbcore: registered new interface driver xpad [ 7.266996] usbcore: registered new interface driver usb_acecad [ 7.273668] usbcore: registered new interface driver aiptek [ 7.279964] usbcore: registered new interface driver gtco [ 7.286071] usbcore: registered new interface driver hanwang [ 7.292448] usbcore: registered new interface driver kbtab [ 7.298676] usbcore: registered new interface driver wacom [ 7.306840] sunxi-rtc 1f00000.rtc: rtc core: registered sunxi-rtc as rtc0 [ 7.314304] sunxi-rtc 1f00000.rtc: RTC enabled [ 7.319889] IR NEC protocol handler initialized [ 7.324836] IR RC5(x) protocol handler initialized [ 7.330079] IR RC6 protocol handler initialized [ 7.335033] IR JVC protocol handler initialized [ 7.339978] IR Sony protocol handler initialized [ 7.345026] IR RC5 (streamzap) protocol handler initialized [ 7.351111] IR SANYO protocol handler initialized [ 7.356256] IR MCE Keyboard/mouse protocol handler initialized [ 7.362625] sunxi cedar version 0.1 [ 7.366646] [cedar]: install start!!! [ 7.370751] cedar_ve: cedar-ve the get irq is 90 [ 7.376452] [cedar]: install end!!! [ 7.392629] sunxi gpu cooling probe start ! [ 7.397234] CPU gpu cooling register Success [ 7.402310] device-mapper: uevent: version 1.0.3 [ 7.407858] device-mapper: ioctl: 4.24.0-ioctl (2013-01-15) initialised: dm-m [ 7.417297] Bluetooth: HCI UART driver ver 2.2 [ 7.422150] Bluetooth: HCI H4 protocol initialized [ 7.427392] Bluetooth: HCI Realtek H5 protocol initialized [ 7.433655] [BT_LPM] bluesleep_init: BlueSleep Mode Driver Ver 1.2 [ 7.441759] cpuidle: using governor ladder [ 7.446885] cpuidle: using governor menu [ 7.453307] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: SD/MMC/SDIO Host Controller Driver(v0.51 [ 7.466357] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: regulator prop vmmc,str vcc-sdcv [ 7.473438] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: regulator prop vqmmc,str vcc-sdcvq33 [ 7.480858] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: regulator prop vdmmc,str vcc-sdcvd [ 7.488113] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: No vmmc regulator found [ 7.494324] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: No vqmmc regulator found [ 7.500600] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: No vdmmc regulator found [ 7.507612] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: Got CD GPIO #166. [ 7.513639] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 0Hz bm PP pm UP vdd 21B [ 7.541349] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.571267] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: base:0xffffff8000e64000 irq:92 [ 7.572887] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.575270] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.580467] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.580511] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.582890] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.636616] leds-gpio leds-gpio: pins are not configured from the driver [ 7.644740] ledtrig-cpu: registered to indicate activity on CPUs [ 7.652053] hidraw: raw HID events driver (C) Jiri Kosina [ 7.658301] mmc0: host does not support reading read-only switch. assuming w. [ 7.670918] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 400000Hz bm PP pm ON vB [ 7.671382] usbcore: registered new interface driver usbhid [ 7.671384] usbhid: USB HID core driver [ 7.672344] zram: Created 1 device(s) ... [ 7.697080] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 50000000Hz bm PP pm ONB [ 7.709323] sunxi-mmc 1c0f000.sdmmc: sdc set ios: clk 50000000Hz bm PP pm ONB [ 7.709405] ashmem: initialized [ 7.712634] AUDIO :get regulator name failed . [ 7.712681] failed to get gpio-spk gpio from dts,spk_gpio:-2 [ 7.735692] mmc0: new high speed SDHC card at address aaaa [ 7.742143] sunxi-codec-machine sound.6: sun50iw2codec 1c22c00.cpudai0-k [ 7.752909] mmcblk0: mmc0:aaaa SL08G 7.40 GiB [ 7.758596] sndhdmi sound.7: sndhdmi 1c22800.daudio mapping ok [ 7.766356] mmcblk0: p1 p2 [ 7.771068] sndspdif sound.8: spdif-hifi 1c21000.spdif-controller mappik [ 7.781679] u32 classifier [ 7.784640] Actions configured [ 7.788384] Netfilter messages via NETLINK v0.30. [ 7.793641] nf_conntrack version 0.5.0 (3740 buckets, 14960 max) [ 7.800729] ctnetlink v0.93: registering with nfnetlink. [ 7.808892] NF_TPROXY: Transparent proxy support initialized, version 4.1.0 [ 7.816501] NF_TPROXY: Copyright (c) 2006-2007 BalaBit IT Ltd. [ 7.824261] xt_time: kernel timezone is -0000 [ 7.829178] ipip: IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling driver [ 7.835454] gre: GRE over IPv4 demultiplexor driver [ 7.840796] ip_gre: GRE over IPv4 tunneling driver [ 7.848811] ip_tables: (C) 2000-2006 Netfilter Core Team [ 7.855097] arp_tables: (C) 2002 David S. Miller [ 7.860279] TCP: bic registered [ 7.863706] TCP: cubic registered [ 7.867340] TCP: westwood registered [ 7.871241] TCP: htcp registered [ 7.874761] Initializing XFRM netlink socket [ 7.879803] NET: Registered protocol family 10 [ 