Qualcomm has unveiled the “micro-power” QCC730 Arm Cortex-M4F dual-band WiFi 4 microcontroller for the IoT market that targets similar applications as the Espressif ESP32 microcontrollers but potentially at lower power consumption with claims of up to 88% lower power than “previous generations” making it suitable for battery-powered industrial, commercial and consumer applications.
To highlight the low-power consumption, the company also mentions that QCC730 devices could become high-performance alternatives to Bluetooth IoT solutions with direct cloud connectivity.
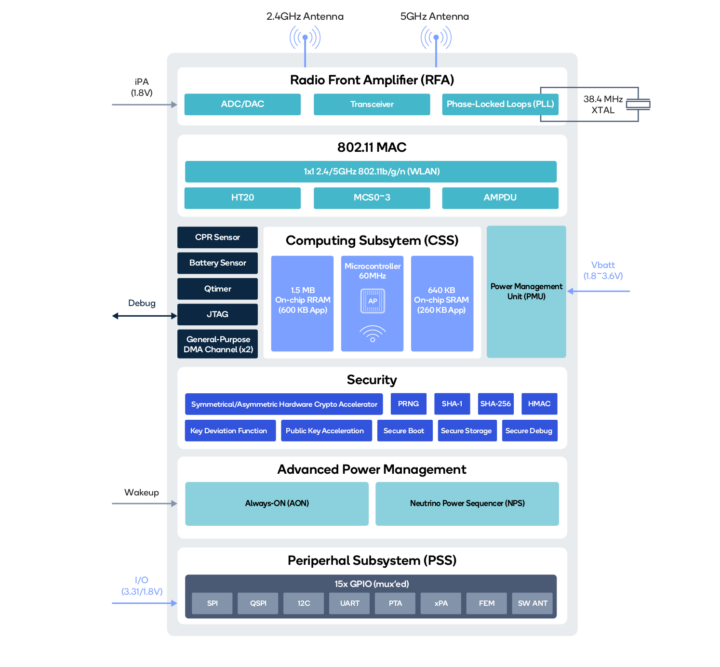
Qualcomm QCC730 specifications:
- CPU core – Arm Cortex-M4F @ 60 MHz
- Memory/ Storage
- 1.5 MB RAM, including 600KB for user app (On-chip RRAM (NVM) to host application without the need for an external NOR flash)
- 640 KB SRAM, including 260KB for user app
- XiP over QSPI Flash
- Wi-Fi
- Standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11a
- Spectral Bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz
- Channels: 20 MHz
- Antenna Configuration: 1×1
- Features: up to MCS3
- Interfaces – Master I2C, 15x muxed GPIO, slave SPI, 2-wire UART, master QSPI
- Security
- Hardware crypto accelerator
- Secure Boot, Cryptographic Accelerator, Qualcomm Trusted Execution Environment & Services, Secure debug
- Power management
- Supply Voltage – 1.85 to 3.6V Vbatt
- Always on hub
- Neutrino Power Sequence (NPS)
- Package – 90-ball WLCSP (3.3 x 3.58 x 0.55 mm) with 0.35 mm pitch
- Manufacturing process – 22 nm ULL process
While Qualcomm highlights the low-power consumption of the QCC730 wireless SoC, they did not provide actual numbers. The new chip adds to Qualcomm IoT solutions such as the QCC711 tri-core ultra-low power Bluetooth Low Energy SoC and the QCC740 “all-in-one” SoC with support for Thread, Zigbee, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Some of the battery power devices powered by the Qualcomm low-power WiFi IoT microcontroller will include smart door locks, smart sensors, wireless cameras, video doorbells, smart tags, and sensors used for building automation.
The QCC730 will be programmable using an open-source IDE and SDK hosted on CodeLinaro, and support the Qualcomm Connectivity IDE based on Microsoft Visual Studio Code (VSCode). The QCC730-specific VSCode extension plugin will be available as open-source software to allow customized VSCode specifically for QCC730. Qualcomm mentions both bare metal programming and RTOS support
Besides the tiny chip itself, Qualcomm will release QCC730 modules optimized for size and cost and development kits that will be sold through “authorized design centers”. If history is any guide, I don’t expect a wide range of cheap Qualcomm QCC730 modules and boards like we have today through Espressif ESP8266 and ESP32 wireless SoCs, but we’ll see, and I might be proven wrong.
A few more details may be found on the product page, but you’d need to be a “verified company” to access additional resources for the QCC730. We’re not off to a good start here!

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress. We also use affiliate links in articles to earn commissions if you make a purchase after clicking on those links.






Does the “open-source software SDK” include the WiFi MAC / PHY drivers? The older Qualcomm Atheros chips had drivers which were entirely blob-free, they were completely open-source? Is Qualcomm going to do the same with this chip?
unless it makes all kinds of low-cost modules and boards, and welcome the community like what ESP does, this will not catch on
Why in this day an age are you launching with WiFi 4?
It’s cheaper and good enough for IoT.
Is this something being revived from CSR?
what is really 88% low power?