7.887509] mip6: Mobile IPv6 [ 7.890831] ip6_tables: (C) 2000-2006 Netfilter Core Team [ 7.897290] sit: IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling driver [ 7.903798] NET: Registered protocol family 17 [ 7.908756] NET: Registered protocol family 15 [ 7.914173] Bluetooth: RFCOMM TTY layer initialized [ 7.919557] Bluetooth: RFCOMM socket layer initialized [ 7.925187] Bluetooth: RFCOMM ver 1.11 [ 7.929279] Bluetooth: BNEP (Ethernet Emulation) ver 1.3 [ 7.935088] Bluetooth: BNEP filters: protocol multicast [ 7.940819] Bluetooth: BNEP socket layer initialized [ 7.946262] Bluetooth: HIDP (Human Interface Emulation) ver 1.2 [ 7.952754] Bluetooth: HIDP socket layer initialized [ 7.958898] Registering SWP/SWPB emulation handler [ 7.967225] there is no tve dac(0) offset value. [ 7.972278] [DISP] boot_disp:0x0 [ 7.975959] [DISP] disp_init_tv,line:641:screen 0 don't support TV! [ 7.983399] usb_serial_number:20080411 [ 7.988254] file system registered [ 7.995923] android_usb gadget: Mass Storage Function, version: 2009/09/11 [ 8.003442] android_usb gadget: Number of LUNs=3 [ 8.008548] lun0: LUN: removable file: (no medium) [ 8.013895] lun1: LUN: removable file: (no medium) [ 8.019222] lun2: LUN: removable file: (no medium) [ 8.025420] android_usb gadget: android_usb ready [ 8.030790] sunxi-rtc 1f00000.rtc: setting system clock to 2017-01-01 00:01:) [ 8.048165] ALSA device list: [ 8.051420] #0: audiocodec [ 8.054582] #1: sndhdmi [ 8.057438] #2: sndspdif [ 8.060905] Freeing unused kernel memory: 572K (ffffffc000b28000 - ffffffc00) Loading, please wait... starting version 229 Begin: Loading essential drivers ... done. Begin: Running /scripts/init-premount ... done. Begin: Mounting root file system ... Begin: Running /scripts/local-top ... done. Begin: Running /scripts/local-premount ... done. Begin: Will now check root file system ... fsck from util-linux 2.27.1 [/sbin/fsck.ext4 (1) -- /dev/mmcblk0p2] fsck.ext4 -y -C0 /dev/mmcblk0p2 e2fsck 1.42.13 (17-May-2015) rootfs: recovering journal Superblock last mount time is in the future. (by less than a day, probably due to the hardware clock being incorrect) Setting free inodes count to 437685 (was 437714) Setting free blocks count to 1633110 (was 1633138) rootfs: clean, 34315/472000 files, 275626/1908736 blocks done. [ 9.119813] EXT4-fs (mmcblk0p2): mounted filesystem with ordered data mode. ) [ 9.138875] EXT4-fs (mmcblk0p2): re-mounted. Opts: data=ordered done. Begin: Running /scripts/local-bottom ... done. Begin: Running /scripts/init-bottom ... done. [ 9.514796] systemd[1]: systemd 229 running in system mode. (+PAM +AUDIT +SE) [ 9.535340] systemd[1]: Detected architecture arm64. Welcome to Ubuntu core 16.04 LTS! [ 9.559310] systemd[1]: Set hostname to . [ 9.858420] systemd[1]: Listening on udev Kernel Socket. [ OK ] Listening on udev Kernel Socket. [ 9.884072] systemd[1]: Started Dispatch Password Requests to Console Direct. [ OK ] Started Dispatch Password Requests to Console Directory Watch. [ 9.913444] systemd[1]: Started Forward Password Requests to Wall Directory . [ OK ] Started Forward Password Requests to Wall Directory Watch. [ 9.942719] systemd[1]: Listening on udev Control Socket. [ OK ] Listening on udev Control Socket. [ 9.972021] systemd[1]: Reached target Encrypted Volumes. [ OK ] Reached target Encrypted Volumes. [ 10.002288] systemd[1]: Listening on Journal Socket (/dev/log). [ OK ] Listening on Journal Socket (/dev/log). [ 10.031569] systemd[1]: Listening on Journal Socket. [ OK ] Listening on Journal Socket. [ 10.051988] systemd[1]: Reached target Paths. [ OK ] Reached target Paths. [ 10.072395] systemd[1]: Created slice User and Session Slice. [ OK ] Created slice User and Session Slice. [ 10.100148] systemd[1]: Reached target Swap. [ OK ] Reached target Swap. [ 10.121591] systemd[1]: Listening on /dev/initctl Compatibility Named Pipe. [ OK ] Listening on /dev/initctl Compatibility Named Pipe. [ 10.150525] systemd[1]: Created slice System Slice. [ OK ] Created slice System Slice. [ 10.179226] systemd[1]: Mounting Debug File System... Mounting Debug File System... [ 10.207403] systemd[1]: Starting Journal Service... Starting Journal Service... [ 10.228309] systemd[1]: Reached target Slices. [ OK ] Reached target Slices. [ 10.267208] systemd[1]: Starting Load Kernel Modules... Starting Load Kernel Modules... [ 10.300115] systemd[1]: Starting Set console keymap... Starting Set console keymap... [ 10.328896] systemd[1]: Starting Remount Root and Kernel File Systems... Starting Remount Root and Kernel File Systems... [ 10.359156] systemd[1]: Starting Create list of required static device nodes. Starting Create list of required st... nodes for the current kernel... [ 10.395675] systemd[1]: Created slice system-serial\x2dgetty.slice. [ OK ] Created slice system-serial\x2dgetty.slice. [ 10.424789] systemd[1]: Reached target Remote File Systems (Pre). [ OK ] Reached target Remote File Systems (Pre). [ 10.454371] systemd[1]: Reached target Remote File Systems. [ OK ] Reached target Remote File Systems. [ 10.498611] systemd[1]: Mounted Debug File System. [ OK ] Mounted Debug File System. [ 10.523661] systemd[1]: Started Journal Service. [ OK ] Started Journal Service. [ OK ] Started Load Kernel Modules. [ OK ] Started Remount Root and Kernel File Systems. [ OK ] Started Create list of required sta...ce nodes for the current kernel. [ OK ] Started Set console keymap. Starting Create Static Device Nodes in /dev... Starting udev Coldplug all Devices... Starting Load/Save Random Seed... Mounting Configuration File System... Mounting FUSE Control File System... Starting Apply Kernel Variables... Starting Flush Journal to Persistent Storage... [ OK ] Mounted Configuration File System. [ OK ] Mounted FUSE Control File System. [ OK ] Started Create Static Device Nodes in /dev. [ OK ] Started Load/Save Random Seed. [ OK ] Started Apply Kernel Variables. [ OK ] Reached target Local File Systems (Pre). Starting udev Kernel Device Manager... [ OK ] Started Flush Journal to Persistent Storage. [ OK ] Started udev Kernel Device Manager. [ OK ] Started udev Coldplug all Devices. [ OK ] Found device /dev/ttyS0. [ 11.534840] node ir_addr_code16 get failed! [ 11.542660] sunxi_ir_startup: cir get supply err [ OK ] Reached target Sound Card. [ OK ] Found device /dev/mmcblk0p1. [ OK ] Listening on Load/Save RF Kill Switch Status /dev/rfkill Watch. Mounting /boot... [ OK ] Found device /sys/subsystem/net/devices/eth0. [ OK ] Mounted /boot. [ OK ] Reached target Local File Systems. Starting Raise network interfaces... Starting Create Volatile Files and Directories... Starting Set console font and keymap... [ OK ] Started ifup for eth0. [ OK ] Started Create Volatile Files and Directories. Starting Update UTMP about System Boot/Shutdown... Starting Network Time Synchronization... [ OK ] Started Update UTMP about System Boot/Shutdown. [ OK ] Started Network Time Synchronization. [ OK ] Reached target System Time Synchronized. [ OK ] Reached target System Initialization. [ OK ] Listening on D-Bus System Message Bus Socket. [ OK ] Reached target Sockets. [ OK ] Started Daily Cleanup of Temporary Directories. [ OK ] Reached target Basic System. Starting Login Service... Starting dnsmasq - A lightweight DHCP and caching DNS server... Starting Permit User Sessions... Starting LSB: Start busybox udhcpd at boot time... Starting Restore /etc/resolv.conf i...re the ppp link was shut down... Starting Save/Restore Sound Card State... Starting LSB: Set the CPU Frequency Scaling governor to "ondemand"... Starting brcm_patchram_plus... [ OK ] Started Daily apt activities. [ OK ] Reached target Timers. [ OK ] Started D-Bus System Message Bus. [ OK ] Started Set console font and keymap. [ OK ] Started Permit User Sessions. [ OK ] Started Restore /etc/resolv.conf if...fore the ppp link was shut down. [ OK ] Started brcm_patchram_plus. [ OK ] Started LSB: Start busybox udhcpd at boot time. [ OK ] Started LSB: Set the CPU Frequency Scaling governor to "ondemand". [ OK ] Started Raise network interfaces. [ OK ] Started Login Service. [ OK ] Started dnsmasq - A lightweight DHCP and caching DNS server. [ OK ] Started Save/Restore Sound Card State. [ OK ] Reached target Host and Network Name Lookups. [ OK ] Reached target Network. [ OK ] Reached target Network is Online. Starting LSB: Advanced IEEE 802.11 management daemon... Starting LSB: disk temperature monitoring daemon... Starting OpenBSD Secure Shell server... Starting /etc/rc.local Compatibility... Starting Set console scheme... [ OK ] Created slice system-getty.slice. [ OK ] Started /etc/rc.local Compatibility. [ OK ] Started Set console scheme. [ OK ] Started LSB: disk temperature monitoring daemon. [ OK ] Started Serial Getty on ttyS0. [ 9.164386] rc.local[1455]: QtE-Demo: no process found [ OK ] Started Getty on tty2. [ OK ] Reached target Login Prompts. [ OK ] Started OpenBSD Secure Shell server. [ OK ] Started LSB: Advanced IEEE 802.11 management daemon. [ OK ] Reached target Multi-User System. [ OK ] Reached target Graphical Interface. Starting Update UTMP about System Runlevel Changes... [ OK ] Started Update UTMP about System Runlevel Changes. Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS NanoPi-NEO2 ttyS0 NanoPi-NEO2 login: pi (automatic login) Last login: Thu Mar 23 09:19:32 UTC 2017 on ttyS0 _____ _ _ _ _____ _ _____ ____ | ___| __(_) ___ _ __ __| | |_ _| ____| | | ____/ ___| | |_ | '__| |/ _ \ '_ \ / _` | | | | | _| | | | _|| | | _|| | | | __/ | | | (_| | | |_| | |___| |___| |__| |___ |_| |_| |_|\___|_| |_|\__,_|_|\__, |_____|_____|_____\____| |___/ Welcome to Ubuntu core 16.04 LTS 3.10.65 System load: 0.16 Up time: 10 sec Memory usage: 7 % of 468Mb IP: CPU temp: 48�ʰC Usage of /: 13% of 7.2G * Documentation: http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/ * Forum: http://www.friendlyarm.com/Forum/ To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>". See "man sudo_root" for details. pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ </command> |
It will login automatically in the console, and you don’t need to to enter the username & password. If you need to use sudo later the password for “pi” user is simply “pi”
Let’s check some of the system details:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ uname -a Linux NanoPi-NEO2 3.10.65 #5 SMP PREEMPT Wed Mar 29 09:50:17 CST 2017 aarch64 ax pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev 224M 0 224M 0% /dev tmpfs 47M 1.7M 46M 4% /run /dev/mmcblk0p2 7.2G 938M 6.3G 13% / tmpfs 235M 0 235M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs 235M 0 235M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mmcblk0p1 100M 20M 80M 21% /boot tmpfs 47M 0 47M 0% /run/user/1000 pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ cat /proc/cpuinfo Processor : AArch64 Processor rev 4 (aarch64) processor : 0 processor : 1 processor : 2 processor : 3 Features : fp asimd aes pmull sha1 sha2 crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: AArch64 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 Hardware : sun50iw2 Serial : 34005035c2003c2a074c pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ lsmod Module Size Used by vfe_v4l2 767532 0 videobuf2_dma_contig 7817 1 vfe_v4l2 videobuf2_memops 1704 1 videobuf2_dma_contig videobuf2_core 23559 1 vfe_v4l2 vfe_io 28412 1 vfe_v4l2 sunxi_ir_rx 7214 0 sunxi_keyboard 5500 0 ss 31327 0 pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ ls -l /sys/class/gpio/ total 0 --w------- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 00:01 export lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 00:01 gpiochip0 -> ../../devices/soc.0/1c2080 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 00:01 gpiochip352 -> ../../devices/soc.0/1f02 --w------- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 00:01 unexport pi@NanoPi-NEO2:~$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_max_freq 1536000 |
Linux 3.10.65 is used, and the root file system was automatically resized during the first boot to make use of the complete storage available on the micro SD card. We have 928 MB used out of 7.2 GB. It will show four Aarch64 cores part of sun50iw2 family. There are some module loaded specifically for camera support such as vfe_v4l2 module, which you could disable in /etc/modules if you don’t need it. I’ll need GPIO support for BakeBit Starter Kit, and it seems enabled by default.
Just like in NanoPi NEO Ubuntu, there’s a Qt demo enabled in /etc/rc.local, so you may want to remove the lines below since we don’t have an LCD display connected to the board:
|
1 2 3 4 |
. /usr/bin/setqt4env /usr/bin/lcd2usb_print "CPU: {{CPU}}" "Mem: {{MEM}}" "IP: {{IP}}" "LoadAvg: {{LO ADAVG}}" 2>&1 > /dev/null& /opt/QtE-Demo/run.sh& |
Armbian Ubuntu 16.04.2 Boot Log and Info
The boot log for Armbian is much shorter (and cleaner):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 |
U-Boot SPL 2017.01-rc1-g5df570f-dirty (Mar 31 2017 - 03:47:52) DRAM: 512 MiB Failed to set core voltage! Can't set CPU frequency Trying to boot from MMC1NOTICE: BL3-1: Running on H5 (1718) in SRAM A2 (@0x440) NOTICE: Configuring SPC Controller NOTICE: BL3-1: v1.0(debug):aa75c8d NOTICE: BL3-1: Built : 03:47:47, Mar 31 2017 INFO: BL3-1: Initializing runtime services INFO: BL3-1: Preparing for EL3 exit to normal world INFO: BL3-1: Next image address: 0x4a000000, SPSR: 0x3c9 U-Boot 2017.01-rc1-g5df570f-dirty (Mar 31 2017 - 03:48:00 +0200) Allwinner Techy CPU: Allwinner H5 (SUN50I) Model: OrangePi PC 2 DRAM: 512 MiB MMC: SUNXI SD/MMC: 0 *** Warning - bad CRC, using default environment Setting up a 720x576i composite-pal console (overscan 32x20) Error: no valid bmp image at 66000000 In: serial Out: vga Err: vga Net: phy interface7 Could not get PHY for ethernet@1c30000: addr 1 No ethernet found. Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 38518 bytes read in 210 ms (178.7 KiB/s) switch to partitions #0, OK mmc0 is current device Scanning mmc 0:1... Found U-Boot script /boot/boot.scr 2392 bytes read in 215 ms (10.7 KiB/s) ## Executing script at 4fc00000 U-boot loaded from SD Boot script loaded from mmc 116 bytes read in 167 ms (0 Bytes/s) 20836 bytes read in 274 ms (74.2 KiB/s) 4704957 bytes read in 518 ms (8.7 MiB/s) 11659272 bytes read in 763 ms (14.6 MiB/s) ## Loading init Ramdisk from Legacy Image at 4fe00000 ... Image Name: uInitrd Image Type: AArch64 Linux RAMDisk Image (gzip compressed) Data Size: 4704893 Bytes = 4.5 MiB Load Address: 00000000 Entry Point: 00000000 Verifying Checksum ... OK ## Flattened Device Tree blob at 4fa00000 Booting using the fdt blob at 0x4fa00000 reserving fdt memory region: addr=4fa00000 size=6000 Loading Ramdisk to 49b83000, end 49fffa7d ... OK Loading Device Tree to 0000000049b7a000, end 0000000049b82fff ... OK Cannot setup simplefb: node not found Starting kernel ... Loading, please wait... starting version 229 Begin: Loading essential drivers ... done. Begin: Running /scripts/init-premount ... done. Begin: Mounting root file system ... Begin: Running /scripts/local-top ... done. Begin: Running /scripts/local-premount ... Scanning for Btrfs filesystems done. Begin: Will now check root file system ... fsck from util-linux 2.27.1 [/sbin/fsck.ext4 (1) -- /dev/mmcblk0p1] fsck.ext4 -a -C0 /dev/mmcblk0p1 /dev/mmcblk0p1: clean, 54146/102336 files, 290800/408832 blocks done. done. Begin: Running /scripts/local-bottom ... done. Begin: Running /scripts/init-bottom ... done. Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS! [ OK ] Listening on Syslog Socket. [ OK ] Listening on fsck to fsckd communication Socket. [ OK ] Created slice System Slice. [ OK ] Created slice system-serial\x2dgetty.slice. [ OK ] Reached target Swap. [ OK ] Reached target Remote File Systems (Pre). [ OK ] Reached target Remote File Systems. [ OK ] Listening on /dev/initctl Compatibility Named Pipe. [ OK ] Listening on udev Control Socket. [ OK ] Started Dispatch Password Requests to Console Directory Watch. [ OK ] Set up automount Arbitrary Executab...ats File System Automount Point. [ OK ] Created slice User and Session Slice. [ OK ] Reached target Slices. [ OK ] Started Forward Password Requests to Wall Directory Watch. [ OK ] Listening on Journal Audit Socket. [ OK ] Listening on udev Kernel Socket. [ OK ] Listening on Journal Socket (/dev/log). [ OK ] Listening on Journal Socket. Starting Restore / save the current clock... Mounting Debug File System... Starting Load Kernel Modules... Starting Nameserver information manager... Mounting Huge Pages File System... Starting Remount Root and Kernel File Systems... Mounting POSIX Message Queue File System... Starting Create list of required st... nodes for the current kernel... Starting Set console keymap... [ OK ] Reached target Encrypted Volumes. [ OK ] Mounted POSIX Message Queue File System. [ OK ] Mounted Huge Pages File System. [ OK ] Mounted Debug File System. [ OK ] Started Restore / save the current clock. [ OK ] Started Load Kernel Modules. [ OK ] Started Remount Root and Kernel File Systems. [ OK ] Started Create list of required sta...ce nodes for the current kernel. [ OK ] Started Nameserver information manager. [ OK ] Started Set console keymap. [ OK ] Reached target Network (Pre). Starting Create Static Device Nodes in /dev... Starting Load/Save Random Seed... Starting udev Coldplug all Devices... Mounting Configuration File System... Starting Apply Kernel Variables... [ OK ] Mounted Configuration File System. [ OK ] Started Create Static Device Nodes in /dev. [ OK ] Started Load/Save Random Seed. [ OK ] Started Apply Kernel Variables. [ OK ] Reached target Local File Systems (Pre). Mounting /tmp... Starting udev Kernel Device Manager... [ OK ] Mounted /tmp. [ OK ] Started udev Coldplug all Devices. [ OK ] Reached target Local File Systems. Starting Set console font and keymap... Starting Armbian enhanced Log2Ram... Starting Raise network interfaces... [ OK ] Started Entropy daemon using the HAVEGE algorithm. [ OK ] Started udev Kernel Device Manager. [ OK ] Found device /dev/ttyS0. [ OK ] Started Armbian enhanced Log2Ram. Starting Journal Service... [ OK ] Reached target Sound Card. [ OK ] Started Journal Service. Starting Flush Journal to Persistent Storage... [ OK ] Started Flush Journal to Persistent Storage. Starting Create Volatile Files and Directories... [ OK ] Started Create Volatile Files and Directories. [ OK ] Started ifup for eth0. Starting Update UTMP about System Boot/Shutdown... [ OK ] Reached target System Time Synchronized. [ OK ] Found device /sys/subsystem/net/devices/eth0. [ OK ] Started Update UTMP about System Boot/Shutdown. [ OK ] Reached target System Initialization. [ OK ] Started Daily Cleanup of Temporary Directories. [ OK ] Started Trigger resolvconf update for networkd DNS. [ OK ] Reached target Paths. Starting Armbian filesystem resize service... [ OK ] Started Daily apt activities. [ OK ] Reached target Timers. [ OK ] Listening on D-Bus System Message Bus Socket. [ OK ] Reached target Sockets. [ OK ] Started Raise network interfaces. [ OK ] Started Armbian filesystem resize service. [ OK ] Reached target Basic System. Starting Permit User Sessions... Starting LSB: Load kernel modules needed to enable cpufreq scaling... [ OK ] Started D-Bus System Message Bus. [ OK ] Started Regular background program processing daemon. Starting LSB: Start/stop sysstat's sadc... Starting System Logging Service... Starting Network Manager... [ OK ] Started Armbian first run tasks. Starting LSB: Armbian gathering hardware information... Starting LSB: Starts LIRC daemon.... Starting Login Service... Starting Save/Restore Sound Card State... [ OK ] Started Permit User Sessions. [ OK ] Started System Logging Service. [ OK ] Started Save/Restore Sound Card State. [ OK ] Started LSB: Start/stop sysstat's sadc. [ OK ] Started LSB: Starts LIRC daemon.. [ OK ] Started LSB: Load kernel modules needed to enable cpufreq scaling. [ OK ] Started Login Service. Starting LSB: set CPUFreq kernel parameters... Starting Set console scheme... [ OK ] Started Set console scheme. [ OK ] Started LSB: set CPUFreq kernel parameters. Starting LSB: Set sysfs variables from /etc/sysfs.conf... [ OK ] Started LSB: Set sysfs variables from /etc/sysfs.conf. [ OK ] Started Network Manager. [ OK ] Reached target Network. Starting OpenBSD Secure Shell server... Starting Network Manager Wait Online... Starting Network Manager Script Dispatcher Service... [ OK ] Started Network Manager Script Dispatcher Service. Starting Hostname Service... [ OK ] Started LSB: Armbian gathering hardware information. [FAILED] Failed to start Set console font and keymap. See 'systemctl status console-setup.service' for details. [ OK ] Started Hostname Service. [ OK ] Created slice system-getty.slice. [ OK ] Started OpenBSD Secure Shell server. Starting Authenticate and Authorize Users to Run Privileged Tasks... [ OK ] Started Network Manager Wait Online. [ OK ] Started Authenticate and Authorize Users to Run Privileged Tasks. [ OK ] Reached target Network is Online. Starting /etc/rc.local Compatibility... Starting LSB: Advanced IEEE 802.11 management daemon... Starting LSB: disk temperature monitoring daemon... Starting LSB: Start NTP daemon... [ OK ] Started /etc/rc.local Compatibility. [ OK ] Started LSB: Advanced IEEE 802.11 management daemon. [ OK ] Started LSB: disk temperature monitoring daemon. [ OK ] Started Getty on tty1. [ OK ] Started Serial Getty on ttyS0. [ OK ] Reached target Login Prompts. [ OK ] Started LSB: Start NTP daemon. [ OK ] Reached target Multi-User System. [ OK ] Reached target Graphical Interface. Starting Update UTMP about System Runlevel Changes... [ OK ] Started Update UTMP about System Runlevel Changes. Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS nanopineo2 ttyS0 nanopineo2 login: |
The image appears to be for OrangePi PC 2 board, and there are some errors about failure to set voltage and CPU frequency, so maybe it will have to be fixed soon.
You’ll need to login with root / 1234, and the first time, you’ll be asked to change root password, and create a new user part of sudoers. I’ve run the same command with the Armbian image as I did with the FriendlyELEC (FE) one:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 |
root@nanopineo2:~# uname -a Linux nanopineo2 4.10.0-sun50iw2 #23 SMP Fri Mar 31 03:48:12 CEST 2017 aarch64 x root@nanopineo2:~# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev 232M 0 232M 0% /dev tmpfs 49M 1.7M 47M 4% /run /dev/mmcblk0p1 7.2G 1.2G 5.9G 17% / tmpfs 242M 0 242M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs 242M 0 242M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs 242M 0 242M 0% /tmp log2ram 50M 756K 50M 2% /var/log tmpfs 49M 0 49M 0% /run/user/0 root@nanopineo2:~# cat /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 Processor : AArch64 Processor rev 4 (aarch64) Hardware : sun50iw1p1 BogoMIPS : 48.00 Features : fp asimd evtstrm aes pmull sha1 sha2 crc32 cpuid CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 8 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 processor : 1 Processor : AArch64 Processor rev 4 (aarch64) Hardware : sun50iw1p1 BogoMIPS : 48.00 Features : fp asimd evtstrm aes pmull sha1 sha2 crc32 cpuid CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 8 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 processor : 2 Processor : AArch64 Processor rev 4 (aarch64) Hardware : sun50iw1p1 BogoMIPS : 48.00 Features : fp asimd evtstrm aes pmull sha1 sha2 crc32 cpuid CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 8 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 processor : 3 Processor : AArch64 Processor rev 4 (aarch64) Hardware : sun50iw1p1 BogoMIPS : 48.00 Features : fp asimd evtstrm aes pmull sha1 sha2 crc32 cpuid CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 8 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 root@nanopineo2:~# lsmod Module Size Used by sun4i_codec 53248 3 sun8i_codec_analog 28672 1 snd_soc_core 176128 2 sun4i_codec,sun8i_codec_analog snd_pcm_dmaengine 16384 1 snd_soc_core snd_pcm 118784 2 snd_pcm_dmaengine,snd_soc_core snd_timer 32768 1 snd_pcm root@nanopineo2:~# ls -l /sys/class/gpio/ total 0 --w------- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 1970 export lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 1970 gpiochip0 -> ../../devices/platform/so0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 1970 gpiochip352 -> ../../devices/platform/2 --w------- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 1970 unexport |
The obvious advantage is that the Armbian image is running the latest Linux 4.10.0 kernel with all new features and security patchsets. The rootfs is also automatically resized during the first boot, but there must be more packages installed by default, since 1.2 GB is used out of 7.2 GB. while we had only 928 MB used in FE image. The reported hardware is sun50iw1p1 against sun50iw2 in FE image, but I assume it does not matter that much. Different modules are loaded by default in that image, no camera modules, but instead audio modules. The listed GPIOs are the same as in FE image.
Linux 4.8 and greater is supposed to support the new GPIO subsystem with the ability to list GPIOs using lsgpio command:
|
1 2 |
cnxsoft@nanopineo2:~$ lsgpio bash: lsgpio: command not found |
But the command is not installed, and not part of any Ubuntu packages, so it would have to be build from source, but I have not checked it yet. All examples provided by FriendlyELEC for their BakeBit Starter Kit are going to use sysfs interface since they provide a Linux 3.10 image.
NanoPi NEO 2 Benchmarks
I’m going to running the same benchmarks as on NanoPi NEO with Phoronix and iperf. Since Ubuntu 16.04 comes with PHP 7, Phoronix Test Suite installation is a little different:
|
1 2 3 |
sudo apt install php-cli php-gd php-xml php-zip wget http://phoronix-test-suite.com/releases/repo/pts.debian/files/phoronix-test-suite_7.0.1_all.deb sudo dpkg -i phoronix-test-suite_7.0.1_all.deb |
I made sure the heatsink faced upwards when running the benchmarks, as in the past I had troubles when the heatsink faced the table since – as you mum or teacher must have told you – heat is going up, and if the heatsink faces down, heat may be trapped.
 Then I ran the benchmark using FE and Armbian images:
Then I ran the benchmark using FE and Armbian images:
|
1 2 |
phoronix-test-suite benchmark 1607222-GA-1607218GA60 phoronix-test-suite benchmark 1704017-RI-1607222GA95 |
You’ll find all results here, but let’s have a look at some of the results starting with Ripper, a multi-thread password cracking program. FA stands for FriendlyARM in the chart.

I’ve included all the boards for broad results. In this particular benchmark NanoPi NEO 2 is about the same speed as NanoPi NEO board, and both images have similar performance. Please note that the image may not have been optimized for the best performance, but rather low power consumption with lower CPU and RAM frequencies, which may explain for example why Orange Pi One is a little faster. You’ll note the importance of have a heatsink, by looking at “NanoPi NEO 512MB No Heatsink” result. The results with the image used on NanoPi NEO 2 also seem more “stable”, as the SE +/- values are much smaller in all tests.
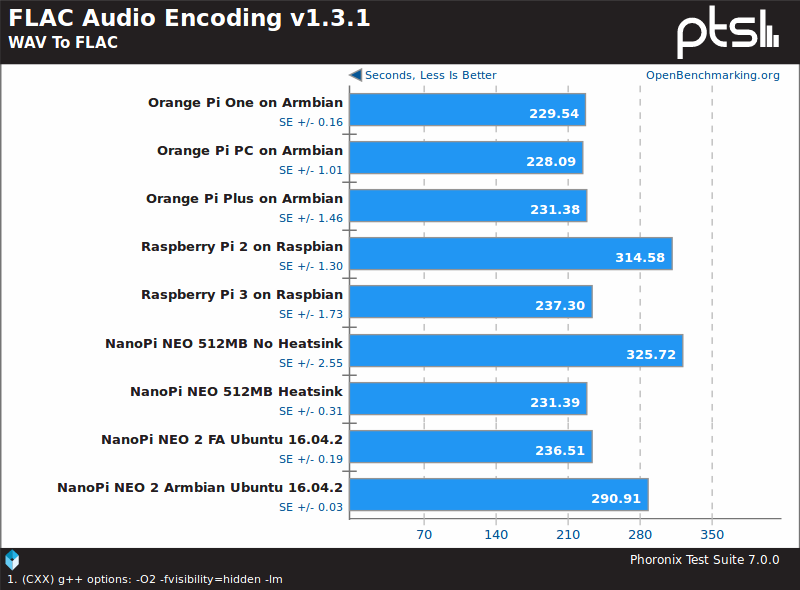
FLAC audio encoding is a single thread test, and here NanoPi NEO and NEO 2 have similar performance using Ubuntu FA image, but for some reason the Armbian image was slower here.
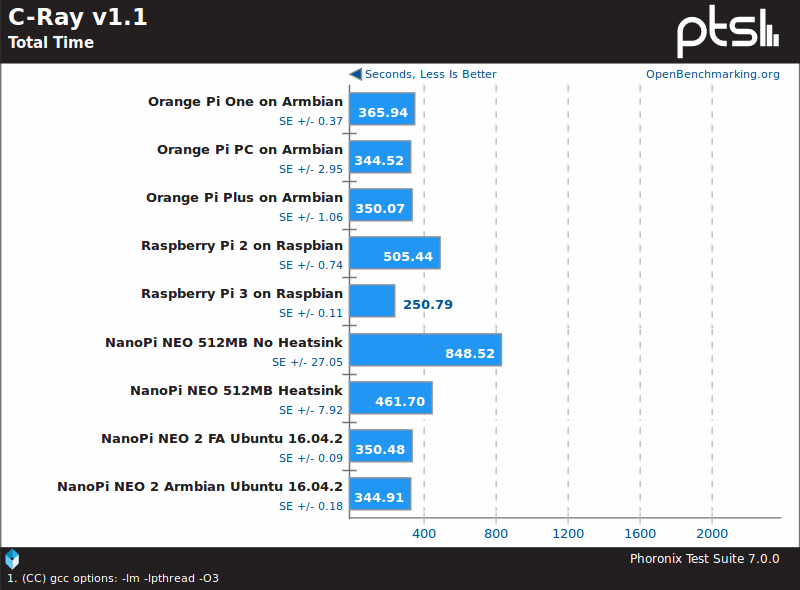
So far we did not see any improvement use NEO 2 over NEO, but if we look at C-Ray benchmark, there’s a clear advantage of using the 64-bit processor (H5) over the 32-bit processor (H3).
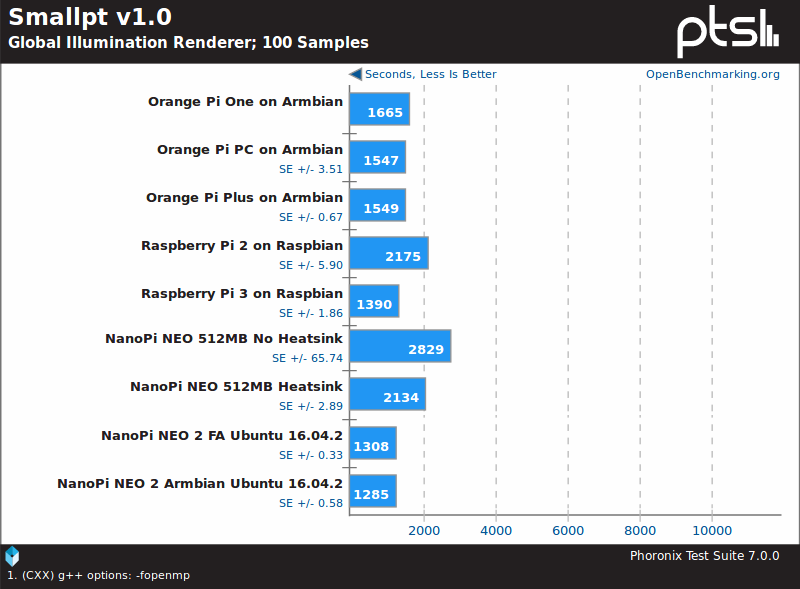
Smallpt v1.0 is another example showing much better performance on NanoPi NEO 2, and it’s even faster than Raspberry Pi 3 board.
But overall, there’s basically no difference between using FriendlyELEC or Armbian Ubuntu image, except for the FLAC audio encoding. But let’s have a look at Ethernet performance.
Ethernet Performance with Ubuntu 16.04.2 + Linux 3.10 FriendlyELEC image.
iperf upload (iperf -s running on computer):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
iperf -t 60 -c computer_ip Client connecting to 192.168.0.104, TCP port 5001 TCP window size: 67.6 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 3] local 192.168.0.105 port 42055 connected with 192.168.0.104 port 5001 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 3] 0.0-60.0 sec 336 MBytes 47.0 Mbits/sec |
iperf download (iperf -s running on board):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
iperf -t 60 -c nanopi-neo-2_ip Client connecting to 192.168.0.105, TCP port 5001 TCP window size: 85.0 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 3] local 192.168.0.104 port 47876 connected with 192.168.0.105 port 5001 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 3] 0.0-60.0 sec 5.69 GBytes 815 Mbits/sec |
full duplex:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
iperf -t 60 -c computer_ip -d Client connecting to 192.168.0.105, TCP port 5001 TCP window size: 348 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 6] local 192.168.0.104 port 46690 connected with 192.168.0.105 port 5001 [ 6] 0.0-60.0 sec 5.53 GBytes 792 Mbits/sec [ 4] 0.0-60.1 sec 113 MBytes 15.7 Mbits/sec |
There seems to be a serious problem with upload speed.
I did an extra test with a 1.6 GB HTTP download to /dev/null:
|
1 |
wget http://192.168.0.104/ubuntu-16.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso -O /dev/null |
The download speed on NanoPi NEO 2 was 57.1 MB/s. Acceptable.
Ethernet Performance on Ubuntu 16.04.2 + Linux 4.10 Armbian image.
I’m repeated the same test with Armbiab image:
iperf upload:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Client connecting to 192.168.0.104, TCP port 5001 TCP window size: 85.0 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 3] local 192.168.0.105 port 44070 connected with 192.168.0.104 port 5001 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 3] 0.0-60.0 sec 6.30 GBytes 901 Mbits/sec |
iperf download:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
------------------------------------------------------------ Server listening on TCP port 5001 TCP window size: 85.3 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 4] local 192.168.0.105 port 5001 connected with 192.168.0.104 port 49080 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 4] 0.0-60.0 sec 5.52 GBytes 790 Mbits/sec |
iperf full duplex:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Client connecting to 192.168.0.104, TCP port 5001 TCP window size: 264 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 5] local 192.168.0.105 port 44074 connected with 192.168.0.104 port 5001 [ 4] local 192.168.0.105 port 5001 connected with 192.168.0.104 port 49066 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 4] 0.0-60.0 sec 2.86 GBytes 409 Mbits/sec [ 5] 0.0-60.0 sec 5.54 GBytes 793 Mbits/sec cnxsoft@nanopineo2:~$ |
HTTP download: 108 MB/s.
So there’s no competition here, Armbian image is much better if you need good Gigabit Ethernet performance. The poor upload performance is gone, and the HTTP download is twice as fast, and close to the maximum theoretically possible throughput.
Finally , I did a quick test with CHARGER DOCTOR to check the power consumption in idle mode: 0.21A @ 4.65V (~0.98 Watt). Last year, NanoPi NEO consumed about 2 Watts in idle mode with a non-optimized Ubuntu + Qt Embedded image.
Based on the results I got here, I’ll probably try Armbian image with BakeBit Starter Kit to test GPIO, I2C, UART,… and only revert to FriendlyELEC image in case one of the module does not work.
NanoPi NEO 2 sells for $14.99, and the heatsink set for $2.97 with shipping adding a few dollars.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress